Current Status of Management in Type 2 Diabetes Mellitus at General Hospitals in South Korea
- Affiliations
-
- 1Division of Diabetes Education Team, Department of Nursing, Seoul National University Bundang Hospital, Seoul National University College of Medicine, Seongnam, Korea.
- 2Korea Association of Diabetes Nurse Educators, Seoul, Korea. jsmercy@naver.com
- 3Division of Diabetes Education Team, Kyung Hee University Hospital at Gangdong, Kyung Hee University School of Medicine, Seoul, Korea.
- 4Department of Healthcare Management and Institute of Global Healthcare Research, Eulji University School of Medicine, Seongnam, Korea.
- 5Division of Diabetes Education Team, Cheil General Hospital & Women's Healthcare Center, Dankook University College of Medicine, Seoul, Korea.
- 6Department of Nursing, Dongnam Health University, Suwon, Korea.
- 7Division of Diabetes Education Team, Seoul National University Hospital, Seoul National University College of Medicine, Seoul, Korea.
- 8Division of Diabetes Education Team , Seoul St. Mary's Hospital, College of Medicine, The Catholic University of Korea, Seoul, Korea.
- 9Division of Diabetes Education Team, Asan Medical Center, University of Ulsan College of Medicine, Seoul, Korea.
- 10Division of Diabetes Education Team, Inje University Seoul Paik Hospital, Inje University College of Medicine, Seoul, Korea.
- 11Division of Diabetes Education Team, Gangnam Severance Hospital, Yonsei University College of Medicine, Seoul, Korea.
- 12Division of Diabetes Education Team, Yeouido St. Mary's Hospital, College of Medicine, The Catholic University of Korea, Seoul, Korea.
- 13Division of Diabetes Education Team, Inje University Ilsan Paik Hospital, Inje University College of Medicine, Goyang, Korea.
- 14Division of Diabetes Education Team, Kwangmyung Sungae Hospital, Gwangmyeong, Korea.
- 15Division of Diabetes Education Team, Bucheon St. Mary's Hospital, College of Medicine, The Catholic University of Korea, Bucheon, Korea.
- 16Diabetes Education Unit, Samsung Medical Center, Sungkyunkwan University School of Medicine, Seoul, Korea.
- KMID: 2174026
- DOI: http://doi.org/10.4093/dmj.2015.39.4.307
Abstract
- BACKGROUND
In Korea, the prevalence, complications, and mortality rate of diabetes are rapidly increasing. However, investigations on the actual condition of diabetes management are very limited due to lack of nation-wide research or multicenter study. Hence, we have minutely inquired the current status of diabetes management and achievement of glucose target goal in general hospital offering education program. That way, we are able to furnish data for policy making of diabetes education and draw up guideline which may allow us to reduce the morbidity and mortality of diabetes.
METHODS
The subjects consisted of 2,610 patients with type 2 diabetes who visited the 13 general hospital in Seoul or Gyeonggi region from March 19 to May 29, 2013. General characteristics, associated diseases, complications, and management status were investigated.
RESULTS
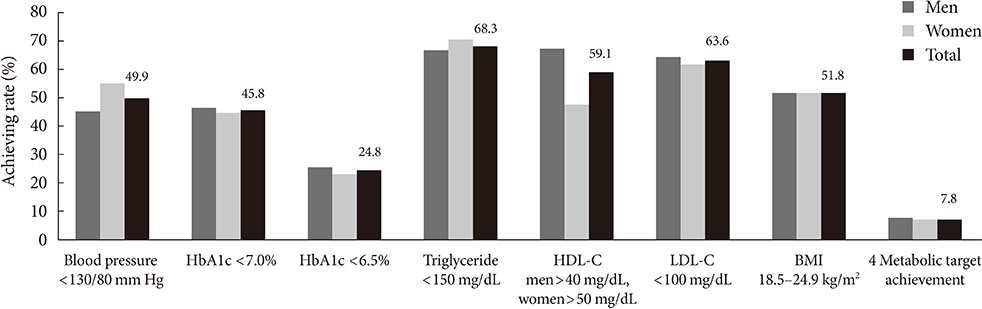
The mean age was 61.0+/-11.6 years, body mass index was 25.0+/-3.3 kg/m2, and family history of diabetes was 50.5%. The mean duration of diabetes was 10.7+/-7.9 years and 53% received education about diabetes. The prevalence of hypertension and dyslipidemia were 59.2% and 65.5%, respectively, and 18.3% of the subjects were accompanied by liver disease. Diabetic retinopathy appeared in 31.6%, nephropathy in 28.1%, and neuropathy in 19.9% of the subjects. The mean glycosylated hemoglobin (HbA1c) level was 7.3%+/-1.3% and the achieving rate based on Korean Diabetes Association guideline (HbA1c <6.5%) was 24.8%, blood pressure (130/80 mm Hg or less) was 49.4%, and low density lipoprotein cholesterol (<100 mg/dL) was 63.6%. The reaching rate to the target level in four parameters (blood glucose, blood pressure, lipids, and body weight) was 7.8%.
