J Korean Med Assoc.
2004 Aug;47(8):781-792. 10.5124/jkma.2004.47.8.781.
Ossification of Posterior Longitudinal Ligament(OPLL) of Cervical Spine
- Affiliations
-
- 1Department of Neurosurgery, Ajou University College of Medicine and Hospital, Korea. khcho54@ajou.ac.kr
- KMID: 2183496
- DOI: http://doi.org/10.5124/jkma.2004.47.8.781
Abstract
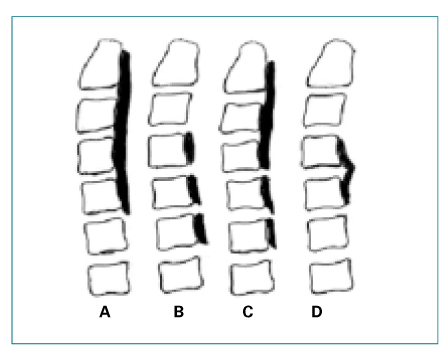
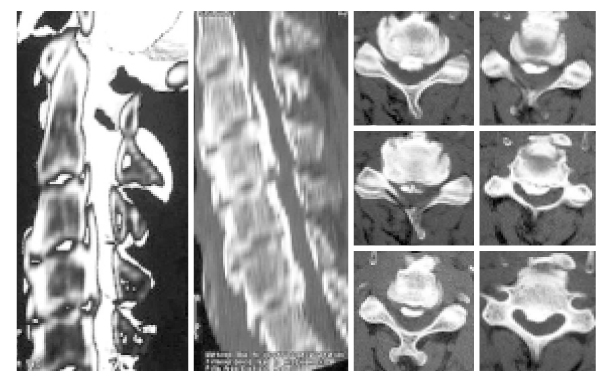
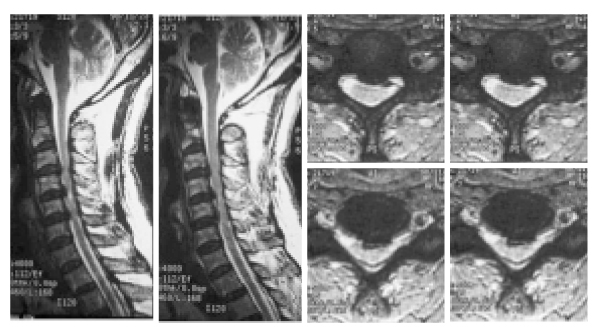
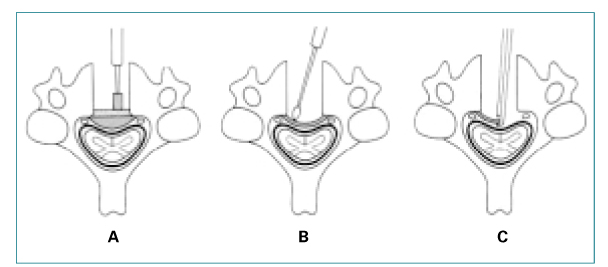
- The most common and neurologically important enthesopathy that is caused by inflammation of tendinous and ligamentous attatchments to bone is ossification of posterior longitudinal ligament (OPLL). The OPLL can occur at the posterior surface of the spinal vertebral bodies from the foramen magnum to the sacrum; however, the cervical portion of the vertebra is mainly affected. The cervical OPLL is originally thought to occur only in individuals of Japanese descent; however the advances in its diagnosis by using computed tomography and magnetic resonance imaging have led to more frequent identification of the disease in other Asians and whites as well. The cervical OPLL is a surgically treatable cause of myelopathy and various surgical approaches including anterior and posterior approach have been introduced. Although the indications of surgical treatment have been defined, the selection of the most effective operation remains controversial.
