J Korean Acad Conserv Dent.
2010 Nov;35(6):461-472. 10.5395/JKACD.2010.35.6.461.
The study of fractural behavior of repaired composite
- Affiliations
-
- 1Division of Dentistry, Department of Conservative Dentistry, Graduate of Kyung Hee University, Seoul, Korea. choikkyu@khu.ac.kr
- KMID: 2176468
- DOI: http://doi.org/10.5395/JKACD.2010.35.6.461
Abstract
OBJECTIVES
This study evaluated microtensile bond strength (microTBS) and short-rod fracture toughness to explain fractural behavior of repaired composite restorations according to different surface treatments.
MATERIALS AND METHODS
Thirty composite blocks for microTBS test and sixty short-rod specimens for fracture toughness test were fabricated and were allocated to 3 groups according to the combination of surface treatment (none-treated, sand blasting, bur roughening). Each group was repaired immediately and 2 weeks later. Twenty-four hours later from repair, microTBS and fracture toughness test were conducted. Mean values analyzed with two-way ANOVA / Tukey's B test (alpha = 0.05) and correlation analysis was done between microTBS and fracture toughness. FE-SEM was employed on fractured surface to examine the crack propagation.
RESULTS
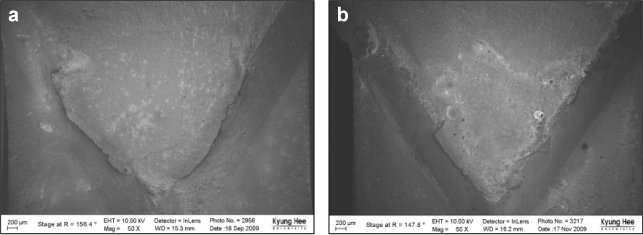
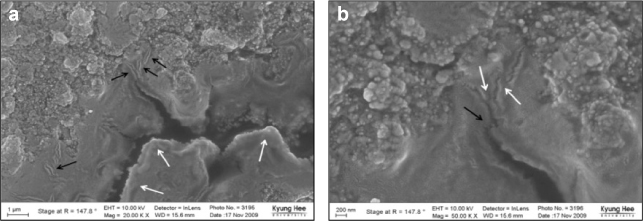
The fresh composite resin showed higher microTBS than the aged composite resin (p < 0.001). Mechanically treated groups showed higher bond strength than non-mechanically treated groups except none-treated fresh group in microTBS (p < 0.05). The fracture toughness value of mechanically treated surface was higher than that of non-mechanically treated surface (p < 0.05). There was no correlation between fracture toughness and microtensile bond strength values. Specimens having high KIC showed toughening mechanism including crack deviation, microcracks and crack bridging in FE-SEM.
CONCLUSIONS
Surface treatment by mechanical interlock is more important for effective composite repair, and the fracture toughness test could be used as an appropriate tool to examine the fractural behavior of the repaired composite with microtensile bond strength.
Keyword
MeSH Terms
Figure
Reference
-
1. Papacchini F, Dall'Oca S, Chieffi N, Goracci C, Sadek FT, Suh BI, Tay FR, Ferrari M. Composite-to-composite microtensile bond strength in the repair of a microfilled hybrid resin: effect of surface treatment and oxygen inhibition. J Adhes Dent. 2007. 9(1):25–31.2. Suh BI. Oxygen-inhibited layer in adhesion dentistry. J Esthet Restor Dent. 2004. 16(5):316–323.
Article3. Rodrigues SA Jr, Ferracane JL, Della Bona A. Influence of surface treatments on the bond strength of repaired resin composite restorative materials. Dent Mater. 2009. 25(4):442–451.
Article4. Fawzy AS, El-Askary FS, Amer MA. Effect of surface treatments on the tensile bond strength of repaired water-aged anterior restorative micro-fine hybrid resin composite. J Dent. 2008. 36(12):969–976.
Article5. Cavalcanti AN, De Lima AF, Peris AR, Mitsui FH, Marchi GM. Effect of surface treatments and bonding agents on the bond strength of repaired composites. J Esthet Restor Dent. 2007. 19(2):90–98. (discussion 99).
Article6. Teixeira EC, Bayne SC, Thompson JY, Ritter AV, Swift EJ. Shear bond strength of self-etching bonding systems in combination with various composites used for repairing aged composites. J Adhes Dent. 2005. 7(2):159–164.7. Tezvergil A, Lassila LV, Vallittu PK. Composite-composite repair bond strength: effect of different adhesion primers. J Dent. 2003. 31(8):521–525.
Article8. Brosh T, Pilo R, Bichacho N, Blutstein R. Effect of combinations of surface treatments and bonding agents on the bond strength of repaired composites. J Prosthet Dent. 1997. 77(2):122–126.
Article9. Bonstein T, Garlapo D, Donarummo J Jr, Bush PJ. Evaluation of varied repair protocols applied to aged composite resin. J Adhes Dent. 2005. 7(1):41–49.10. Cesar PF, Meyer Faara PM, Miwa Caldart R, Gastaldoni Jaeger R, da Cunha Ribeiro F. Tensile bond strength of composite repairs on Artglass using different surface treatments. Am J Dent. 2001. 14(6):373–377.11. Mecholsky JJ Jr. Fracture mechanics principles. Dent Mater. 1995. 11(2):111–112.
Article12. Tam LE, Dev S, Pilliar RM. Fracture toughness ov conventional or photopolymerized glass ionomer/dentin interfaces. Oper Dent. 1995. 20(4):144–150.13. Ryu GJ, Choi GW, Park SJ, Choi KK. A Study on Fractural Behavior of Dentin-Resin Interface. J Korean Acad Conserv Dent. 2007. 32(3):208–221.
