Management of Type 2 Diabetes Mellitus in Older Adults
- Affiliations
-
- 1Department of Internal Medicine, CHA Bundang Medical Center, CHA University School of Medicine, Seongnam, Korea. spark@cha.ac.kr
- 2College of Nursing & Institute of Health Sciences, Gyeongsang National University, Jinju, Korea.
- KMID: 2174391
- DOI: http://doi.org/10.4093/dmj.2012.36.5.336
Abstract
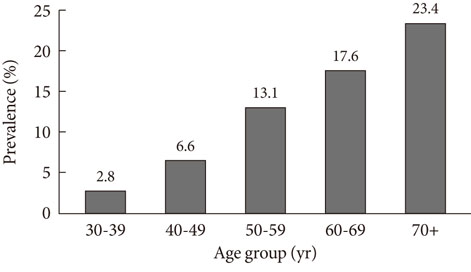
- In the near future, the majority of patients with diabetes will be adults aged 65 or older. Unlike young adults with diabetes, elderly diabetic people may be affected by a variety of comorbid conditions such as depression, cognitive impairment, muscle weakness (sarcopenia), falls and fractures, and physical frailty. These geriatric syndromes should be considered in the establishment of treatment goals in older adults with diabetes. Although there are several guidelines for the management of diabetes, only a few are specifically designed for the elderly with diabetes. In this review, we present specific conditions of elderly diabetes which should be taken into account in the management of diabetes in older adults. We also present advantages and disadvantages of various glucose-lowering agents that should be considered when choosing a proper regimen for older adults with diabetes.
Figure
Cited by 4 articles
-
Goal Attainment Rate for Parameters of Metabolic Adjustment in Elderly Patients with Type 2 Diabetes Taking a Hypoglycemic Agent
Kang Hee Shim, Moon Sook Hwang, Jeong Eun Park, Jin Hee Jung, Jung Hwa Lee, Bok Rye Song
J Korean Diabetes. 2018;19(1):58-70. doi: 10.4093/jkd.2018.19.1.58.Satisfaction Survey on Information Technology-Based Glucose Monitoring System Targeting Diabetes Mellitus in Private Local Clinics in Korea
Hun-Sung Kim, So Jung Yang, Yoo Jin Jeong, Young-Eun Kim, Seok-Won Hong, Jae Hyoung Cho
Diabetes Metab J. 2017;41(3):213-222. doi: 10.4093/dmj.2017.41.3.213.Higher Prevalence and Progression Rate of Chronic Kidney Disease in Elderly Patients with Type 2 Diabetes Mellitus
Kyung-Soo Kim, Seok Won Park, Yong-Wook Cho, Soo-Kyung Kim
Diabetes Metab J. 2018;42(3):224-232. doi: 10.4093/dmj.2017.0065.Education for Insulin Injection in Elderly Diabetic Patients
Gi Yeon Lee
J Korean Diabetes. 2022;23(3):201-205. doi: 10.4093/jkd.2022.23.3.201.
Reference
-
1. Ministry for Health, Welfare and Family Affairs. The Fifth Korea National Health and Nutrition Examination Survey (KNHANES V-1). updated 2012 Jan 5. Available from: http://knhanes.cdc.go.kr.2. Centers for Disease Control and Prevention. National diabetes fact sheet 2011. updated 2012 Jan 10. Available from: http://www.cdc.gov/diabetes/pubs/pdf/ndfs_2011.pdf.3. American Diabetes Association. Standards of medical care in diabetes: 2012. Diabetes Care. 2012. 35:Suppl 1. S11–S63.4. Brown AF, Mangione CM, Saliba D, Sarkisian CA. California Healthcare Foundation/American Geriatrics Society Panel on Improving Care for Elders with Diabetes. Guidelines for improving the care of the older person with diabetes mellitus. J Am Geriatr Soc. 2003. 51:5 Suppl Guidelines. S265–S280.5. Gregg EW, Engelgau MM, Narayan V. Complications of diabetes in elderly people. BMJ. 2002. 325:916–917.6. Sinclair A, Morley JE, Rodriguez-Manas L, Paolisso G, Bayer T, Zeyfang A, Bourdel-Marchasson I, Vischer U, Woo J, Chapman I, Dunning T, Meneilly G, Rodriguez-Saldana J, Gutierrez Robledo LM, Cukierman-Yaffe T, Gadsby R, Schernthaner G, Lorig K. Diabetes mellitus in older people: position statement on behalf of the International Association of Gerontology and Geriatrics (IAGG), the European Diabetes Working Party for Older People (EDWPOP), and the International Task Force of Experts in Diabetes. J Am Med Dir Assoc. 2012. 