J Clin Neurol.
2008 Jun;4(2):75-83. 10.3988/jcn.2008.4.2.75.
Cardiac Troponin T Elevation After Stroke: Relationships Between Elevated Serum Troponin T, Stroke Location, and Prognosis
- Affiliations
-
- 1Department of Neurology, Kangbuk Samsung Hospital, Sungkyunkwan University School of Medicine, Seoul, Korea. kybzzz.kim@samsung.com
- 2Department of Radiology, Kangbuk Samsung Hospital, Sungkyunkwan University School of Medicine, Seoul, Korea.
- 3Department of Laboratory Medicine, Kangbuk Samsung Hospital, Sungkyunkwan University School of Medicine, Seoul, Korea.
- 4Department of Physical Medicine and Rehabilitation, Kangbuk Samsung Hospital, Sungkyunkwan University School of Medicine, Seoul, Korea.
- 5Department of Neurology, Chung-Ang University Hospital, Chung-Ang University School of Medicine, Seoul, Korea.
- KMID: 2178926
- DOI: http://doi.org/10.3988/jcn.2008.4.2.75
Abstract
- Background and Purpose
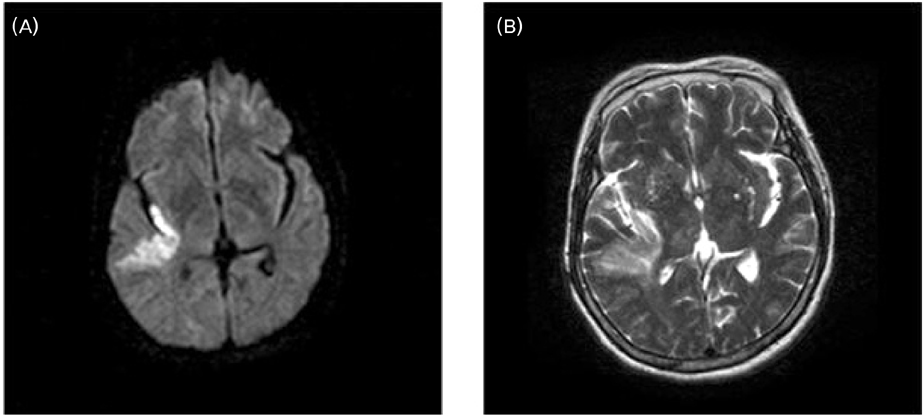
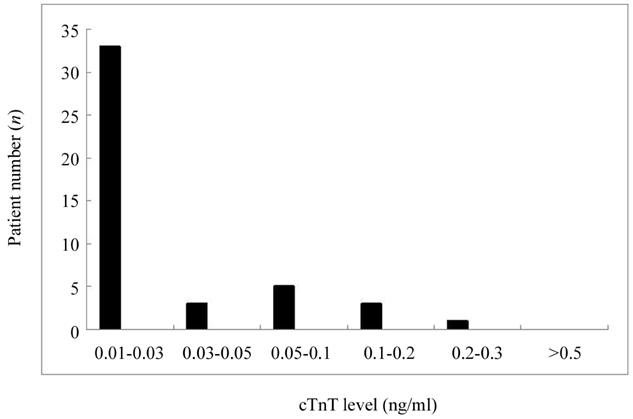
Elevation of serum cardiac troponin T (cTnT) is regarded as a specific marker of acute coronary syndrome. Serum cTnT can be increased in patients with acute ischemic stroke, but its clinical implications remain unclear. The aim of this study was to identify the relationships between elevated cTnT and stroke severity, location, and prognosis. Methods: From January 2005 to December 2006, this study recruited 455 consecutive patients who were admitted to Kangbuk Samsung Hospital due to acute ischemic stroke within 3 days of onset, which was confirmed by diffusion magnetic resonance imaging. A total of 416 patients was finally included and divided into 2 groups: an elevated cTnT group (n=45) and a normal cTnT group (n=371). The short-term prognosis was assessed by 30-day modified Rankin Scale responder analysis was compared between the two groups. Results: Serum cTnT was elevated in 10.8% of cases, with elevated cTnT associated with greater stroke severity, as assessed by the National Institutes of Health Stroke Scale score, Insular-lobe involvement was more common in patients with elevated cTnT than in the normal cTnT group. Short-term prognosis was more unfavorable in the elevated cTnT group than in the normal cTnT group. Multivariate regression analysis indicated that elevated cTnT was independently related to insular involvement, cardioembolism, and unfavorable outcome. Conclusions: Elevated cTnT in acute ischemic stroke was associated with severe neurological deficits at stroke onset and damages to the insular lobe. The outcome of acute ischemic stroke was worse for patients with elevated cTnT than for those with normal cTnT. The pathomechanism underlying acute ischemic stroke and subclinical myocardial damage warrants further study.
