Diabetes Metab J.
2014 Feb;38(1):58-63. 10.4093/dmj.2014.38.1.58.
Assessment of the Association between Mean Hemoglobin A1c Levels for 5 Years and Coronary Artery Disease by Coronary Angiography in Nondiabetic Patients
- Affiliations
-
- 1Department of Internal Medicine, Maryknoll Medical Center, Busan, Korea.
- 2Department of Internal Medicine, Inje University College of Medicine, Busan, Korea. kmkdoc@paik.ac.kr
- KMID: 2174186
- DOI: http://doi.org/10.4093/dmj.2014.38.1.58
Abstract
- BACKGROUND
The effects of glucose on cardiovascular events or mortality in nondiabetic patients has been recently reported. However, since atherosclerosis can be formed over a long period of time, it is necessary to devote several years to unveil the relationship between the two factors. Here, we attempted to find out the relationship between the mean hemoglobin A1c (HbA1c) level and HbA1c variability for 5 years and coronary artery disease (CAD) by using coronary angiography (CAG) to assess nondiabetic patients.
METHODS
We reviewed patients who performed CAG who were followed up for at least 5 years after the initial diagnosis. The fasting blood test was performed annually for glucose and HbA1c level. CAD was defined as more than 50% of luminal narrowing. The severity of CAD was divided into two groups depending on whether no vessels were involved or one more vessel were involved (CAD(-) or CAD(+), respectively).
RESULTS
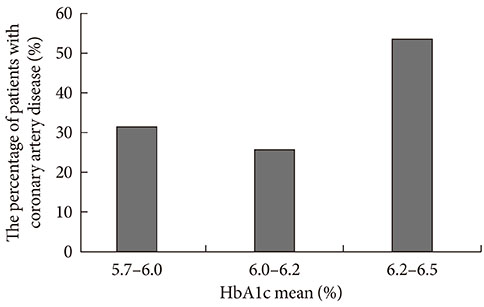
The patients in CAD(+) group had higher mean HbA1c level for 5 years than CAD(-) group (5.71+/-0.40 vs. 5.86+/-0.68; P=0.04). Mean HbA1c was a significant predictor for CAD in multiple regression (odds ratio, 2.224; P=0.028). The percentage of patients with CAD was significantly higher in patients with >6.2% of mean HbA1c levels compared to patients with <6.2% of mean HbA1c levels (P<0.019).
CONCLUSION
When the mean HbA1c levels were above 6.2%, the risk of CAD was higher. Also this study shows that HbA1c level can be one of the predictors for CAD even if the patients do not have diabetes.
MeSH Terms
Figure
Reference
-
1. Haffner SJ, Cassells H. Hyperglycemia as a cardiovascular risk factor. Am J Med. 2003; 115:Suppl 8A. 6S–11S.2. Haffner SM, Lehto S, Ronnemaa T, Pyorala K, Laakso M. Mortality from coronary heart disease in subjects with type 2 diabetes and in nondiabetic subjects with and without prior myocardial infarction. N Engl J Med. 1998; 339:229–234.3. Meigs JB, Larson MG, D'Agostino RB, Levy D, Clouse ME, Nathan DM, Wilson PW, O'Donnell CJ. Coronary artery calcification in type 2 diabetes and insulin resistance: the Framingham Offspring Study. Diabetes Care. 2002; 25:1313–1319.4. Meigs JB, Nathan DM, D'Agostino RB Sr, Wilson PW. Framingham Offspring Study. Fasting and postchallenge glycemia and cardiovascular disease risk: the Framingham Offspring Study. Diabetes Care. 2002; 25:1845–1850.5. Wei M, Gaskill SP, Haffner SM, Stern MP. The San Antonio Heart Study. Effects of diabetes and level of glycemia on all-cause and cardiovascular mortality. Diabetes Care. 1998; 21:1167–1172.6. Carr ME. Diabetes mellitus: a hypercoagulable state. J Diabetes Complications. 2001; 15:44–54.7. Nielson C, Lange T, Hadjokas N. Blood glucose and coronary artery disease in nondiabetic patients. Diabetes Care. 2006; 29:998–1001.8. Rivera JJ, Choi EK, Yoon YE, Chun EJ, Choi SI, Nasir K, Brancati FL, Blumenthal RS, Chang HJ. Association between increasing levels of hemoglobin A1c and coronary atherosclerosis in asymptomatic individuals without diabetes mellitus. Coron Artery Dis. 2010; 21:157–163.9. Balkau B, Shipley M, Jarrett RJ, Pyorala K, Pyorala M, Forhan A, Eschwege E. High blood glucose concentration is a risk factor for mortality in middle-aged nondiabetic men: 20-year follow-up in the Whitehall Study, the Paris Prospective Study, and the Helsinki Policemen Study. Diabetes Care. 1998; 21:360–367.10. Nasir K, Santos RD, Tufail K, Rivera J, Carvalho JA, Meneghello R, Brady TD, Blumenthal RS. High-normal fasting blood glucose in non-diabetic range is associated with increased coronary artery calcium burden in asymptomatic men. Atherosclerosis. 