MeSH Terms
Figure
Reference
-
1. Tsukimoto H. A case report : Autopsy of syndrome of compression of spinal cord owing to ossification within spinal canal of cervical spine. Arch Jpn Chir. 1960. 29:1003–1007.2. Hosoda Y, Yoshimura Y, Higaki S. A new breed of mouse showing multiple osteochondral lesions-twy mouse. Ryumachi. 1981. 21:Suppl. 157–164.3. Nakamura I, Ikegawa S, Okawa A, Okuda S, Koshizuka Y, Nakamura Y, et al. Association of the human NPPS gene with ossification of the posterior longitudinal ligament of the spine (OPLL). Hum Genet. 1999. 104:492–497.
Article4. Youmans JR. Youmans Neurological surgery. 1996. 4ed. Philadelphia: WB Saunders;2328–2342.5. Abe H, Tsuru M, Ito T, Iwasaki Y, Koiwa M. Anterior decompression for ossification of the posterior longitudinal ligament of the cervical spine. J Neurosurg. 1981. 55:108–116.
Article6. Rozario RA, Levine H, Stein BA. Cervical myelopathy and radiculopathy secondary to ossification of posterior longitudinal ligament. Surg Neurol. 1978. 10:17–20.7. Hirabayashi K, Toyama Y, Chiba K. Expensive laminoplasty for myelopathy in ossification of the longitudinal ligament. Clin Orthop. 1999. 359:35–48.
Article8. Keiji K, Teiji T, Takashi Y. Spinous process-splitting laminoplasty with an extended foraminotomy for cervical myelopathy. Neurosurgery. 1995. 37:430–435.
Article9. Seichi A, Takeshita K, Ohishi I, Kawaguchi H, Akune T, Nakamura K, et al. Long-term results of double-door laminoplasty for cervical stenotic myelopathy. Spine. 2001. 26:479–487.
Article10. Yonenobu K, Fuji T, Ono K, Okada K, Yamamoto T, Harada N. Choice of surgical treatment for multisegmental cervical spondylotic myelopathy. Spine. 1985. 10:710–716.
Article11. Hanai K, Inouye Y, Kawai K, Tago k, Itoh Y. Anterior decompression for myelopathy resulting from ossification of posterior longitudinal ligament. J Bone Joint Surg Br. 1982. 64:561–564.12. Hoshi K, Kurokawa T, Nakamura K, Hoshino Y, Saita K, Miyshi K. Expansive cervical laminoplasties. observations on comparative changes in spinous process lengths following longitudinal laminal divisions using autogenous bone or hydroxyapatite spacers. Spinal Cord. 1996. 34:725–728.
Article13. Chiba K, Toyama Y, Watanabe M, Maruiwa H, Matsumoto M, Hirabayashi K. Impact of longitudinal distance of the cervical spine on the results of expansive open-door laminoplasty. Spine. 2000. 25:2893–2898.
Article14. Edwards CC II, Heller JG, Silcox DH III. T-saw laminoplasty for the management of cervical spondylotic myelopathy-Clinical and radiographic outcome. Spine. 2000. 25:1788–1794.
Article15. Hirabayashi K, Watanabe K, Wakano K, Suzuki N, Satomi K, Ishii Y. Expansive open-door laminoplasty for cervical spinal stenotic myelopathy. Spine. 1983. 8:693–699.
Article16. Kazuo Yonenobu, Takenori Oda. Posterior approach to the degenerative cervical spine. Eur Spine J. 2003. 12 Suppl 2:S195–S201.
- Full Text Links
- Actions
-
Cited
- CITED
-
- Close
- Share
- Similar articles
-
- Anterior Decompression and Interbody Fusion for Ossification of the Posterior Longitudinal Ligament of the Cervical Spine: Case Report
- Ossification of the Posterior Longitudinal Ligament: 2 cases report
- A Case Quadriplegia due to Minor Head Trauma Associated with Ossification of the Posterior Longitudinal Ligament of the Cervical Spine
- Genetics of Ossification of the Posterior Longitudinal Ligament of the Spine: A Mini Review
- Increased Prevalence of Ossification of Posterior Longitudinal Ligament and Increased Bone Mineral Density in Patients with Ossification of Nuchal Ligament