J Breast Cancer.
2009 Dec;12(4):324-330. 10.4048/jbc.2009.12.4.324.
Factors Affecting the Ipsilateral Breast Tumor Recurrence after Breast Conserving Therapy in Patients with T1 and T2 Tumors
- Affiliations
-
- 1Department of Surgery, Seoul National University College of Medicine, Seoul, Korea. hanw@snu.ac.kr
- 2Department of Surgery, College of Medicine, Gyeongsang National University, Jinju, Korea.
- 3Department of Surgery, University of Ulsan, College of Medicine and Asan Medical Center, Seoul, Korea.
- 4Department of Surgery, Korea Institution and Medical Science, Korea Cancer Center Hospital, Seoul, Korea.
- 5Department of Pathology, Seoul National University College of Medicine, Seoul, Korea.
- 6Department of Radiation Oncology, Seoul National University College of Medicine, Seoul, Korea.
- KMID: 2175534
- DOI: http://doi.org/10.4048/jbc.2009.12.4.324
Abstract
- PURPOSE
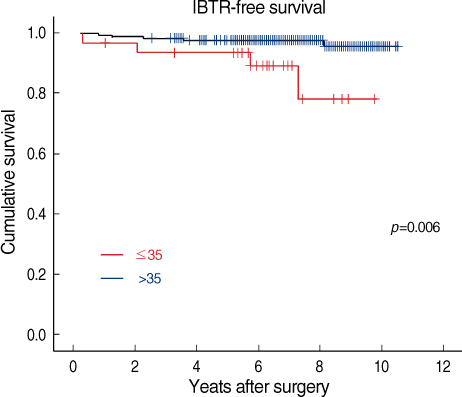
Nearly half of all breast cancers are treated with breast conserving therapy (BCT). The purpose of this study was to identify the risk factors for ipsilateral breast tumor recurrence (IBTR) after BCT in T1 and T2 breast cancer patients. METHODS: The medical records of 294 T1 or T2 breast cancer patients who underwent BCT at Seoul National University Hospital between January 1998 and December 2002 were retrospectively reviewed. Kaplan-Meier curves and Cox proportional regression analysis were used to identify the significant clinicopathologic factors that influence IBTR. RESULTS: Among the 294 patients, 12 patients (4.8%) developed IBTR after a median follow-up of 82 months. Univariate analysis demonstrated that younger age (< or =35 year) had significant associations with IBTR (p=0.006). Tumor size, lymph node status, histologic grade, extensive intraductal component, lymphovascular invasion, and close resection margins were not significant factor associated with IBTR. The triple negative breast cancer subtype also did not have significant association with IBTR. Multivariate analysis showed that the younger age at diagnosis was a significant predictor of IBTR with a HR of 3.86 (p=0.036; 95% CI, 1.09-13.60). CONCLUSION: Younger age at diagnosis (< or =35) may be associated with an increased risk of IBTR in patients who underwent BCT.
MeSH Terms
Figure
Cited by 1 articles
-
Validation of a Web-Based Tool to Predict the Ipsilateral Breast Tumor Recurrence (IBTR! 2.0) after Breast-Conserving Therapy for Korean Patients
Seung Pil Jung, Sung Mo Hur, Se Kyung Lee, Sangmin Kim, Min-Young Choi, Soo Youn Bae, Jiyoung Kim, Min Kuk Kim, Won Ho Kil, Jun-Ho Choe, Jung-Han Kim, Jee Soo Kim, Seok Jin Nam, Jeoung Won Bae, Jeong Eon Lee
J Breast Cancer. 2013;16(1):97-103. doi: 10.4048/jbc.2013.16.1.97.
Reference
-
1. Morrow M, Harris JR. Local Management of Invasive Cancer: Breast. In: Harris JR, Lippman ME, Morrow M, Osborne CK, editors. Diseases of the Breast. 3rd ed. Philadelphia: Lippincott Williams & Wilkins; 2004. pp. 719-744.2. Fisher B, Anderson S, Bryant J, Margolese RG, Deutsch M, Fisher ER, et al. Twenty-year follow-up of a randomized trial comparing total mastectomy, lumpectomy, and lumpectomy plus irradiation for the treatment of invasive breast cancer. N Engl J Med. 2002; 347:1233–1241.
Article3. Veronesi U, Cascinelli N, Mariani L, Greco M, Saccozzi R, Luini A, et al. Twenty-year follow-up of a randomized study comparing breast-conserving surgery with radical mastectomy for early breast cancer. N Engl J Med. 2002; 347:1227–1232.