13:497–502.7. Inzucchi SE, Bergenstal RM, Buse JB, Diamant M, Ferrannini E, Nauck M, Peters AL, Tsapas A, Wender R, Matthews DR. Management of hyperglycaemia in type 2 diabetes: a patient-centered approach. Position statement of the American Diabetes Association (ADA) and the European Association for the Study of Diabetes (EASD). Diabetologia. 2012. 55:1577–1596.8. Rejeski WJ, Ip EH, Bertoni AG, Bray GA, Evans G, Gregg EW, Zhang Q. Look AHEAD Research Group. Lifestyle change and mobility in obese adults with type 2 diabetes. N Engl J Med. 2012. 366:1209–1217.9. Wang CP, Hazuda HP. Better glycemic control is associated with maintenance of lower-extremity function over time in Mexican American and European American older adults with diabetes. Diabetes Care. 2011. 34:268–273.10. Park SW, Goodpaster BH, Strotmeyer ES, de Rekeneire N, Harris TB, Schwartz AV, Tylavsky FA, Newman AB. Decreased muscle strength and quality in older adults with type 2 diabetes: the Health, Aging, and Body Composition Study. Diabetes. 2006. 55:1813–1818.11. Park SW, Goodpaster BH, Strotmeyer ES, Kuller LH, Broudeau R, Kammerer C, de Rekeneire N, Harris TB, Schwartz AV, Tylavsky FA, Cho YW, Newman AB. Health, Aging, and Body Composition Study. Accelerated loss of skeletal muscle strength in older adults with type 2 diabetes: the Health, Aging, and Body Composition Study. Diabetes Care. 2007. 30:1507–1512.12. Park SW, Goodpaster BH, Lee JS, Kuller LH, Boudreau R, de Rekeneire N, Harris TB, Kritchevsky S, Tylavsky FA, Nevitt M, Cho YW, Newman AB. Health, Aging, and Body Composition Study. Excessive loss of skeletal muscle mass in older adults with type 2 diabetes. Diabetes Care. 2009. 32:1993–1997.13. Volpato S, Bianchi L, Lauretani F, Bandinelli S, Guralnik JM, Zuliani G, Ferrucci L. Role of muscle mass and muscle quality in the association between diabetes and gait speed. Diabetes Care. 2012. 35:1672–1679.14. Schwartz AV, Hillier TA, Sellmeyer DE, Resnick HE, Gregg E, Ensrud KE, Schreiner PJ, Margolis KL, Cauley JA, Nevitt MC, Black DM, Cummings SR. Older women with diabetes have a higher risk of falls: a prospective study. Diabetes Care. 2002. 25:1749–1754.15. Volpato S, Leveille SG, Blaum C, Fried LP, Guralnik JM. Risk factors for falls in older disabled women with diabetes: the Women's Health and Aging Study. J Gerontol A Biol Sci Med Sci. 2005. 60:1539–1545.16. Strotmeyer ES, Cauley JA, Schwartz AV, Nevitt MC, Resnick HE, Bauer DC, Tylavsky FA, de Rekeneire N, Harris TB, Newman AB. Nontraumatic fracture risk with diabetes mellitus and impaired fasting glucose in older white and black adults: the Health, Aging, and Body Composition Study. Arch Intern Med. 2005. 165:1612–1617.17. van Daele PL, Stolk RP, Burger H, Algra D, Grobbee DE, Hofman A, Birkenhager JC, Pols HA. Bone density in non-insulin-dependent diabetes mellitus. The Rotterdam Study. Ann Intern Med. 1995. 122:409–414.18. Rakic V, Davis WA, Chubb SA, Islam FM, Prince RL, Davis TM. Bone mineral density and its determinants in diabetes: the Fremantle Diabetes Study. Diabetologia. 2006. 49:863–871.19. Cheng G, Huang C, Deng H, Wang H. Diabetes as a risk factor for dementia and mild cognitive impairment: a meta-analysis of longitudinal studies. Intern Med J. 2012. 42:484–491.20. Bruce DG, Davis WA, Casey GP, Clarnette RM, Brown SG, Jacobs IG, Almeida OP, Davis TM. Severe hypoglycaemia and cognitive impairment in older patients with diabetes: the Fremantle Diabetes Study. Diabetologia. 2009. 52:1808–1815.21. de Galan BE, Zoungas S, Chalmers J, Anderson C, Dufouil C, Pillai A, Cooper M, Grobbee DE, Hackett M, Hamet P, Heller SR, Lisheng L, Macmahon S, Mancia G, Neal B, Pan CY, Patel A, Poulter N, Travert F, Woodward M. ADVANCE Collaborative Group. Cognitive function and risks of cardiovascular disease and hypoglycaemia in patients with type 2 diabetes: the Action in Diabetes and Vascular Disease: Preterax and Diamicron Modified Release Controlled Evaluation (ADVANCE) trial. Diabetologia. 