Chonnam Med J.
2011 Apr;47(1):20-26. 10.4068/cmj.2011.47.1.20.
A Novel Risk Stratification Model for Patients with Non-ST Elevation Myocardial Infarction in the Korea Acute Myocardial Infarction Registry (KAMIR): Limitation of the TIMI Risk Scoring System
- Affiliations
-
- 1Chonnam National University Hospital, Gwangju, Korea. myungho@chollian.net
- 2Yeungnam University Hospital, Daegu, Korea.
- 3Kyungpuk National University Hospital, Daegu, Korea.
- 4Chungnam National University Hospital, Daejeon, Korea.
- 5Kyung Hee University Hospital, Seoul, Korea.
- 6Chungbuk National University Hospital, Cheongju, Korea.
- 7The Catholic University of Korea Hospital, Seoul, Korea.
- 8Asan Medical Center, Seoul, Korea.
- KMID: 2172240
- DOI: http://doi.org/10.4068/cmj.2011.47.1.20
Abstract
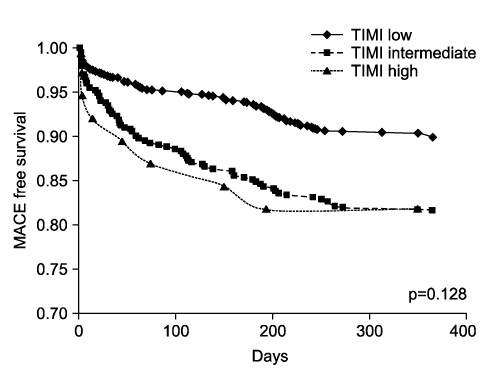
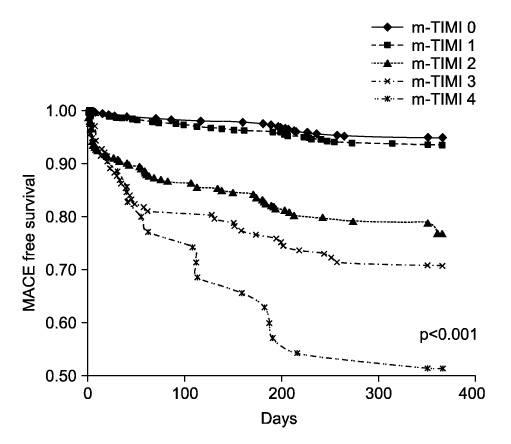
- The Thrombolysis in Myocardial Infarction (TIMI) risk score (TRS) has proven value in predicting prognosis in unstable angina/non ST-elevation myocardial infarction (NSTEMI) as well as in ST-elevation myocardial infarction. The TRS system has little implication, however, in the extent of myocardial damage in high-risk patients with NSTEMI. A total of 1621 patients (63.6+/-12.2 years; 1043 males) with NSTEMI were enrolled in the Korea Acute Myocardial Infarction Registry (KAMIR). We analyzed the risk for major adverse cardiac events (MACE) during a 6-month follow-up period. The TRS system showed good correlation with MACE for patients in the low and intermediate groups but had poor correlation when the high-risk group was included (p=0.128). The MACE rate was 3.8% for TRS 1, 9.4% for TRS 2, 10.7% for TRS 3, and 12.3% for TRS 4 (HR=1.29, p=0.026). Among the biomarkers and clinical risk factors, elevated N-terminal pro-brain natriuretic peptide (NT-proBNP) (HR=2.61, p=0.001) and Killip class above III showed good correlation with MACE (HR=0.302, p<0.001). Therefore, we revised an alternative clinical scoring system by including these two variables that reflect left ventricular dysfunction: age > 65 years, history of ischemic heart disease, Killip class above III, and elevated pro-BNP levels above the 75th percentile. This modified scoring system, when tested for validity, showed good predictive value for MACE (HR=1.64, p<0.001). Compared with the traditional TRS, the novel alternative scoring system based on age, history of ischemic heart disease, Killip class, and NT-proBNP showed a better predictive value for 6-month MACE in high-risk patients with NSTEMI.