Keyword
MeSH Terms
Figure
Cited by 1 articles
-
Prognostic Implications of Elevated Cardiac Troponin T in Patients with Acute Ischemic Stroke
Chae Lim Jung, Tae-Dong Jeong, Ki-Sook Hong
Lab Med Online. 2017;7(1):28-33. doi: 10.3343/lmo.2017.7.1.28.
Reference
-
1. James P, Ellis CJ, Whitlock RM, McNeil AR, Henley J, Anderson NE. Relation between troponin T concentration and mortality in patients presenting with an acute stroke: observational study. BMJ. 2000. 320:1502–1504.
Article2. Yasue H, Yoshimura M, Sumida H, Kikuta K, Kugiyama K, Jougasaki M, et al. Localization and mechanism of secretion of B-type natriuretic peptide in comparison with those of A-type natriuretic peptide in normal subjects and patients with heart failure. Circulation. 1994. 90:195–203.
Article3. Inoue S, Murakami Y, Sano K, Katoh H, Shimada T. Atrium as a source of brain natriuretic polypeptide in patients with atrial fibrillation. J Card Fail. 2000. 6:92–96.
Article4. Takahashi K, Totsune K, Sone M, Ohneda M, Murakami O, Itoi K, et al. Human brain natriuretic peptide-like immunoreactivity in human brain. Peptides. 1992. 13:121–123.
Article5. Wijdicks EF, Schievink WI, Burnett JC Jr. Natriuretic peptide system and endothelin in aneurysmal subarachnoid hemorrhage. J Neurosurg. 1997. 87:275–280.
Article6. Sviri GE, Feinsod M, Soustiel JF. Brain natriuretic peptide and cerebral vasospasm in subarachnoid hemorrhage: clinical and TCD correlations. Stroke. 2000. 31:118–122.
Article7. Levy A. The exiting causes of ventricular fibrillation in animals under chloroform anesthesia. Heart. 1913. 4:319–378.8. Norris JW, Hachinski VC, Myers MG, Callow J, Wong T, Moore RW. Serum cardiac enzymes in stroke. Stroke. 1979. 10:548–553.
Article9. Myers MG, Norris JW, Hachinski VC, Weingert ME, Sole MJ. Cardiac sequelae of acute stroke. Stroke. 1982. 13:838–842.
Article10. Christensen H, Johannesen HH, Christensen AF, Bendtzen K, Boysen G. Serum cardiac troponin I in acute stroke is related to serum cortisol and TNF-alpha. Cerebrovasc Dis. 2004. 18:194–199.
Article11. Trooyen M, Indredavik B, Rossvoll O, Slordahl SA. Myocardial injury in acute stroke assessed by troponin I. Tidsskr Nor Laegeforen. 2001. 121:421–425.12. Di Angelantonio E, Fiorelli M, Toni D, Sacchetti ML, Lorenzano S, Falcou A, et al. Prognostic significance of admission levels of troponin I in patients with acute ischaemic stroke. J Neurol Neurosurg Psychiatry. 2005. 76:76–81.
Article13. Ay H, Koroshetz WJ, Benner T, Vangel MG, Melinosky C, Arsava EM, et al. Neuroanatomic correlates of strokerelated myocardial injury. Neurology. 2006. 66:1325–1329.