2009. 52:2328–2336.22. van der Feltz-Cornelis CM. Depression in diabetes mellitus: to screen or not to screen? A patient-centred approach. Br J Diabetes Vasc Dis. 2011. 11:276–281.23. Anderson RJ, Freedland KE, Clouse RE, Lustman PJ. The prevalence of comorbid depression in adults with diabetes: a meta-analysis. Diabetes Care. 2001. 24:1069–1078.24. Egede LE, Zheng D, Simpson K. Comorbid depression is associated with increased health care use and expenditures in individuals with diabetes. Diabetes Care. 2002. 25:464–470.25. Egede LE, Zheng D. Independent factors associated with major depressive disorder in a national sample of individuals with diabetes. Diabetes Care. 2003. 26:104–111.26. Finkelstein EA, Bray JW, Chen H, Larson MJ, Miller K, Tompkins C, Keme A, Manderscheid R. Prevalence and costs of major depression among elderly claimants with diabetes. Diabetes Care. 2003. 26:415–420.27. Egede LE. Diabetes, major depression, and functional disability among U.S. adults. Diabetes Care. 2004. 27:421–428.28. Alagiakrishnan K, Sclater A. Psychiatric disorders presenting in the elderly with type 2 diabetes mellitus. Am J Geriatr Psychiatry. 2012. 20:645–652.29. Action to Control Cardiovascular Risk in Diabetes Study Group. Gerstein HC, Miller ME, Byington RP, Goff DC Jr, Bigger JT, Buse JB, Cushman WC, Genuth S, Ismail-Beigi F, Grimm RH Jr, Probstfield JL, Simons-Morton DG, Friedewald WT. Effects of intensive glucose lowering in type 2 diabetes. N Engl J Med. 2008. 358:2545–2559.30. ACCORD Study Group. Gerstein HC, Miller ME, Genuth S, Ismail-Beigi F, Buse JB, Goff DC Jr, Probstfield JL, Cushman WC, Ginsberg HN, Bigger JT, Grimm RH Jr, Byington RP, Rosenberg YD, Friedewald WT. Long-term effects of intensive glucose lowering on cardiovascular outcomes. N Engl J Med. 2011. 364:818–828.31. ADVANCE Collaborative Group. Patel A, MacMahon S, Chalmers J, Neal B, Billot L, Woodward M, Marre M, Cooper M, Glasziou P, Grobbee D, Hamet P, Harrap S, Heller S, Liu L, Mancia G, Mogensen CE, Pan C, Poulter N, Rodgers A, Williams B, Bompoint S, de Galan BE, Joshi R, Travert F. Intensive blood glucose control and vascular outcomes in patients with type 2 diabetes. N Engl J Med. 2008. 358:2560–2572.32. Duckworth W, Abraira C, Moritz T, Reda D, Emanuele N, Reaven PD, Zieve FJ, Marks J, Davis SN, Hayward R, Warren SR, Goldman S, McCarren M, Vitek ME, Henderson WG, Huang GD. VADT Investigators. Glucose control and vascular complications in veterans with type 2 diabetes. N Engl J Med. 2009. 360:129–139.33. Bosi E. Metformin: the gold standard in type 2 diabetes: what does the evidence tell us? Diabetes Obes Metab. 2009. 11:Suppl 2. 3–8.34. de Jager J, Kooy A, Lehert P, Wulffele MG, van der Kolk J, Bets D, Verburg J, Donker AJ, Stehouwer CD. Long term treatment with metformin in patients with type 2 diabetes and risk of vitamin B-12 deficiency: randomised placebo controlled trial. BMJ. 2010. 340:c2181.35. Wulffele MG, Kooy A, Lehert P, Bets D, Ogterop JC, Borger van der Burg B, Donker AJ, Stehouwer CD. Effects of short-term treatment with metformin on serum concentrations of homocysteine, folate and vitamin B12 in type 2 diabetes mellitus: a randomized, placebo-controlled trial. J Intern Med. 2003. 254:455–463.36. Schwartz AV, Vittinghoff E, Sellmeyer DE, Feingold KR, de Rekeneire N, Strotmeyer ES, Shorr RI, Vinik AI, Odden MC, Park SW, Faulkner KA, Harris TB. Health, Aging, and Body Composition Study. Diabetes-related complications, glycemic control, and falls in older adults. Diabetes Care. 2008. 