Keyword
MeSH Terms
Figure
Reference
-
1. Cannon CP, Weintraub WS, Demopoulos LA, Vicari R, Frey MJ, Lakkis N, et al. Comparison of early invasive and conservative strategies in patients with unstable coronary syndromes treated with the glycoprotein IIb/IIIa inhibitor tirofiban. N Engl J Med. 2001. 344:1879–1887.
Article2. Antman EM, Cohen M, McCabe C, Goodman SG, Murphy SA, Braunwald E. TIMI 11B and ESSENCE Investigators. Enoxaparin is superior to unfractionated heparin for preventing clinical events at 1-year follow-up of TIMI 11B and ESSENCE. Eur Heart J. 2002. 23:308–314.
Article3. Morrow DA, Antman EM, Snapinn SM, McCabe CH, Theroux P, Braunwald E. An integrated clinical approach to predicting the benefit of tirofiban in non-ST elevation acute coronary syndromes. Application of the TIMI risk score for UA/NSTEMI in PRISM-PLUS. Eur Heart J. 2002. 23:223–229.
Article4. Antman EM, Cohen M, Bernink PJ, McCabe CH, Horacek T, Papuchis G, et al. The TIMI risk score for unstable angina/non-ST elevation MI: a method for prognostication and therapeutic decision making. JAMA. 2000. 284:835–842.
Article5. Omland T, Persson A, Ng L, O'Brien R, Karlsson T, Herlitz J, et al. N-terminal pro-B-type natriuretic peptide and long-term mortality in acute coronary syndromes. Circulation. 2002. 106:2913–2918.
Article6. Morrow DA, de Lemos JA, Sabatine MS, Murphy SA, Demopoulos LA, DiBattiste PM, et al. Evaluation of B-type natriuretic peptide for risk assessment in unstable angina/non-ST-elevation myocardial infarction: B-type natriuretic peptide and prognosis in TACTICS-TIMI 18. J Am Coll Cardiol. 2003. 41:1264–1272.
Article7. de Lemos JA, Morrow DA, Bentley JH, Omland T, Sabatine MS, McCabe CH, et al. The prognostic value of B-type natriuretic peptide in patients with acute coronary syndromes. N Engl J Med. 2001. 345:1014–1021.
Article8. Galvani M, Ottani F, Oltrona L, Ardissino D, Gensini GF, Maggioni AP, et al. N-terminal pro-brain natriuretic peptide on admission has prognostic value across the whole spectrum of acute coronary syndromes. Circulation. 2004. 110:128–134.
Article9. Lee KL, Woodlief LH, Topol EJ, Weaver WD, Betriu A, Col J, et al. Predictors of 30-day mortality in the era of reperfusion for acute myocardial infarction. Results from an international trial of 41,021 patients. GUSTO-I Investigators. Circulation. 1995. 91:1659–1668.
Article10. Morrow DA, Antman EM, Charlesworth A, Cairns R, Murphy SA, de Lemos JA, et al. TIMI risk score for ST-elevation myocardial infarction: a convenient, bedside, clinical score for risk assessment at presentation: an intravenous nPA for treatment of infarcting myocardium early II trial substudy. Circulation. 2000. 102:2031–2037.
Article11. Addala S, Grines CL, Dixon SR, Stone GW, Boura JA, Ochoa AB, et al. Predicting mortality in patients with ST-elevation myocardial infarction treated with primary percutaneous coronary intervention (PAMI risk score). Am J Cardiol. 2004. 93:629–632.
Article12. De Luca G, Suryapranata H, van't Hof AW, de Boer MJ, Hoorntje JC, Dambrink JH, et al. Prognostic assessment of patients with acute myocardial infarction treated with primary angioplasty: implications for early discharge. Circulation. 2004. 109:2737–2743.
Article13. Scirica BM, Cannon CP, Antman EM, Murphy SA, Morrow DA, Sabatine MS, et al. Validation of the thrombolysis in myocardial infarction (TIMI) risk score for unstable angina pectoris and non-ST-elevation myocardial infarction in the TIMI III registry. Am J Cardiol. 2002. 90:303–305.
