Chronic Daily Headache in Korea: Prevalence, Clinical Characteristics, Medical Consultation and Management
- Affiliations
-
- 1Department of Neurology, Uijeongbu St. Mary's Hospital, The Catholic University of Korea College of Medicine, Uijeongbu, Korea.
- 2Department of Neurology, Kangbuk Samsung Hospital, Sungkyunkwan University School of Medicine, Seoul, Korea.
- 3Department of Neurology, Chungnam National University College of Medicine, Daejeon, Korea.
- 4Department of Neurology, Seoul St. Mary's Hospital, The Catholic University of Korea College of Medicine, Seoul, Korea.
- 5Department of Neurology, Hallym University College of Medicine, Anyang, Korea. chumk@hallym.ac.kr
- KMID: 2179451
- DOI: http://doi.org/10.3988/jcn.2014.10.3.236
Abstract
- BACKGROUND AND PURPOSE
Chronic daily headache (CDH) is a commonly reported reason for visiting hospital neurology departments, but its prevalence, clinical characteristics, and management have not been well documented in Korea. The objective of this study was to characterize the 1-year prevalence, clinical characteristics, medical consultations, and treatment for CDH in Korea.
METHODS
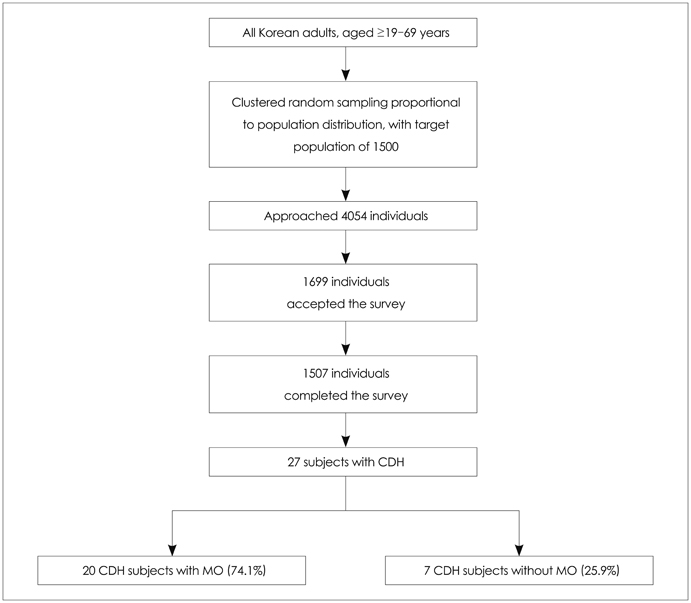
The Korean Headache Survey (KHS) is a nationwide descriptive survey of 1507 Korean adults aged between 19 and 69 years. The KHS investigated headache characteristics, sociodemographics, and headache-related disability using a structured interview. We used the KHS data for this study.
RESULTS
The 1-year prevalence of CDH was 1.8% (95% confidence interval, 1.1-2.5%), and 25.7% of the subjects with CDH met the criteria for medication overuse. Two-thirds (66.7%) of CDH subjects were classified as having chronic migraine, and approximately half of the CDH subjects (48.1%) reported that their headaches either substantially or severely affected their quality of life. Less than half (40.7%) of the subjects with CDH reported having consulted a doctor for their headaches and 40.7% had not received treatment for their headaches during the previous year.
CONCLUSIONS
The prevalence of CDH was 1.8% and medication overuse was associated with one-quarter of CDH cases in Korea. Many subjects with CDH do not seek medical consultation and do not receive appropriate treatment for their headaches.
