J Breast Cancer.
2009 Dec;12(4):302-308. 10.4048/jbc.2009.12.4.302.
Risk Factors of Local Recurrence after Breast Conserving Therapy in Invasive Breast Cancer
- Affiliations
-
- 1Depatment of Surgery, University of Ulsan College of Medicine, Asan Medical Center, Seoul, Korea. ahnsh@amc.seoul.kr
- 2Depatment of Pathology, University of Ulsan College of Medicine, Asan Medical Center, Seoul, Korea.
- 3Depatment of Radiation Oncology, University of Ulsan College of Medicine, Asan Medical Center, Seoul, Korea.
- KMID: 2175527
- DOI: http://doi.org/10.4048/jbc.2009.12.4.302
Abstract
- PURPOSE
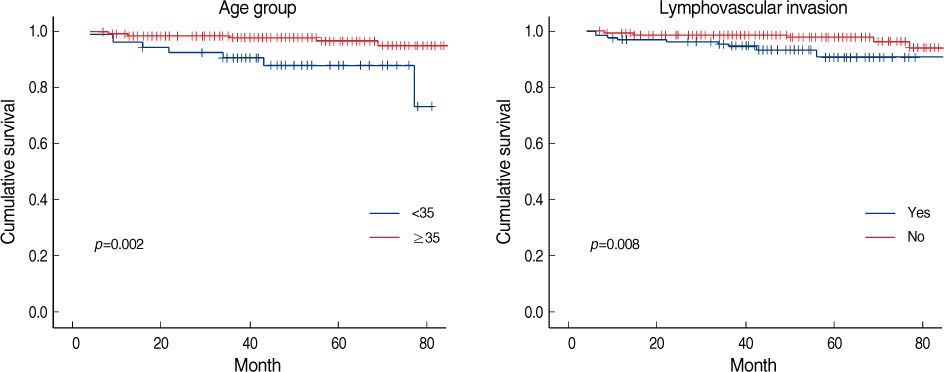
Twenty-year follow-up results of two pioneering randomized controlled trials have demonstrated equal patient survival after mastectomy and breast conservation therapy. The use of breast conservation therapy has undoubtedly provided substantial progress towards a better quality of life for women with breast cancer. Outcomes of breast conservation therapy performed at Asan medical center were retrospectively reviewed and analyses were performed to determine significant risk factors of local recurrence. METHODS: A total of 578 women with stage I, stage II or stage III breast cancer were treated with conservative surgery and radiation therapy between January 1997 and December 2002. Outcomes of local recurrence and survival were recorded. RESULTS: During a median follow-up of 54.1 months, 21 patients (3.6%) developed local recurrence as first event and 10 patients (1.7%) developed regional recurrence and 19 patients (3.3%) developed systemic recurrence. Univariate analysis of the prognostic factors determined that age (p=0.005), nuclear grade (p=0.013), estrogen receptor negativity (p=0.008), lymphovascular invasion (p=0.009), progesterone receptor negativity (p=0.016) and lack of hormone therapy (p=0.005) were statistically significant factors associated only with locoregional recurrence. Results of multivariate analysis determined that lymphovascular invasion (p=0.045) strongly independent predictors for local recurrence. CONCLUSION: Age, nuclear grade, estrogen receptor negativity, lymphovascular invasion, progesterone receptor negativity and lack of hormone therapy were associated with local recurrence after Breast conserving surgery. The lymphovascular invasion was the strongest independent risk factors for local recurrence.
MeSH Terms
Figure
Cited by 1 articles
-
Analysis of factors related systemic recurrence after breast conserving surgery in stage I breast cancer
Yoon-Seok Kim, Dong-Won Ryu, Chung-Han Lee
Kosin Med J. 2018;33(3):289-296. doi: 10.7180/kmj.2018.33.3.289.
Reference
-
1. Fisher B, Anderson S, Bryant J, Margolese RG, Deutsch M, Fisher ER, et al. Twenty-year follow-up of a randomized trial comparing total mastectomy, lumpectomy, and lumpectomy plus irradiation for the treatment of invasive breast cancer. N Engl J Med. 2002. 347:1233–1241.
Article2. van Dongen JA, Voogd AC, Fentiman IS, Legrand C, Sylvester RJ, Tong D, et al. Long-term results of a randomized trial comparing breast-conserving therapy with mastectomy: European Organization for Research and Treatment of Cancer 10801 trial. J Natl Cancer Inst. 2000. 92:1143–1150.
Article3. The Korean Breast Cancer Society. Survival analysis of Korean breast cancer patients diagnosed between 1993 and 2002 in Korea: a nationwide study of the cancer registry. J Breast Cancer. 2006. 9:214–229.4. Son BH, Kwak BS, Kim JK, Kim HJ, Hong SJ, Lee JS, et al. Changing patterns in the clinical characteristics of Korean patients with breast cancer during the last 15 years. Arch Surg. 2006. 141:155–160.
Article5. Locker AP, Ellis IO, Morgan DA, Elston CW, Mitchell A, Blamey RW. Factors influencing local recurrence after excision and radiotherapy for primary breast cancer. Br J Surg. 1989. 76:890–894.
