J Korean Foot Ankle Soc.
2014 Jun;18(2):68-71. 10.14193/jkfas.2014.18.2.68.
Results of Culture Test at the Time of Removal of Metal Implants Used for Ankle Fracture Management
- Affiliations
-
- 1Department of Orthopedic Surgery, Sanggye Paik Hospital, Inje University College of Medicine, Seoul, Korea. youngos@paik.ac.kr
- KMID: 2181663
- DOI: http://doi.org/10.14193/jkfas.2014.18.2.68
Abstract
- PURPOSE
The purpose of this study is to report the results of culture test at the time of removal of metal devices used for management of ankle fractures and for analysis of contributing factors.
MATERIALS AND METHODS
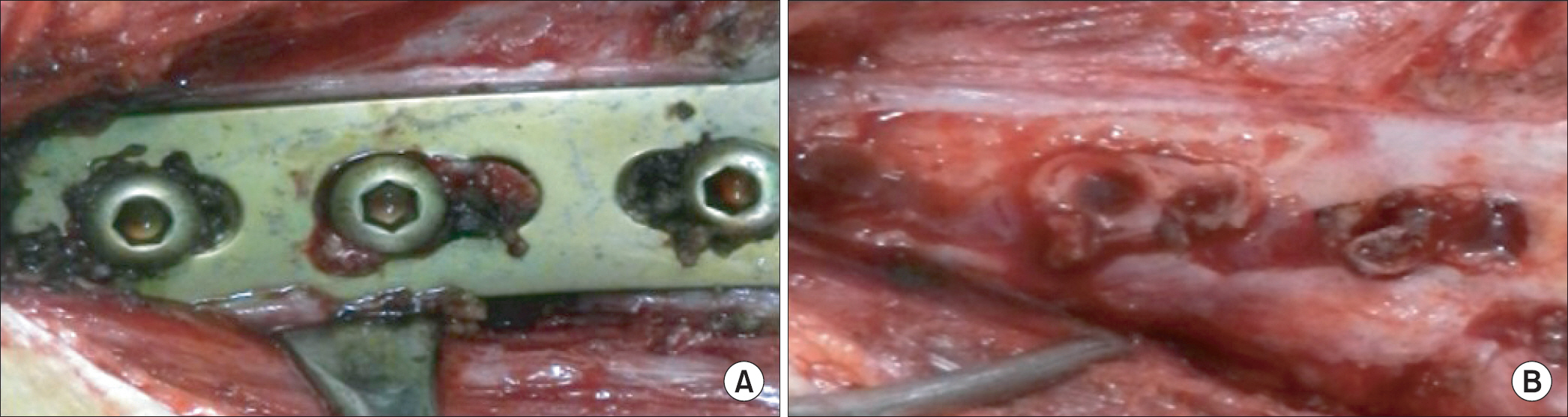
We reviewed medical records of 132 patients with lower tibia and ankle fracture who had their metal devices removed during the period from January 2010 to February 2014. Patients with clinical signs of infection were excluded. Culture test was performed by taking the granulation tissue around the metal device at the time of removal. We divided the subjects into two groups, culture positive and negative. We then performed a retrospective review of each medical record of multiple factors that might contribute to the culture results, including laboratory results, medical history, material and size of metal device, indwelling period, and whether or not it was open injury.
RESULTS
Among 132 cases, six were culture positive. Enterococcus was detected in two cases and the others were Staphylococcus. No significant difference in medical history of patients and laboratory results, including C-reactive protein level, was observed between the culture positive and negative group. Culture positive rate was 5.4% in titanium and 3.9% in stainless steel. In terms of metal size, culture positive rate was 5.1% in small plates, 6.7% in large plates, and culture negative in intramedullary nails. The average indwelling period of metal device was 61.5 weeks in the culture positive group, and 68.6 weeks in the negative group. Nine cases were open fractures and all were in the culture negative group.
CONCLUSION
Whether or not the culture result was positive, there were no meaningful contributing factors. Presence of bacterium on the metal device could not be screened by any laboratory results or other factors.