Article14. Dhuru VB, Lloyd CH. The fracture toughness of repaired composite. J Oral Rehabil. 1986. 13(5):413–421.
Article15. Tam LE, Pilliar RM. Fracture toughness of dentin/resin-composite adhesive interfaces. J Dent Res. 1993. 72(5):953–959.
Article16. Tam LE, Pilliar RM. Effects of dentin surface treatments on the fracture toughness and tensile bond strength of a dentin-composite adhesive interface. J Dent Res. 1994. 73(9):1530–1538.
Article17. Barker LM. A simplified methods for measuring plane strain fracture toughness. Eng Fract Mech. 1977. 9:361–369.18. Tam LE, Pilliar RM. Fracture surface characterization of dentin-bonded interfacial fracture toughness specimens. J Dent Res. 1994. 73(3):607–619.
Article19. Lee YS, Choi KK, Park SJ. Effect of resin matrix on degree of conversion and fracture toughness of dental composites. J Korean Acad Conserv Dent. 2002. 27(1):77–86.
Article20. Ruyter IE, Oysaed H. Composites for use in posterior teeth: composition and conversion. J Biomed Mater Res. 1987. 21(1):11–23.
Article21. Filho JD, Poskus LT, Guimarães JG, Barcellos AA, Silva EM. Degree of conversion and plasticization of dimethacrylate-based polymeric matrices: influence of light-curing mode. J Oral Sci. 2008. 50(3):315–321.
Article22. Sturdevant CM. Roberson TM, Heymann H, Swift EJ, editors. Sturdevant's art and science of operative dentistry. 2006. 5th ed.201–203.23. Goncalves F, Kawano Y, Pfeifer C, Stansbury JW, Braga RR. Influence of BisGMA, TEGDMA, and BisEMA contents on viscosity, conversion, and flexural strength of experimental resins and composites. Eur J Oral Sci. 2009. 117(4):442–446.
Article24. Eick JD, Gwinnett AJ, Pashley DH, Robinson SJ. Current concepts on adhesion to dentin. Crit Rev Oral Biol Med. 1997. 8(3):306–335.
Article25. Lapcík L Jr, Stasko A, Sáha P. Electron paramagnetic resonance study of free-radical kinetics in ultra-violet-light cured dimethacrylate copolymers. J Mater Sci Mater Med. 1998. 9(5):257–262.26. Miyazaki M, Onose H, Iida N, Kazama H. Determination of residual double bonds in resin-dentin interface by Raman spectroscopy. Dent Mater. 2003. 19(3):245–251.
Article27. Cavalcanti AN, Lobo MM, Fontes CM, Liporoni P, Mathias P. Microleakage at the Composite-repair Interface: Effect of Different Surface Treatment Methods. Oper Dent. 2005. 30(1):113–117.28. Lovell LG, Newman SM, Bowman CN. The effects of light intensity, temperature, and comonomer composition on the polymerization behavior of dimethacrylate dental resins. J Dent Res. 1999. 78(8):1469–1476.
Article29. Santerre JP, Shajii L, Leung BW. Relation of dental composite formulations to their degradation and the release of hydrolyzed polymeric-resin-derived products. Crit Rev Oral Biol Med. 2001. 12(2):136–151.
Article30. Ye Q, Spencer P, Wang Y, Misra A. Relationship of solvent to the photopolymerization process, properties, and structure in model dentin adhesives. J Biomed Mater Res A. 2007. 80(2):342–350.
Article31. Passos SP, Ozcan M, Vanderlei AD, Leite FP, Kimpara ET, Bottino MA. Bond strength durability of direct and indirect composite systems following surface conditioning for repair. J Adhes Dent. 2007. 9(5):443–447.32. Choi SY, Jeong SW, Hwang YC, Kim SH, Yun C, Oh WM, Hwang IN. Shear bond strength of repaired composite resin restorations. J Korean Acad Conserv Dent. 2002. 27(6):569–576.
Article33. Ferracane JL, Marker VA. Solvent degradation and reduced fracture toughness in aged composites. J Dent Res. 1992. 71(1):13–19.
Article34. Craig RG, Powers JM. Restorative Dental Materials. 2002. 11th. St Louis: Mosby.35. Nalla RK, Kinney JH, Ritchie RO. Effect of orientation on the in vitro fracture toughness of dentin: the role of toughening mechanisms. Biomaterials. 2003. 24(22):3955–3968.
Article36. Young RJ, Beaumont P. Failure of brittle polymers by slow crack growth. Part 2. Failure processes in a silica particle-filled epoxy resin composite. J Mater Sci. 1975. 10:1343–1350.37. Kim KH, Park JH, Imai Y, Kishi T. Microfracture mechanisms of dental resin composites containing spherically-shaped filler particles. J Dent Res. 1994. 73(2):499–504.
Article38. KIM SC. Polymer Engeneering I. 1994. 287–310.39. Soderholm KJ. Review of the fracture toughness approach. Dent Mater. 2010. 26(2):e63–e77.
Article40. Kruzic JJ, Nalla RK, Kinney JH, Ritchie R. Crack blunting, crack bridging and resistance-curve fracture mechanics in dentin: effect of hydration. Biomaterials. 2003. 24(28):5209–5221.
Article
- Full Text Links
- Actions
-
Cited
- CITED
-
- Close
- Share
- Similar articles
-
- The Effect of Lateral Approximations on the Survival of the Free Composite Flap
- The effect of different bonding systems on shear bond strength of repaired composite resin
- Microtensile bond strength of repaired indirect resin composite
- Fracture resistance of crown-root fractured teeth repaired with dual-cured composite resin and horizontal posts
- Use of Auricular Composite Graft to Repair Nostril Stenosis: A Case Report