2007; 195:e155–e160.11. Levitan EB, Song Y, Ford ES, Liu S. Is nondiabetic hyperglycemia a risk factor for cardiovascular disease? A meta-analysis of prospective studies. Arch Intern Med. 2004; 164:2147–2155.12. Hashimoto K, Ikewaki K, Yagi H, Nagasawa H, Imamoto S, Shibata T, Mochizuki S. Glucose intolerance is common in Japanese patients with acute coronary syndrome who were not previously diagnosed with diabetes. Diabetes Care. 2005; 28:1182–1186.13. The Diabetes Control and Complications Trial Research Group. The effect of intensive treatment of diabetes on the development and progression of long-term complications in insulin-dependent diabetes mellitus. N Engl J Med. 1993; 329:977–986.14. UK Prospective Diabetes Study (UKPDS) Group. Intensive blood-glucose control with sulphonylureas or insulin compared with conventional treatment and risk of complications in patients with type 2 diabetes (UKPDS 33). UK Prospective Diabetes Study (UKPDS) Group. Lancet. 1998; 352:837–853.15. Sander D, Schulze-Horn C, Bickel H, Gnahn H, Bartels E, Conrad B. Combined effects of hemoglobin A1c and C-reactive protein on the progression of subclinical carotid atherosclerosis: the INVADE study. Stroke. 2006; 37:351–357.16. Park S, Barrett-Connor E, Wingard DL, Shan J, Edelstein S. GHb is a better predictor of cardiovascular disease than fasting or postchallenge plasma glucose in women without diabetes. The Rancho Bernardo Study. Diabetes Care. 1996; 19:450–456.17. Norhammar A, Tenerz A, Nilsson G, Hamsten A, Efendic S, Ryden L, Malmberg K. Glucose metabolism in patients with acute myocardial infarction and no previous diagnosis of diabetes mellitus: a prospective study. Lancet. 2002; 359:2140–2144.18. Blake GJ, Pradhan AD, Manson JE, Williams GR, Buring J, Ridker PM, Glynn RJ. Hemoglobin A1c level and future cardiovascular events among women. Arch Intern Med. 2004; 164:757–761.19. Oh HG, Rhee EJ, Kim TW, Lee KB, Park JH, Yang KI, Jeong D, Park HK. Higher glycated hemoglobin level is associated with increased risk for ischemic stroke in non-diabetic Korean male adults. Diabetes Metab J. 2011; 35:551–557.20. Khaw KT, Wareham N, Bingham S, Luben R, Welch A, Day N. Association of hemoglobin A1c with cardiovascular disease and mortality in adults: the European prospective investigation into cancer in Norfolk. Ann Intern Med. 2004; 141:413–420.21. Kilpatrick ES, Rigby AS, Atkin SL. A1C variability and the risk of microvascular complications in type 1 diabetes: data from the Diabetes Control and Complications Trial. Diabetes Care. 2008; 31:2198–2202.22. Waden J, Forsblom C, Thorn LM, Gordin D, Saraheimo M, Groop PH. Finnish Diabetic Nephropathy Study Group. A1C variability predicts incident cardiovascular events, microalbuminuria, and overt diabetic nephropathy in patients with type 1 diabetes. Diabetes. 2009; 58:2649–2655.23. Bjornholt JV, Erikssen G, Aaser E, Sandvik L, Nitter-Hauge S, Jervell J, Erikssen J, Thaulow E. Fasting blood glucose: an underestimated risk factor for cardiovascular death. Results from a 22-year follow-up of healthy nondiabetic men. Diabetes Care. 1999; 22:45–49.24. Tominaga M, Eguchi H, Manaka H, Igarashi K, Kato T, Sekikawa A. Impaired glucose tolerance is a risk factor for cardiovascular disease, but not impaired fasting glucose. The Funagata Diabetes Study. Diabetes Care. 1999; 22:920–924.25. Blake DR, Meigs JB, Muller DC, Najjar SS, Andres R, Nathan DM. Impaired glucose tolerance, but not impaired fasting glucose, is associated with increased levels of coronary heart disease risk factors: results from the Baltimore Longitudinal Study on Aging. Diabetes. 2004; 53:2095–2100.26. Ceriello A, Esposito K, Piconi L, Ihnat MA, Thorpe JE, Testa R, Boemi M, Giugliano D. Oscillating glucose is more deleterious to endothelial function and oxidative stress than mean glucose in normal and type 2 diabetic patients. Diabetes. 2008; 57:1349–1354.27. Ma WY, Li HY, Pei D, Hsia TL, Lu KC, Tsai LY, Wei JN, Su CC. Variability in hemoglobin A1c predicts all-cause mortality in patients with type 2 diabetes. J Diabetes Complications. 2012; 26:296–300.
- Full Text Links
- Actions
-
Cited
- CITED
-
- Close
- Share
- Similar articles
-
- A1c Variability Can Predict Coronary Artery Disease in Patients with Type 2 Diabetes with Mean A1c Levels Greater than 7
- Spontaneous Coronary Artery Dissection and Woven Coronary Artery: Three Cases and a Review of the Literature
- A Case of Single Coronary Artery c Effort Angina
- Direct Visualization of Coronary Artery and Flow using Transthoracic Doppler Echocardiography
- Diabetes Mellitus and Coronary Angiography