Keyword
MeSH Terms
Figure
Reference
-
References
1. Perren SM, Cordey J, Rahn BA, Gautier E, Schneider E. Early temporary porosis of bone induced by internal fixation implants. A reaction to necrosis, not to stress protection? Clin Orthop Relat Res. 1988; 232:139–51.2. Vinh DC, Embil JM. Device-related infections: a review. J Long Term Eff Med Implants. 2005; 15:467–88.
Article3. Zalavras CG, Christensen T, Rigopoulos N, Holtom P, Patzakis MJ. Infection following operative treatment of ankle fractures. Clin Orthop Relat Res. 2009; 467:1715–20.
Article4. Sanderson PJ. Infection in orthopaedic implants. J Hosp Infect. 1991; 18(Suppl A):367–75.
Article5. Böstman O, Pihlajamäki H. Routine implant removal after fracture surgery: a potentially reducible consumer of hospital resources in trauma units. J Trauma. 1996; 41:846–9.6. Rutkow IM. Orthopaedic operations in the United States, 1979 through 1983. J Bone Joint Surg Am. 1986; 68:716–9.
Article7. Sourlas L, Papadakis M, Lallos S, Brilakis E, Efstathopoulos N. Tibial shaft fracture after removal of an ACE tibial nail. J Long Term Eff Med Implants. 2011; 21:193–6.
Article8. Beaupre GS, Csongradi JJ. Refracture risk after plate removal in the forearm. J Orthop Trauma. 1996; 10:87–92.9. Sanderson PL, Ryan W, Turner PG. Complications of metalwork removal. Injury. 1992; 23:29–30.
Article10. Minkowitz RB, Bhadsavle S, Walsh M, Egol KA. Removal of painful orthopaedic implants after fracture union. J Bone Joint Surg Am. 2007; 89:1906–12.
Article11. Keel SB, Jaffe KA, Petur Nielsen G, Rosenberg AE. Orthopaedic implant-related sarcoma: a study of twelve cases. Mod Pathol. 2001; 14:969–77.
Article12. Wang S, Shi X. Molecular mechanisms of metal toxicity and carcinogenesis. Mol Cell Biochem. 2001; 222:3–9.
Article13. Gristina AG, Naylor PT, Myrvik QN. Mechanisms of musculoskeletal sepsis. Orthop Clin North Am. 1991; 22:363–71.
Article14. Gristina AG, Naylor PT, Webb LX. Molecular mechanisms in musculoskeletal sepsis: the race for the surface. Instr Course Lect. 1990; 39:471–82.15. Wagner C, Aytac S, Hänsch GM. Biofilm growth on implants: bacteria prefer plasma coats. Int J Artif Organs. 2011; 34:811–7.
Article16. Schaer TP, Stewart S, Hsu BB, Klibanov AM. Hydrophobic poly-cationic coatings that inhibit biofilms and support bone healing during infection. Biomaterials. 2012; 33:1245–54.
Article17. Moussa FW, Anglen JO, Gehrke JC, Christensen G, Simpson WA. The significance of positive cultures from orthopedic fixation devices in the absence of clinical infection. Am J Orthop (Belle Mead NJ). 1997; 26:617–20.18. Levy PY, Ollivier M, Drancourt M, Raoult D, Argenson JN. Relation between nasal carriage of Staphylococcus aureus and surgical site infection in orthopedic surgery: the role of nasal contamination. A systematic literature review and metaanalysis. Orthop Traumatol Surg Res. 2013; 99:645–51.
Article19. Williams DF. Titanium: epitome of biocompatibility or cause for concern. J Bone Joint Surg Br. 1994; 76:348–9.
Article
- Full Text Links
- Actions
-
Cited
- CITED
-
- Close
- Share
- Similar articles
-
- Timing and Reason for Implant Removal after Ankle Fracture Surgery
- Delayed Foreign-body Reaction of Ankle Fracture Treated with a Biodegradable Plate and Screws: A Case Report
- Comparative Study for the Results of Ankle Fracture Depending onthe Extension of the Posterior Malleolus Fracture
- Tillaux Fracture in an Adolescent with a Trimalleolar Ankle Fracture
- EFFECTS OF THE ION BEAM ASSISTED DEPOSITION OF HYDROXYAPATITE ON OSSEOINTEGRATION OF THE ENDOSSEOUS IMPLANTS IN RABBIT TIBIAE