CONCLUSION
The blood glucose control rate was lower than other parameters, and the implementation rate of diabetes education was only 53%. Thus more appropriate glucose control and systematic diabetes education are imperative.
MeSH Terms
-
Blood Glucose
Blood Pressure
Body Mass Index
Cholesterol, LDL
Diabetes Mellitus, Type 2*
Diabetic Retinopathy
Dyslipidemias
Education
Glucose
Gyeonggi-do
Hemoglobin A, Glycosylated
Hospitals, General*
Humans
Hypertension
Korea*
Liver Diseases
Mortality
Policy Making
Prevalence
Seoul
Blood Glucose
Cholesterol, LDL
Glucose
Figure
Cited by 4 articles
-
Physician-Directed Diabetes Education without a Medication Change and Associated Patient Outcomes
Hun-Sung Kim, Hyunah Kim, Hae-Kyung Yang, Eun Young Lee, Yoo Jin Jeong, Tong Min Kim, So Jung Yang, Seo Yeon Baik, Seung-Hwan Lee, Jae Hyoung Cho, In Young Choi, Hyeon Woo Yim, Bong-Yun Cha
Diabetes Metab J. 2017;41(3):187-194. doi: 10.4093/dmj.2017.41.3.187.Features of Long-Standing Korean Type 2 Diabetes Mellitus Patients with Diabetic Retinopathy: A Study Based on Standardized Clinical Data
Sejeong Park, Sang Youl Rhee, Su Jin Jeong, Kiyoung Kim, Suk Chon, Seung-Young Yu, Jeong-Taek Woo
Diabetes Metab J. 2017;41(5):393-404. doi: 10.4093/dmj.2017.41.5.393.Sociodemographic Factors Associated with Participation in Diabetes Education among Community-Dwelling Adults with Diabetes
Young-Hoon Lee
Yonsei Med J. 2020;61(2):169-178. doi: 10.3349/ymj.2020.61.2.169.Management Status of Patients with Type 2 Diabetes Mellitus at General Hospitals in Korea: A 5-Year Follow-Up Study
Jin Hee Jung, Jung Hwa Lee, Hyang Mi Jang, Young Na, Hee Sun Choi, Yeon Hee Lee, Yang Gyo Kang, Na Rae Kim, Jeong Rim Lee, Bok Rye Song, Kang Hee Sim
J Korean Diabetes. 2022;23(1):64-75. doi: 10.4093/jkd.2022.23.1.64.
Reference
-
1. Whiting DR, Guariguata L, Weil C, Shaw J. IDF diabetes atlas: global estimates of the prevalence of diabetes for 2011 and 2030. Diabetes Res Clin Pract. 2011; 94:311–321.2. Yoon KH, Lee JH, Kim JW, Cho JH, Choi YH, Ko SH, Zimmet P, Son HY. Epidemic obesity and type 2 diabetes in Asia. Lancet. 2006; 368:1681–1688.3. Chan JC, Malik V, Jia W, Kadowaki T, Yajnik CS, Yoon KH, Hu FB. Diabetes in Asia: epidemiology, risk factors, and pathophysiology. JAMA. 2009; 301:2129–2140.4. Choi YJ, Kim HC, Kim HM, Park SW, Kim J, Kim DJ. Prevalence and management of diabetes in Korean adults: Korea National Health and Nutrition Examination Surveys 1998-2005. Diabetes Care. 2009; 32:2016–2020.5. Kim DJ. The epidemiology of diabetes in Korea. Diabetes Metab J. 2011; 35:303–308.6. Ramachandran A, Snehalatha C, Shetty AS, Nanditha A. Trends in prevalence of diabetes in Asian countries. World J Diabetes. 2012; 3:110–117.7. Xu Y, Wang L, He J, Bi Y, Li M, Wang T, Wang L, Jiang Y, Dai M, Lu J, Xu M, Li Y, Hu N, Li J, Mi S, Chen CS, Li G, Mu Y, Zhao J, Kong L, Chen J, Lai S, Wang W, Zhao W, Ning G. 2010 China Noncommunicable Disease Surveillance Group. Prevalence and control of diabetes in Chinese adults. JAMA. 2013; 310:948–959.8. Yang W, Lu J, Weng J, Jia W, Ji L, Xiao J, Shan Z, Liu J, Tian H, Ji Q, Zhu D, Ge J, Lin L, Chen L, Guo X, Zhao Z, Li Q, Zhou Z, Shan G, He J. China National Diabetes and Metabolic Disorders Study Group. Prevalence of diabetes among men and women in China. N Engl J Med. 2010; 362:1090–1101.9. Anjana RM, Pradeepa R, Deepa M, Datta M, Sudha V, Unnikrishnan R, Bhansali A, Joshi SR, Joshi PP, Yajnik CS, Dhandhania VK, Nath LM, Das AK, Rao PV, Madhu SV, Shukla DK, Kaur T, Priya M, Nirmal E, Parvathi SJ, Subhashini S, Subashini R, Ali MK, Mohan V. ICMR-INDIAB Collaborative Study Group. Prevalence of diabetes and prediabetes (impaired fasting glucose and/or impaired glucose tolerance) in urban and rural India: phase I results of the Indian Council of Medical Research-INdia DIABetes (ICMR-INDIAB) study. Diabetologia. 