31:391–396.37. Nattrass M, Lauritzen T. Review of prandial glucose regulation with repaglinide: a solution to the problem of hypoglycaemia in the treatment of type 2 diabetes? Int J Obes Relat Metab Disord. 2000. 24:Suppl 3. S21–S31.38. Bourdel-Marchasson I, Schweizer A, Dejager S. Incretin therapies in the management of elderly patients with type 2 diabetes mellitus. Hosp Pract (Minneap). 2011. 39:7–21.39. Schweizer A, Dejager S, Bosi E. Comparison of vildagliptin and metformin monotherapy in elderly patients with type 2 diabetes: a 24-week, double-blind, randomized trial. Diabetes Obes Metab. 2009. 11:804–812.40. Schweizer A, Dejager S, Foley JE, Shao Q, Kothny W. Clinical experience with vildagliptin in the management of type 2 diabetes in a patient population >/=75 years: a pooled analysis from a database of clinical trials. Diabetes Obes Metab. 2011. 13:55–64.41. Shankar R, Engel SS, Xu L, Golm GT, Davies MJ, Kaufman KD, Goldstein BJ. Sitagliptin provides similar glycemic improvement with less hypoglycemia in the elderly with type 2 diabetes mellitus compared to sulfonylurea. Diabetes. 2012. 61:Suppl 1. A278.42. Schwartz SL. Treatment of elderly patients with type 2 diabetes mellitus: a systematic review of the benefits and risks of dipeptidyl peptidase-4 inhibitors. Am J Geriatr Pharmacother. 2010. 8:405–418.43. Mamtani R, Haynes K, Bilker WB, Vaughn DJ, Strom BL, Glanz K, Lewis JD. Association between longer therapy with thiazolidinediones and risk of bladder cancer: a cohort study. J Natl Cancer Inst. 2012. 104:1411–1421.44. Azoulay L, Yin H, Filion KB, Assayag J, Majdan A, Pollak MN, Suissa S. The use of pioglitazone and the risk of bladder cancer in people with type 2 diabetes: nested case-control study. BMJ. 2012. 344:e3645.45. Schwartz AV. TZDs and Bone: a review of the recent clinical evidence. PPAR Res. 2008. 2008:297893.46. Meier C, Kraenzlin ME, Bodmer M, Jick SS, Jick H, Meier CR. Use of thiazolidinediones and fracture risk. Arch Intern Med. 2008. 168:820–825.47. Lee A, Patrick P, Wishart J, Horowitz M, Morley JE. The effects of miglitol on glucagon-like peptide-1 secretion and appetite sensations in obese type 2 diabetics. Diabetes Obes Metab. 2002. 4:329–335.48. Narita T, Yokoyama H, Yamashita R, Sato T, Hosoba M, Morii T, Fujita H, Tsukiyama K, Yamada Y. Comparisons of the effects of 12-week administration of miglitol and voglibose on the responses of plasma incretins after a mixed meal in Japanese type 2 diabetic patients. Diabetes Obes Metab. 2012. 14:283–287.49. Hucking K, Kostic Z, Pox C, Ritzel R, Holst JJ, Schmiegel W, Nauck MA. Alpha-Glucosidase inhibition (acarbose) fails to enhance secretion of glucagon-like peptide 1 (7-36 amide) and to delay gastric emptying in type 2 diabetic patients. Diabet Med. 2005. 22:470–476.50. Yki-Jarvinen H, Dressler A, Ziemen M. HOE 901/300s Study Group. Less nocturnal hypoglycemia and better post-dinner glucose control with bedtime insulin glargine compared with bedtime NPH insulin during insulin combination therapy in type 2 diabetes. HOE 901/3002 Study Group. Diabetes Care. 2000. 23:1130–1136.51. Sinclair AJ, Paolisso G, Castro M, Bourdel-Marchasson I, Gadsby R, Rodriguez Manas L. European Diabetes Working Party for Older People 2011 clinical guidelines for type 2 diabetes mellitus. Executive summary. Diabetes Metab. 2011. 37:Suppl 3. S27–S38.
- Full Text Links
- Actions
-
Cited
- CITED
-
- Close
- Share
- Similar articles
-
- Intervention Strategies for Older Adults with Diabetes
- Medical Nutrition Therapy for Older Adults with Diabetes
- Pharmacological management of diabetes in older adults
- Special Considerations in Diabetes Self-Management Education for Older Adults with Diabetes: A Study Focusing on Community Senior Welfare Centers
- Management of Type 1 Diabetes Mellitus in Adults