Health Behaviors and Health-related Quality of Life among Vulnerable Children in a Community
- Affiliations
-
- 1College of Nursing, Korea University, Seoul, Korea. jinachoo@korea.ac.kr
- KMID: 2173826
- DOI: http://doi.org/10.12799/jkachn.2015.26.3.292
Abstract
- PURPOSE
The purpose of this study was to examine the association between health behaviors and health-related quality of life (HRQOL) among vulnerable children in a community.
METHODS
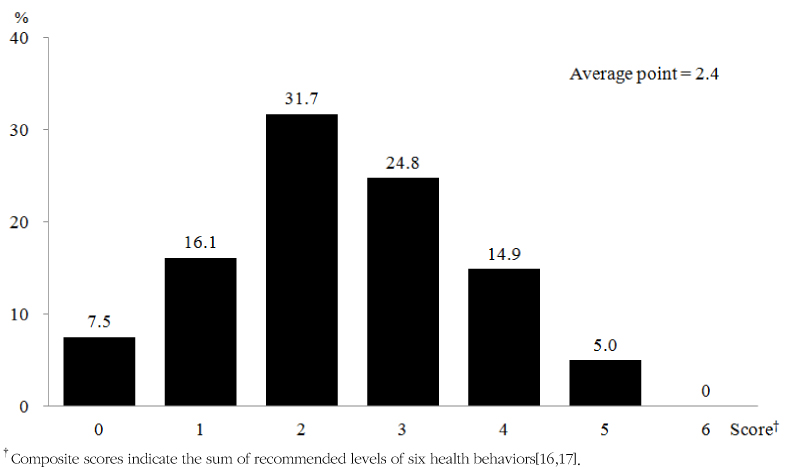
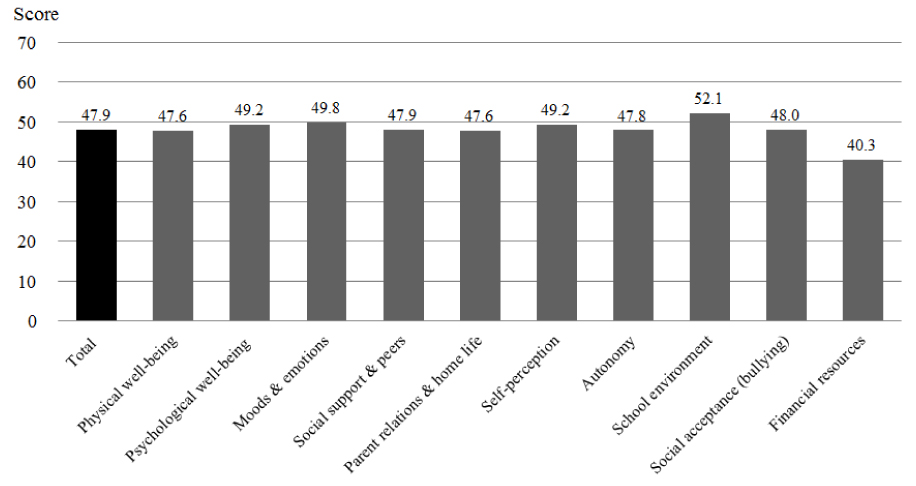
Using data from 'The Obesity Prevention Framework for Vulnerable Children', a secondary analysis was conducted for 165 children (ages 8~12 years) and their parents who were recruited from 16 K-gu Community Child Centers in Seoul. Six types of health behaviors related to eating and activity were assessed. Each behavior was categorized into the non-recommended vs. recommended levels. The scores of the recommended levels of the six health behaviors were summed up for the composite score of health behaviors. HRQOL was measured by KIDSCREEN-52.
RESULTS
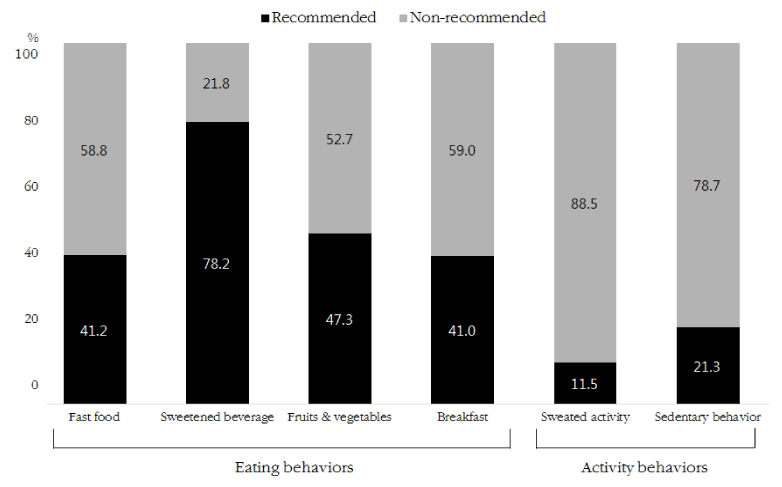
The groups with a non-recommended level of fast food intake and sedentary behavior had a significantly lower total score of KIDSCREEN-52 than those with a recommended level. Moreover, the lower composite score of health behaviors was significantly associated with the lower total score of KIDSCREEN-52.