Article4. Ahn SH, Yoo KY. Korean Breast Cancer Society. Chronological changes of clinical characteristics in 31,115 new breast cancer patients among Koreans during 1996-2004. Breast Cancer Res Treat. 2006; 99:209–214.5. Clarke M, Collins R, Darby S, Davies C, Elphinstone P, Evans E, et al. Effects of radiotherapy and of differences in the extent of surgery for early breast cancer on local recurrence and 15-year survival: An overview of the randomised trials. Lancet. 2005; 366:2087–2106.6. Wapnir IL, Anderson SJ, Mamounas EP, Geyer CE Jr, Jeong JH, Tan-Chiu E, et al. Prognosis after ipsilateral breast tumor recurrence and locoregional recurrences in five national surgical adjuvant breast and bowel project node-positive adjuvant breast cancer trials. J Clin Oncol. 2006; 24:2028–2037.
Article7. Kang SH, Lee SJ. The effect of margin width on local recurrence after breast conservation therapy. J Korean Surg Soc. 2007; 73:385–394.8. Suh CO, Chung EJ, Lee HD, Lee KS, Oh KK, Kim GE. Risk factors for recurrence after conservative treatment in early breast cancer. J Korean Soc Ther Radiol. 1997; 15:331–338.9. Nguyen PL, Taghian AG, Katz MS, Niemierko A, AbiRaad RF, Boon WL, et al. Breast cancer subtype approximated by estrogen receptor, progesterone receptor, and her-2 is associated with local and distant recurrence after breast-conserving therapy. J Clin Oncol. 2008; 26:2373–2378.
Article10. Lee JW, Han W, Ko E, Cho J, Jung SY, Kim EK, et al. Alteration of estrogen receptor, progesterone receptor, and her-2 expression in breast cancer after neoadjuvant chemotherapy. J Breast Cancer. 2007; 10:206–210.
Article11. Dent R, Trudeau M, Pritchard KI, Hanna WM, Kahn HK, Sawka CA, et al. Triple-negative breast cancer: clinical features and patterns of recurrence. Clin Cancer Res. 2007; 13:4429–4434.
Article12. Arriagada R, Le MG, Guinebretiere JM, Dunant A, Rochard F, Tursz T. Late local recurrences in a randomised trial comparing conservative treatment with total mastectomy in early breast cancer patients. Ann Oncol. 2003; 14:1617–1622.
Article13. Voogd AC, Nielsen M, Peterse JL, Blichert-Toft M, Bartelink H, Overgaard M, et al. Differences in risk factors for local and distant recurrence after breast-conserving therapy or mastectomy for stage i and ii breast cancer: Pooled results of two large european randomized trials. J Clin Oncol. 2001; 19:1688–1697.
Article14. Haffty BG, Harrold E, Khan AJ, Pathare P, Smith TE, Turner BC, et al. Outcome of conservatively managed early-onset breast cancer by brca1/2 status. Lancet. 2002; 359:1471–1477.15. Benson JR, Jatoi I, Keisch M, Esteva FJ, Makris A, Jordan VC. Early breast cancer. Lancet. 2009; 373:1463–1479.
Article16. Jacquemier J, Kurtz JM, Amalric R, Brandone H, Ayme Y, Spitalier JM. An assessment of extensive intraductal component as a risk factor for local recurrence after breast-conserving therapy. Br J Cancer. 1990; 61:873–876.
Article17. Borger J, Kemperman H, Hart A, Peterse H, van Dongen J, Bartelink H. Risk factors in breast-conservation therapy. J Clin Oncol. 1994; 12:653–660.
Article18. Sasson AR, Fowble B, Hanlon AL, Torosian MH, Freedman G, Boraas M, et al. Lobular carcinoma in situ increases the risk of local recurrence in selected patients with stages i and ii breast carcinoma treated with conservative surgery and radiation. Cancer. 2001; 91:1862–1869.
Article19. Fourquet A, Campana F, Zafrani B, Mosseri V, Vielh P, Durand JC, et al. Prognostic factors of breast recurrence in the conservative management of early breast cancer: a 25-year follow-up. Int J Radiat Oncol Biol Phys. 1989; 17:719–725.
Article20. Locker AP, Ellis IO, Morgan DA, Elston CW, Mitchell A, Blamey RW. Factors influencing local recurrence after excision and radiotherapy for primary breast cancer. Br J Surg. 1989; 76:890–894.
Article21. Freedman GM, Hanlon AL, Fowble BL, Anderson PR, Nicolaou N. Recursive partitioning identifies patients at high and low risk for ipsilateral tumor recurrence after breast-conserving surgery and radiation. J Clin Oncol. 2002; 20:4015–4021.
Article22. Jobsen JJ, van der Palen J, Meerwaldt JH. The impact of age on local control in women with pt1 breast cancer treated with conservative surgery and radiation therapy. Eur J Cancer. 2001; 37:1820–1827.