MeSH Terms
Figure
Cited by 3 articles
-
Recurrent Painful Ophthalmoplegic Neuropathy: a Case Report
Jae Hwi Park, Ho Kyu Lee, Myeong Ju Koh, Jung Hwan Oh, Sung Joo Park
Investig Magn Reson Imaging. 2019;23(2):172-174. doi: 10.13104/imri.2019.23.2.172.Chronic Daily Headache and Medication Overuse Headache in First-Visit Headache Patients in Korea: A Multicenter Clinic-Based Study
Myoung-Jin Cha, Heui-Soo Moon, Jong-Hee Sohn, Byung-Su Kim, Tae-Jin Song, Jae-Moon Kim, Jeong Wook Park, Kwang-Yeol Park, Soo-Kyoung Kim, Byung-Kun Kim, Soo-Jin Cho
J Clin Neurol. 2016;12(3):316-322. doi: 10.3988/jcn.2016.12.3.316.Characteristics of Elderly-Onset (≥65 years) Headache Diagnosed Using the International Classification of Headache Disorders, Third Edition Beta Version
Tae-Jin Song, Yong-Jae Kim, Byung-Kun Kim, Byung-Su Kim, Jae-Moon Kim, Soo-Kyoung Kim, Heui-Soo Moon, Myoung-Jin Cha, Kwang-Yeol Park, Jong-Hee Sohn, Min Kyung Chu, Soo-Jin Cho
J Clin Neurol. 2016;12(4):419-425. doi: 10.3988/jcn.2016.12.4.419.
Reference
-
1. Mathew NT. Chronic refractory headache. Neurology. 1993; 43:6 Suppl 3. S26–S33.2. Pascual J, Colás R, Castillo J. Epidemiology of chronic daily headache. Curr Pain Headache Rep. 2001; 5:529–536.
Article3. Buse DC, Manack AN, Fanning KM, Serrano D, Reed ML, Turkel CC, et al. Chronic Migraine Prevalence, Disability, and Sociodemographic Factors: Results from the American Migraine Prevalence and Prevention Study. Headache. 2012; 52:1456–1470.
Article4. Lantéri-Minet M, Auray JP, El Hasnaoui A, Dartigues JF, Duru G, Henry P, et al. Prevalence and description of chronic daily headache in the general population in France. Pain. 2003; 102:143–149.
Article5. Hagen K, Zwart JA, Vatten L, Stovner L, Bovim G. Prevalence of migraine and non-migrainous headache-head-HUNT, a large population-based study. Cephalalgia. 2000; 20:900–906.
Article6. Queiroz L, Peres M, Kowacs F, Piovesan E, Ciciarelli M, Souza J, et al. Chronic daily headache in Brazil: a nationwide population-based study. Cephalalgia. 2008; 28:1264–1269.
Article7. Rasmussen BK, Jensen R, Schroll M, Olesen J. Epidemiology of headache in a general population-a prevalence study. J Clin Epidemiol. 1991; 44:1147–1157.
Article8. Dodick DW, Turkel CC, DeGryse RE, Aurora SK, Silberstein SD, Lipton RB, et al. OnabotulinumtoxinA for treatment of chronic migraine: pooled results from the double-blind, randomized, placebo-controlled phases of the PREEMPT clinical program. Headache. 2010; 50:921–936.
Article9. Headache Classification Committee. Olesen J, Bousser MG, Diener HC, Dodick D, First M, et al. New appendix criteria open for a broader concept of chronic migraine. Cephalalgia. 2006; 26:742–746.
Article10. Headache Classification Subcommittee of the International Headache Society (IHS). The International Classification of Headache Disorders, 3rd edition (beta version). Cephalalgia. 2013; 33:629–808.11. Kim B, Chu M, Lee T, Kim J, Chung C, Lee K. Prevalence and Impact of Migraine and Tension-Type Headache in Korea: A Nationwide Population-Based Survey. J Clin Neurol. 2012; 8:204–211.
Article12. Council for International Organizations of Medical Sciences [Internet]. International ethical guidelines for bomedical research involving human subjects. Geneva: Council for International Organizations of Medical Sciences;2002. updated 2002. cited 2013 Sep 11. Available from: http://www.cioms.ch/publications/guidelines/guidelines_nov_2002_blurb.htm.13. World Medical Association [Internet]. WMA declaration of Helsinki - Ethical Principles for Medical Research Involving Human Subjects. Ferney-Voltaire: World Medical Association;2001. updated 2001. cited 2013 Sep 11. Available from: http://www.wma.net/en/30publications/10policies/b3/index.html.pdf?print-media-type&footer-right=[page]/[toPage].14. Statistics Korea [Internet]. Korean Statistical Information Service. Daejeon: Statics Korea;2009. updated 2009. cited 2013 Sep 18. Available from: http://kosis.kr.15. Yoon Y, Kim K, Lee M. Redesigning KNSO's Household Survey Sample. Surv Res. 2004; 5:103–130.16. Kosinski M, Bayliss M, Bjorner J, Ware J Jr, Garber W, Batenhorst A, et al. A six-item short-form survey for measuring headache impact: The HIT-6. Qual Life Res. 2003; 12:963–974.17. Chu MK, Im HJ, Ju YS, Yu KH, Ma HI, Kim YJ, et al. Validity and Reliability Assessment of Korean Headache Impact Test-6 (HIT-6). J Korean Neurol Assoc. 2009; 27:1–6.18. Alders E, Hentzen A, Tan C. A Community-Based Prevalence: Study on Headache in Malaysia. Headache. 1996; 36:379–384.