CONCLUSION
Among the vulnerable children, the six recommended health behaviors and their composite score were in significant positive associations with the HRQOL levels. Therefore, nursing strategies for enhancing the recommended levels of health behaviors are needed for vulnerable children.
MeSH Terms
Figure
Cited by 3 articles
-
Development of Forest-based Health Promotion Program for Vulnerable School Children
Kyung-Sook Bang, Sungjae Kim, Min Kyung Song, KyungIm Kang, Yeseul Jeong
Perspect Nurs Sci. 2020;17(1):1-11. doi: 10.16952/pns.2020.17.1.1.A Systematic Review of Interventions with Low-Income School-Age Children and Adolescents
Ji-hye Hwang, HyunJee Choi, Hyo Jin Jeong, Chorong Kim, YunJung Woo
Perspect Nurs Sci. 2018;15(2):92-106. doi: 10.16952/pns.2018.15.2.92.The Differences in Obesity Rates According to Status of Co-Residence with Their Parents in Korean Adolescents: The Implication of the Gender of Single Parent Living with Adolescents
Nahee Kim, Young Gyu Cho, Jae-Heon Kang, Hyun Ah Park, Kyoungwoo Kim, Yang-Im Hur, Duho Kwon
Korean J Health Promot. 2018;18(4):177-183. doi: 10.15384/kjhp.2018.18.4.177.
Reference
-
1. The Organization for Economic Co-operation and Development. Doing better for families [Internet]. Paris: The Organization for Economic Co-operation and Development;2011. cited 2015 July 29. Available from: http://dx.doi.org/10.1787/9789264098732-en.2. Statistics Korea. 2013 economic and financial data for Korea [Internet]. Seoul: Statistics Korea;2013. cited 2015 July 3. Available from: http://kostat.go.kr/portal/korea/kor_nw/2/4/4/index.board?bmode=read&bSeq=&aSeq=310209&pageNo=1&rowNum=10&navCount=10&currPg=&sTarget=title&sTxt=.3. Kim HR, Lee SH, Choi JM, Oh YI. Report No.: 2011-07. Children's obesity and underweight among low income families in Korea: Status, implications and policy options. Sejong: Korea Institute for Health and Social Affairs;2011. 07.4. Craig LC, McNeill G, Macdiarmid JI, Masson LF, Holmes BA. Dietary patterns of school-age children in Scotland: Association with socioeconomic indicators, physical activity and obesity. Br J Nutr. 2010; 103(3):319–334.
Article5. Drenowatz C, Eisenmann JC, Pfeiffer KA, Welk G, Heelan K, Gentile D, et al. Influence of socio-economic status on habitual physical activity and sedentary behavior in 8- to 11-year old children. BMC Public Health. 2010; 10(1):214.
Article6. United States Department of Agriculture. Dietary guidelines for Americans 2010 [Internet]. Washington, DC: United States Department of Health and Human Services;2010. cited 2014 April 14. Available from: http://www.cnpp.usda.gov/dgas2010-policydocument.htm.7. Evans DR. Enhancing quality of life in the population at large. Soc Indic Res. 1994; 33(1-3):47–88. DOI: 10.1007/978-94-011-0171-4_2.
Article8. The KIDSCREEN Group Europe. The KIDSCREEN Questionnaires-quality of life questionnaires for children and adolescents. Lengerich: Pabst Science Publishers;2006. p. 231.9. Mansour ME, Kotagal U, Rose B, Ho M, Brewer D, Roy-Chaudhury A, et al. Health-related quality of life in urban elementary schoolchildren. Pediatrics. 2003; 111(6):1372–1381. DOI: 10.1542/peds.111.6.1372.
Article10. Chen G, Ratcliffe J, Olds T, Magarey A, Jones M, Leslie E. BMI, health behaviors, and quality of life in children and adolescents: A school-based study. Pediatrics. 2014; 133(4):e868–e874. DOI: 10.1542/peds.2013-0622d.
Article11. Wu XY, Ohinmaa A, Veugelers PJ. Diet quality, physical activity, body weight and health-related quality of life among grade 5 students in Canada. Public Health Nutr. 2012; 15(1):75–81. DOI: 10.1017/s1368980011002412.
Article12. Dalton WT 3rd, Schetzina KE, Pfortmiller DT, Slawson DL, Frye WS. Health behaviors and health-related quality of life among middle school children in Southern Appalachia: data from the winning with wellness project. J Pediatr Psychol. 2011; 36(6):677–686. DOI: 10.1093/jpepsy/jsq108.
Article13. Schlesinger S, Walter J, Hampe J, von Schonfels W, Hinz S, Kuchler T, et al. Lifestyle factors and health-related quality of life in colorectal cancer survivors. Cancer Causes Control. 2014; 25(1):99–110. DOI: 10.1007/s10552-013-0313-y.