Article6. Anderson SJ, Wapnir I, Dignam JJ, Fisher B, Mamounas EP, Jeong JH, et al. Prognosis after ipsilateral breast tumor recurrence and locoregional recurrences in patients treated by breast-conserving therapy in five National Surgical Adjuvant Breast and Bowel Project protocols of node-negative breast cancer. J Clin Oncol. 2009. 27:2466–2473.
Article7. Blichert-Toft M, Nielsen M, During M, Moller S, Rank F, Overgaard M, et al. Long-term results of breast conserving surgery vs. mastectomy for early stage invasive breast cancer: 20-year follow-up of the Danish randomized DBCG-82TM protocol. Acta Oncol. 2008. 47:672–681.
Article8. Touboul E, Buffat L, Belkacemi Y, Lefranc JP, Uzan S, Lhuillier P, et al. Local recurrences and distant metastases after breast-conserving surgery and radiation therapy for early breast cancer. Int J Radiat Oncol Biol Phys. 1999. 43:25–38.
Article9. Punglia RS, Morrow M, Winer EP, Harris JR. Local therapy and survival in breast cancer. N Engl J Med. 2007. 356:2399–2405.
Article10. McCloskey SA, Botnick LE, Rose CM, Malcolm AW, Ozohan ML, Mena R, et al. Long-term outcomes after breast conservation therapy for early stage breast cancer in a community setting. Breast J. 2006. 12:138–144.
Article11. Kim SI, Park BW, Lee KS. The impact of patient age upon locoregional and systemic failures after breast conservation therapy: comparison of the results from the groups above and below 35 years. J Korean Breast Cancer Soc. 2001. 4:68–73.
Article12. Paik NS, Noh WC, Bang HY, Hwang DY, Choi DW, Lee JI, et al. Recurrence following breast conserving therapy. J Korean Breast Cancer Soc. 2000. 3:64–75.
Article13. Kang SH, Chung KY, Kim YS, Kim JH. Disease free survival and prognostic factors for patients with breast conserving surgery. J Korean Surg Soc. 2004. 67:274–278.14. Kuerer HM, Arthur DW, Haffty BG. Repeat breast-conserving surgery for in-breast local breast carcinoma recurrence: the potential role of partial breast irradiation. Cancer. 2004. 100:2269–2280.
Article15. Fredriksson I, Liljegren G, Arnesson LG, Emdin SO, Palm-Sjovall M, Fornander T, et al. Local recurrence in the breast after conservative surgery: a study of prognosis and prognostic factors in 391 women. Eur J Cancer. 2002. 38:1860–1870.
Article16. Leong C, Boyages J, Jayasinghe UW, Bilous M, Ung O, Chua B, et al. Effect of margins on ipsilateral breast tumor recurrence after breast conservation therapy for lymph node-negative breast carcinoma. Cancer. 2004. 100:1823–1832.
Article17. Clarke M, Collins R, Darby S, Davies C, Elphinstone P, Evans E, et al. Effects of radiotherapy and of differences in the extent of surgery for early breast cancer on local recurrence and 15-year survival: an overview of the randomised trials. Lancet. 2005. 366:2087–2106.
Article18. Freedman GM, Anderson PR, Li T, Nicolaou N. Locoregional recurrence of triple-negative breast cancer after breast-conserving surgery and radiation. Cancer. 2009. 115:946–951.
Article19. Nuyten DS, Kreike B, Hart AA, Chi JT, Sneddon JB, Wessels LF, et al. Predicting a local recurrence after breast-conserving therapy by gene expression profiling. Breast Cancer Res. 2006. 8:R62.
Article20. Veronesi U, Marubini E, Del Vecchio M, Manzari A, Andreola S, Greco M, et al. Local recurrences and distant metastases after conservative breast cancer treatments: partly independent events. J Natl Cancer Inst. 1995. 87:19–27.
Article21. Nixon AJ, Schnitt SJ, Gelman R, Gage I, Bornstein B, Hetelekidis S, et al. Relationship of tumor grade to other pathologic features and to treatment outcome of patients with early stage breast carcinoma treated with breast-conserving therapy. Cancer. 1996. 78:1426–1431.
Article22. Hanna WM, Kahn HJ, Chapman JA, Fish EB, Lickley HL, McCready DR. Pathologic characteristics of breast cancer that predict for local recurrence after lumpectomy alone. Breast J. 1999. 5:105–111.
Article23. Fisher B, Costantino J, Redmond C, Poisson R, Bowman D, Couture J, et al. A randomized clinical trial evaluating tamoxifen in the treatment of patients with node-negative breast cancer who have estrogen-receptor-positive tumors. N Engl J Med. 1989. 320:479–484.
Article
- Full Text Links
- Actions
-
Cited
- CITED
-
- Close
- Share
- Similar articles
-
- Multiple Margin Positivity of Frozen Section Is an Independent Risk Factor for Local Recurrence in Breast-Conserving Surgery
- Breast-Conserving Surgery With or Without Radiation Therapy for Early Breast Cancer
- Oncoplastic Breast Surgery
- Comparison of Outcomes of Standard and Oncoplastic Breast-Conserving Surgery
- Analysis of factors related systemic recurrence after breast conserving surgery in stage I breast cancer