Article19. Ho KH, Ong BK. Headache characteristics and race in Singapore: Results of a randomized national survey. Headache. 2001; 41:279–284.
Article20. Lu SR, Fuh JL, Chen WT, Juang KD, Wang SJ. Chronic daily headache in Taipei, Taiwan: prevalence, follow-up and outcome predictors. Cephalalgia. 2001; 21:980–986.
Article21. Rao GN, Kulkarni GB, Gururaj G, Rajesh K, Subbakrishna DK, Steiner TJ, et al. The burden of headache disorders in India: methodology and questionnaire validation for a community-based survey in Karnataka State. J Headache Pain. 2012; 13:543–550.
Article22. Wang SJ, Fuh JL, Lu SR, Liu CY, Hsu LC, Wang PN, et al. Chronic daily headache in Chinese elderly Prevalence, risk factors, and biannual follow-up. Neurology. 2000; 54:314–319.
Article23. Yu S, Liu R, Zhao G, Yang X, Qiao X, Feng J, et al. The prevalence and burden of primary headaches in China: a population-based door-to-door survey. Headache. 2012; 52:582–591.
Article24. Bigal ME, Tepper SJ, Sheftell FD, Rapoport AM, Lipton RB. Field testing alternative criteria for chronic migraine. Cephalalgia. 2006; 26:477–482.
Article25. Grande RB, Aaseth K, Gulbrandsen P, Lundqvist C, Russell MB. Prevalence of Primary Chronic Headache in a Population-Based Sample of 30-to 44-Year-Old Persons. Neuroepidemiology. 2008; 30:76–83.
Article26. Katsarava Z, Dzagnidze A, Kukava M, Mirvelashvili E, Djibuti M, Janelidze M, et al. Primary headache disorders in the Republic of Georgia: prevalence and risk factors. Neurology. 2009; 73:1796–1803.
Article27. Scher AI, Stewart WF, Liberman J, Lipton RB. Prevalence of frequent headache in a population sample. Headache. 1998; 38:497–506.
Article28. Bigal ME, Lipton RB. Obesity is a risk factor for transformed migraine but not chronic tension-type headache. Neurology. 2006; 67:252–257.
Article29. Stark RJ, Ravishankar K, Siow HC, Lee KS, Pepperle R, Wang SJ. Chronic migraine and chronic daily headache in the Asia-Pacific region: A systematic review. Cephalalgia. 2013; 33:266–283.
Article30. Stewart WF, Lipton RB, Liberman J. Variation in migraine prevalence by race. Neurology. 1996; 47:52–59.
Article31. Lasch KE. Culture and pain. Pain Clinical Updates. 2002; 10:1–9.32. Lipton RB, Scher AI, Steiner TJ, Bigal ME, Kolodner K, Liberman JN, et al. Patterns of health care utilization for migraine in England and in the United States. Neurology. 2003; 60:441–448.
Article33. Scher AI, Stewart WF, Ricci JA, Lipton RB. Factors associated with the onset and remission of chronic daily headache in a population-based study. Pain. 2003; 106:81–89.
Article34. Castillo J, Muñoz P, Guitera V, Pascual J. Epidemiology of chronic daily headache in the general population. Headache. 1999; 39:190–196.
Article35. Bigal ME, Serrano D, Reed M, Lipton RB. Chronic migraine in the population. Neurology. 2008; 71:559–566.36. Suh GI, Park JW, Shin HE. Differences in Clinical Features and Disability according to the Frequency of Medication Use in Patients with Chronic Migraine. J Clin Neurol. 2012; 8:198–203.