2011; 54:3022–3027.10. Statistisc Korea. Cause of death statistics 2012. updated 2013 Nov 25. Available from: http://kostat.go.kr/portal/korea/kor_nw/2/1/index.board?bmode=read&aSeq=308559.11. Kim JH, Kim DJ, Jang HC, Choi SH. Epidemiology of micro- and macrovascular complications of type 2 diabetes in Korea. Diabetes Metab J. 2011; 35:571–577.12. Jin DC. Current status of dialysis therapy in Korea. Korean J Intern Med. 2011; 26:123–131.13. Ko SH, Cha BY. Diabetic peripheral neuropathy in type 2 diabetes mellitus in Korea. Diabetes Metab J. 2012; 36:6–12.14. van Dieren S, Beulens JW, van der Schouw YT, Grobbee DE, Neal B. The global burden of diabetes and its complications: an emerging pandemic. Eur J Cardiovasc Prev Rehabil. 2010; 17:Suppl 1. S3–S8.15. American Diabetes Association. Economic costs of diabetes in the U.S. in 2012. Diabetes Care. 2013; 36:1033–1046.16. Lee KW. Costs of diabetes mellitus in Korea. Diabetes Metab J. 2011; 35:567–570.17. Kim TH, Chun KH, Kim HJ, Han SJ, Kim DJ, Kwak J, Kim YS, Woo JT, Park Y, Nam M, Baik SH, Ahn KJ, Lee KW. Direct medical costs for patients with type 2 diabetes and related complications: a prospective cohort study based on the Korean National Diabetes Program. J Korean Med Sci. 2012; 27:876–882.18. Chang TJ, Jiang YD, Chang CH, Chung CH, Yu NC, Chuang LM. Accountability, utilization and providers for diabetes management in Taiwan, 2000-2009: an analysis of the National Health Insurance database. J Formos Med Assoc. 2012; 111:605–616.19. Reutens AT, Atkins RC. Epidemiology of diabetic nephropathy. Contrib Nephrol. 2011; 170:1–7.20. Gaede P, Lund-Andersen H, Parving HH, Pedersen O. Effect of a multifactorial intervention on mortality in type 2 diabetes. N Engl J Med. 2008; 358:580–591.21. Stratton IM, Cull CA, Adler AI, Matthews DR, Neil HA, Holman RR. Additive effects of glycaemia and blood pressure exposure on risk of complications in type 2 diabetes: a prospective observational study (UKPDS 75). Diabetologia. 2006; 49:1761–1769.22. Shi L, Ye X, Lu M, Wu EQ, Sharma H, Thomason D, Fonseca VA. Clinical and economic benefits associated with the achievement of both HbA1c and LDL cholesterol goals in veterans with type 2 diabetes. Diabetes Care. 2013; 36:3297–3304.23. ADVANCE Collaborative Group. Patel A, MacMahon S, Chalmers J, Neal B, Billot L, Woodward M, Marre M, Cooper M, Glasziou P, Grobbee D, Hamet P, Harrap S, Heller S, Liu L, Mancia G, Mogensen CE, Pan C, Poulter N, Rodgers A, Williams B, Bompoint S, de Galan BE, Joshi R, Travert F. Intensive blood glucose control and vascular outcomes in patients with type 2 diabetes. N Engl J Med. 2008; 358:2560–2572.24. Korean Diabetes Association. Treatment guideline for diabetes. 4th ed. Seoul: Gold Planning and Development;2011. p. 40–129.25. Ko SH, Kim SR, Kim DJ, Oh SJ, Lee HJ, Shim KH, Woo MH, Kim JY, Kim NH, Kim JT, Kim CH, Kim HJ, Jeong IK, Hong EK, Cho JH, Mok JO, Yoon KH. Committee of Clinical Practice Guidelines, Korean Diabetes Association. 