Article14. Choo J, Kim HJ, Yang HM, Kim S. Report No.: General 13-8. An obesity prevention framework for vulnerable children based on a methodology of community-based participatory research: Using a strategy of training community lay health advisors. Seoul: Korea Health Promotion Foundation;2013. 11.15. Ravens-Sieberer U, Gosch A, Rajmil L, Erhart M, Bruil J, Duer W, et al. KIDSCREEN-52 quality-of-life measure for children and adolescents. Expert Rev Pharmacoecon Outcomes Res. 2005; 5(3):353–364. DOI: 10.1586/14737167.5.3.353.
Article16. Ministry of Health & Welfare. The Korean dietary guidelines for children [Internet]. Sejong: Ministry of Health & Welfare;2009. cited 2015 January 31. Available from: http://www.mw.go.kr/front_new/jb/sjb030301vw.jsp?PAR_MENU_ID=03&MENU_ID=031603&CONT_SEQ=224044&page=1.17. Kvaavik E, Andersen LF, Klepp KI. The stability of soft drinks intake from adolescence to adult age and the association between long-term consumption of soft drinks and lifestyle factors and body weight. Public Health Nutr. 2005; 8(2):149–157. DOI: 10.1079/phn2004669.
Article18. KIDSCREEN. Questionnaires [internet]. Hamburg: Germany;2011. cited 2014 December 23. Available from: http://www.kidscreen.org/.19. Lee BJ, Kwak GJ, Gu IH, Kim MH, Kim SS, Kim JH, et al. Report No.: 11-1351000-000228-01. A nationwide survey: The status of Korean children and adolescents. Seoul National University Report. Sejong: Ministry of Health & Welfare;2009. 01.20. Ministry of Education. Results of 2013 school health examination [Internet]. Sejong: Ministry of Education;2013. cited 2015 January 31. Available from: http://www.moe.go.kr/web/45859/ko/board/view.do?bbsId=294&boardSeq=52706.21. Dave JM, Evans AE, Pfeiffer KA, Watkins KW, Saunders RP. Correlates of availability and accessibility of fruits and vegetables in homes of low-income hispanic families. Health Educ Res. 2010; 25(1):97–108. DOI: 10.1093/her/cyp044.
Article22. Lee HY, Park YG, You SR, Jung SW, Ko JW. Report No.: 12-R09. Report of longitudinal analysis III: Socially disadvantaged children and adolescents. Sejong: National Youth Policy Institute;2012. 12.23. Morales PF, Sanchez-Lopez M, Moya-Martinez P, Garcia-Prieto JC, Martinez-Andres M, Garcia NL, et al. Health-related quality of life, obesity, and fitness in schoolchildren: The cuenca study. Qual Life Res. 2013; 22(7):1515–1523. DOI: 10.1007/s11136-012-0282-8.
Article24. Young EM, Fors SW, Hayes DM. Associations between perceived parent behaviors and middle school student fruit and vegetable consumption. J Nutr Educ Behav. 2004; 36(1):2–8. DOI: 10.1016/s1499-4046(06)60122-x.
Article25. Chen X, Sekine M, Hamanishi S, Wang H, Gaina A, Yamagami T, et al. Lifestyles and health-related quality of life in Japanese school children: A cross-sectional study. Prev Med. 2005; 40(6):668–678. DOI: 10.1016/j.ypmed.2004.09.034.
Article26. June KJ, Kim JY, Park SM, Lee JY. Breakfast skipping and related factors in children in poverty. J Korean Acad Community Health Nurs. 2011; 22(2):204–211. DOI: 10.12799/jkachn.2011.22.2.204.
Article27. World Health Organization. Global health risks [Internet]. Geneva: World Health Organization;2009. cited 2015 January 31. Available from:http://www.who.int/healthinfo/global_burden_disease/global_health_risks/en/.28. Mathers M, Canterford L, Olds T, Hesketh K, Ridley K, Wake M. Electronic media use and adolescent health and well-being: Cross-sectional community study. Acad Pediatr. 2009; 9(5):307–314. DOI: 10.1016/j.acap.2009.04.003.
Article29. Syväoja HJ, Kantomaa MT, Ahonen T, Hakonen H, Kankaanpää A, Tammelin TH. Physical activity, sedentary behavior, and academic performance in Finnish children. Med Sci Sports Exerc. 2013; 45(11):2098–2104. DOI: 10.1249/mss.0b013e318296d7b8.30. Kwon YH, Kim CN. The relationship between computer game addiction and the impulsiveness, aggression, and emotional intelligence of elementary school students. J Korean Community Nurs. 2004; 15(3):460–470.
- Full Text Links
- Actions
-
Cited
- CITED
-
- Close
- Share
- Similar articles
-
- Levels of Health-related Quality of Life (EQ-5D) and Its Related Factors among Vulnerable Elders Receiving Home Visiting Health Care Services in Some Rural Areas
- The Effects of Related Factors on Health-related Quality of Life for the Frail Elderly
- Resilience and Health-Related Quality of Life in Children with Chronic Illness
- Influence of Depression and Social Support on Health-related Quality of Life among Migrant Workers: The Mediating Effect of Health Promoting Behavior
- Evaluation of Community Health Center for Vulnerable Population in Urban Areas