Article37. Bigal ME, Sheftell FD, Rapoport AM, Lipton RB, Tepper SJ. Chronic daily headache in a tertiary care population: correlation between the International Headache Society diagnostic criteria and proposed revisions of criteria for chronic daily headache. Cephalalgia. 2002; 22:432–438.
Article38. D'Amico D. Pharmacological prophylaxis of chronic migraine: a review of double-blind placebo-controlled trials. Neurol Sci. 2010; 31:Suppl 1. S23–S28.39. Diener HC, Dodick DW, Aurora SK, Turkel CC, DeGryse RE, Lipton RB, et al. OnabotulinumtoxinA for treatment of chronic migraine: results from the double-blind, randomized, placebo-controlled phase of the PREEMPT 2 trial. Cephalalgia. 2010; 30:804–814.
Article40. Silberstein SD, Lipton RB, Dodick DW, Freitag FG, Ramadan N, Mathew N, et al. Efficacy and Safety of Topiramate for the Treatment of Chronic Migraine: A Randomized, Double-Blind, Placebo-Controlled Trial. Headache. 2007; 47:170–180.
Article41. Yurekli VA, Akhan G, Kutluhan S, Uzar E, Koyuncuoglu HR, Gultekin F. The effect of sodium valproate on chronic daily headache and its subgroups. J Headache Pain. 2008; 9:37–41.
Article42. Diener HC, Dodick DW, Goadsby PJ, Lipton RB, Olesen J, Silberstein SD. Chronic migraine-classification, characteristics and treatment. Nat Rev Neurol. 2012; 8:162–171.
Article43. Bigal ME, Rapoport AM, Lipton RB, Tepper SJ, Sheftell FD. Assessment of migraine disability using the migraine disability assessment (MIDAS) questionnaire: a comparison of chronic migraine with episodic migraine. Headache. 2003; 43:336–342.
Article44. D'Amico D, Grazzi L, Usai S, Raggi A, Leonardi M, Bussone G. Disability in chronic daily headache: state of the art and future directions. Neurol Sci. 2011; 32:Suppl 1. S71–S76.45. Wang SJ. Epidemiology of migraine and other types of headache in Asia. Curr Neurol Neurosci Rep. 2003; 3:104–108.
Article46. Roh JK, Kim JS, Ahn YO. Epidemiologic and Clinical Characteristics of Migraine and Tension-Type Headache in Korea. Headache. 2003; 38:356–365.
Article47. Rasmussen BK, Jensen R, Olesen J. Questionnaire versus clinical interview in the diagnosis of headache. Headache. 1991; 31:290–295.
Article48. Headache Classification Subcommittee of the International Headache Society. The international classification of headache disorders: 2nd edition. Cephalalgia. 2004; 24:Suppl 1. 9–160.49. Göbel H, Petersen-Braun M, Soyka D. The epidemiology of headache in Germany: a nationwide survey of a representative sample on the basis of the headache classification of the International Headache Society. Cephalalgia. 1994; 14:97–106.
Article50. Lavados P, Tenhamm E. Epidemiology of tension-type headache in Santiago, Chile: a prevalence study. Cephalalgia. 1998; 18:552–558.
Article51. Wiendels NJ, Knuistingh Neven A, Rosendaal FR, Spinhoven P, Zitman FG, et al. Chronic frequent headache in the general population: prevalence and associated factors. Cephalalgia. 2006; 26:1434–1442.
Article52. Russell MB. Tension-type headache in 40-year-olds: a Danish population-based sample of 4000. J Headache Pain. 2005; 6:441–447.
Article
- Full Text Links
- Actions
-
Cited
- CITED
-
- Close
- Share
- Similar articles
-
- Clinical Characteristics of Chronic Headache Patients With Fibromyalgia: A Hospital-based Study
- A clinical study on headache in the elderly
- Clinical Charateristics of Chronic Daily Headache Patients Visit to University Hospital
- A Case of Chronic Daily Headache Attributed to Hashimoto's Thyroiditis
- Clinical Characteristics and Efficacy of Prophylactic Treatment of Pediatric Chronic Daily Headache