Article14. Barber M, Morton JJ, Macfarlane PW, Barlow N, Roditi G, Stott DJ. Elevated troponin levels are associated with sympathoadrenal activation in acute ischemic stroke. Cerebrovasc Dis. 2007. 23:260–266.
Article15. Etgen T, Baum H, Sander K, Sander D. Cardiac troponins and N-terminal pro-brain natriuretic peptide in acute ischemic stroke do not relate to clinical prognosis. Stroke. 2005. 36:270–275.
Article16. Klingelhöfer J, Sander D. Cardiovascular consequences of clinical stroke. Baillieres Clin Neurol. 1997. 6:309–335.17. Connor RC. Heart damage associated with intracranial lesions. Br Med J. 1968. 3:29–31.
Article18. Weidler DJ. Myocardial damage and cardiac arrhythmias after intracranial hemorrhage. A critical review. Stroke. 1974. 5:759–764.
Article19. Jacob WA, Van Bogaert A, De Groodt-Lasseel MH. Myocardial ultrastructure and haemodynamic reactions during experimental subarachnoid haemorrhage. J Mol Cell Cardiol. 1972. 4:287–298.
Article20. Raab W, Stark E, Macmillan WH, Gigee WR. Sympathogenic origin and antiadrenergic prevention of stress-induced myocardial lesions. Am J Cardiol. 1961. 8:203–211.
Article21. Oppenheimer SM, Wilson JX, Guiraudon C, Cechetto DF. Insular cortex stimulation produces lethal cardiac arrhythmias: a mechanism of sudden death. Brain Res. 1991. 550:115–121.
Article22. Oppenheimer SM, Cechetto DF. Cardiac chronotropic organization of the rat insular cortex. Brain Res. 1990. 533:66–72.
Article23. Cechetto DF, Wilson JX, Smith KE, Wolski D, Silver MD, Hachinski VC. Autonomic and myocardial changes in middle cerebral artery occlusion: stroke models in the rat. Brain Res. 1989. 502:296–305.
Article24. Alpert JS, Thygesen K, Antman E, Bassand JP. Joint European Society of Cardiology/American College of Cardiology Committee. Myocardial infarction redefined-a consensus document of the Joint European Society of Cardiology/American College of Cardiology Committee for the redefinition of myocardial infarction. J Am Coll Cardiol. 2000. 09. 36(3):959–969.
Article25. Adams HP Jr, Leclerc JR, Bluhmki E, Clarke W, Hansen MD, Hacke W. Measuring outcomes as a function of baseline severity of ischemic stroke. Cerebrovasc Dis. 2004. 18:124–129.
Article26. Advisory Council for the National Institute of Neurological Diseases and Blindness. A classification and outline of cerebrovascular diseases. Neurology. 1958. 8:395–434.27. Adams HP Jr, Bendixen BH, Kappelle LJ, Biller J, Love BB, Gordon DL, et al. Classification of subtype of acute ischemic stroke. Definitions for use in a multicenter clinical trial. TOAST. Trial of Org 10172 in Acute Stroke Treatment. Stroke. 1993. 24:35–41.
Article28. Yasui Y, Breder CD, Saper CB, Cechetto DF. Autonomic responses and efferent pathways from the insular cortex in the rat. J Comp Neurol. 1991. 303:355–374.
Article29. Oppenheimer SM, Gelb A, Girvin JP, Hachinski VC. Cardiovascular effects of human insular cortex stimulation. Neurology. 1992. 42:1727–1732.
Article
- Full Text Links
- Actions
-
Cited
- CITED
-
- Close
- Share
- Similar articles
-
- Prognostic Implications of Elevated Cardiac Troponin T in Patients with Acute Ischemic Stroke
- Prognostic Significance of Troponin Elevation for Long-Term Mortality after Ischemic Stroke
- Is it Necessary to Study both Creatine Kinase MB and Troponin for an Acute Diagnosis of Myocardial Infarction?
- Initial Troponin Level as a Predictor of Prognosis in Patients with Intracerebral Hemorrhage
- The relationship of serum creatinine and cardiac troponin I after off-pump coronary artery bypass graft surgery