Article23. Komoike Y, Akiyama F, Iino Y, Ikeda T, Akashi-Tanaka S, Ohsumi S, et al. Ipsilateral breast tumor recurrence (IBTR) after breast-conserving treatment for early breast cancer: risk factors and impact on distant metastases. Cancer. 2006; 106:35–41.24. Kim KJ, Huh SJ, Yang JH, Park W, Nam SJ, Kim JH, et al. Treatment results and prognostic factors of early breast cancer treated with a breast conserving operation and radiotherapy. Jpn J Clin Oncol. 2005; 35:126–133.
Article25. Han W, Kim SW, Park IA, Kang D, Youn YK, Oh SK, et al. Young age: an independent risk factor for disease-free survival in women with operable breast cancer. BMC Cancer. 2004; 4:82.
Article26. Han W, Kang SY; Korean Breast Cancer Society. Relationship between age at diagnosis and outcome of premenopausal breast cancer: age less than 35 years is a reasonable cut-off for defining young age-onset breast cancer. Breast Cancer Res Treat. 2010; 119:193–200.27. Luini A, Rososchansky J, Gatti G, Zurrida S, Caldarella P, Viale G, et al. The surgical margin status after breast-conserving surgery: discussion of an open issue. Breast Cancer Res Treat. 2009; 113:397–402.
Article28. Wazer DE, DiPetrillo T, Schmidt-Ullrich R, Weld L, Smith TJ, Marchant DJ, et al. Factors influencing cosmetic outcome and complication risk after conservative surgery and radiotherapy for early-stage breast carcinoma. J Clin Oncol. 1992; 10:356–363.
Article29. Noh WC, Paik NS, Kim MS, Yang KM, Cho CK, Choi DW, et al. Ipsilateral breast tumor recurrence after breast-conserving therapy: a comparison of quadrantectomy versus lumpectomy at a single institution. World J Surg. 2005; 29:1001–1006.
Article30. Veronesi U, Volterrani F, Luini A, Saccozzi R, Del Vecchio M, Zucali R, et al. Quadrantectomy versus lumpectomy for small size breast cancer. Eur J Cancer. 1990; 26:671–673.
Article31. Freedman G, Fowble B, Hanlon A, Nicolaou N, Fein D, Hoffman J, et al. Patients with early stage invasive cancer with close or positive margins treated with conservative surgery and radiation have an increased risk of breast recurrence that is delayed by adjuvant systemic therapy. Int J Radiat Oncol Biol Phys. 1999; 44:1005–1015.
Article32. Park CC, Mitsumori M, Nixon A, Recht A, Connolly J, Gelman R, et al. Outcome at 8 years after breast-conserving surgery and radiation therapy for invasive breast cancer: influence of margin status and systemic therapy on local recurrence. J Clin Oncol. 2000; 18:1668–1675.
Article33. Peterson ME, Schultz DJ, Reynolds C, Solin LJ. Outcomes in breast cancer patients relative to margin status after treatment with breast-conserving surgery and radiation therapy: the university of pennsylvania experience. Int J Radiat Oncol Biol Phys. 1999; 43:1029–1035.
Article34. Solin LJ, Fowble BL, Schultz DJ, Goodman RL. The significance of the pathology margins of the tumor excision on the outcome of patients treated with definitive irradiation for early stage breast cancer. Int J Radiat Oncol Biol Phys. 1991; 21:279–287.
Article35. Singletary SE. Surgical margins in patients with early-stage breast cancer treated with breast conservation therapy. Am J Surg. 2002; 184:383–393.
Article36. Haffty BG, Yang Q, Reiss M, Kearney T, Higgins SA, Weidhaas J, et al. Locoregional relapse and distant metastasis in conservatively managed triple negative early-stage breast cancer. J Clin Oncol. 2006; 24:5652–5657.
Article
- Full Text Links
- Actions
-
Cited
- CITED
-
- Close
- Share
- Similar articles
-
- Comparison of Psychiatric Symptoms between Total Mastectomy and Breast Conserving Surgery in Breast Cancer Patients
- Recurrent and Second Breast Cancer Detected on Follow-Up Mammography and Breast Ultrasound after Breast-Conserving Surgery: Imaging Findings and Clinicopathologic Factors
- Ipsilateral Breast Tumor Recurrence with Metachronous Contralateral Axillary Lymph Node Metastasis after Breast-Conserving Surgery with Axillary Lymph Node Dissection
- Breast-Conserving Surgery With or Without Radiation Therapy for Early Breast Cancer
- Clinical Outcome after Breast Conserving Surgery and Radiation Therapy for Early Breast Cancer