2011 Clinical practice guidelines for type 2 diabetes in Korea. Diabetes Metab J. 2011; 35:431–436.26. Chan JC, Gagliardino JJ, Baik SH, Chantelot JM, Ferreira SR, Hancu N, Ilkova H, Ramachandran A, Aschner P. IDMPS Investigators. Multifaceted determinants for achieving glycemic control: the International Diabetes Management Practice Study (IDMPS). Diabetes Care. 2009; 32:227–233.27. Kim KS. Healthcare Benefit quality assessment of chronic disease. Health Insur Rev Assess Serv. 2012; 6:14–20.28. Albright AL, Gregg EW. Preventing type 2 diabetes in communities across the U.S.: the National Diabetes Prevention Program. Am J Prev Med. 2013; 44:4 Suppl 4. S346–S351.29. Park SW, Kim DJ, Min KW, Baik SH, Choi KM, Park IB, Park JH, Son HS, Ahn CW, Oh JY, Lee J, Chung CH, Kim J, Kim H. Current status of diabetes management in Korea using National Health Insurance Database. J Korean Diabetes Assoc. 2007; 31:362–367.30. Lim S, Kim DJ, Jeong IK, Son HS, Chung CH, Koh G, Lee DH, Won KC, Park JH, Park TS, Ahn J, Kim J, Park KG, Ko SH, Ahn YB, Lee I. A nationwide survey about the current status of glycemic control and complications in diabetic patients in 2006: the committee of the Korean diabetes association on the epidemiology of diabetes mellitus. Korean Diabetes J. 2009; 33:48–57.31. Lee YS. The current status of type 2 diabetes management at a university hospital. Korean Diabetes J. 2009; 33:241–250.32. Kim SA, Park WS, Ohrr HC, Kang HY, Lee DH, Yi SW, Kwak YH, Song JS. Prevalence and management status of diabetes mellitus in Korea. Korean J Med. 2005; 68:10–17.33. Guo XH, Yuan L, Lou QQ, Shen L, Sun ZL, Zhao F, Dai X, Huang J, Yang HY. Chinese Diabetes Education Status Survey Study Group. A nationwide survey of diabetes education, self-management and glycemic control in patients with type 2 diabetes in China. Chin Med J (Engl). 2012; 125:4175–4180.34. Pan C, Yang W, Jia W, Weng J, Tian H. Management of Chinese patients with type 2 diabetes, 1998-2006: the Diabcare-China surveys. Curr Med Res Opin. 2009; 25:39–45.35. Stark Casagrande S, Fradkin JE, Saydah SH, Rust KF, Cowie CC. The prevalence of meeting A1C, blood pressure, and LDL goals among people with diabetes, 1988-2010. Diabetes Care. 2013; 36:2271–2279.36. Lim DJ, Kwon HS, Kim HS, Lee JH, Ko SH, Lee JM, Kim SR, Lee WC, Son HS, Cha BY, Lee KW, Son HY, Kang SK, Yoon KH. Clinical characteristics of the diabetic patients managed at the different medical institutions in Seoul and Gyeonggi province. Korean J Med. 2006; 71:173–181.37. Korean Diabetes Association. Diabetes fact sheet 2012. cited 2013 Sep 21. Available from: http://www.diabetes.or.kr/general/index.html.38. Ali MK, Bullard KM, Saaddine JB, Cowie CC, Imperatore G, Gregg EW. Achievement of goals in U.S. diabetes care, 1999-2010. N Engl J Med. 2013; 368:1613–1624.39. de Pablos-Velasco P, Parhofer KG, Bradley C, Eschwege E, Gonder-Frederick L, Maheux P, Wood I, Simon D. Current level of glycaemic control and its associated factors in patients with type 2 diabetes across Europe: data from the PANORAMA study. Clin Endocrinol (Oxf). 2014; 80:47–56.40. Chuang LM, Tsai ST, Huang BY, Tai TY. Diabcare-Asia 1998 Study Group. The status of diabetes control in Asia: a cross-sectional survey of 24 317 patients with diabetes mellitus in 1998. Diabet Med. 2002; 19:978–985.
- Full Text Links
- Actions
-
Cited
- CITED
-
- Close
- Share
- Similar articles
-
- Current Status and Effects of Nutrition Education Programs for Diabetic Patients in Korea
- Epidemiologic Characteristics of Diabetes Mellitus in Korea: Current Status of Diabetic Patients Using Korean Health Insurance Database
- Why Does the MOHW Consider Type 2 Diabetes Mellitus to be a Slight Illness?
- Effect of Diabetes Education Program on Glycemic Control and Self Management for Patients with Type 2 Diabetes Mellitus
- Comprehensive Management in Patients with Type 2 Diabetes Mellitus