Article14. Peters RJ, Mehta SR, Fox KA, Zhao F, Lewis BS, Kopecky SL, et al. Effects of aspirin dose when used alone or in combination with clopidogrel in patients with acute coronary syndromes: observations from the Clopidogrel in Unstable angina to prevent Recurrent Events (CURE) study. Circulation. 2003. 108:1682–1687.
Article15. Ohman EM, Granger CB, Harrington RA, Lee KL. Risk stratification and therapeutic decision making in acute coronary syndromes. JAMA. 2000. 284:876–878.
Article16. Boersma E, Pieper KS, Steyerberg EW, Wilcox RG, Chang WC, Lee KL, et al. Predictors of outcome in patients with acute coronary syndromes without persistent ST-segment elevation Results from an international trial of 9461 patients. The PURSUIT Investigators. Circulation. 2000. 101:2557–2567.
Article17. Invasive compared with non-invasive treatment in unstable coronary-artery disease: FRISC II prospective randomised multicentre study. FRagmin and Fast Revascularisation during InStability in Coronary artery disease Investigators. Lancet. 1999. 354:708–715.18. Cohen M, Demers C, Gurfinkel EP, Turpie AG, Fromell GJ, Goodman S, et al. Low-molecular-weight heparins in non-ST-segment elevation ischemia: the ESSENCE trial. Efficacy and Safety of Subcutaneous Enoxaparin versus intravenous unfractionated heparin, in non-Q-wave Coronary Events. Am J Cardiol. 1998. 82:19L–24L.19. Budaj A, Yusuf S, Mehta SR, Fox KA, Tognoni G, Zhao F, et al. Benefit of clopidogrel in patients with acute coronary syndromes without ST-segment elevation in various risk groups. Circulation. 2002. 106:1622–1626.
Article20. Malmberg K, Yusuf S, Gerstein HC, Brown J, Zhao F, Hunt D, et al. Impact of diabetes on long-term prognosis in patients with unstable angina and non-Q-wave myocardial infarction: results of the OASIS (Organization to Assess Strategies for Ischemic Syndromes) Registry. Circulation. 2000. 102:1014–1019.
Article21. McGuire DK, Emanuelsson H, Granger CB, Magnus Ohman E, Moliterno DJ, White HD, et al. Influence of diabetes mellitus on clinical outcomes across the spectrum of acute coronary syndromes. Findings from the GUSTO-IIb study. GUSTO IIb Investigators. Eur Heart J. 2000. 21:1750–1758.
Article22. Granger CB, Goldberg RJ, Dabbous O, Pieper KS, Eagle KA, Cannon CP, et al. Predictors of hospital mortality in the global registry of acute coronary events. Arch Intern Med. 2003. 163:2345–2353.
Article23. Eagle KA, Lim MJ, Dabbous OH, Pieper KS, Goldberg RJ, Van de Werf F, et al. A validated prediction model for all forms of acute coronary syndrome: estimating the risk of 6-month postdischarge death in an international registry. JAMA. 2004. 291:2727–2733.
Article24. Wiviott SD, de Lemos JA, Morrow DA. Pathophysiology, prognostic significance and clinical utility of B-type natriuretic peptide in acute coronary syndromes. Clin Chim Acta. 2004. 346:119–128.
Article25. Omland T, Persson A, Ng L, O'Brien R, Karlsson T, Herlitz J, et al. N-terminal pro-B-type natriuretic peptide and long-term mortality in acute coronary syndromes. Circulation. 2002. 106:2913–2918.
Article26. Bazzino O, Fuselli JJ, Botto F, Perez De Arenaza D, Bahit C, Dadone J. PACS group of investigators. Relative value of N-terminal probrain natriuretic peptide, TIMI risk score, ACC/AHA prognostic classification and other risk markers in patients with non-ST-elevation acute coronary syndromes. Eur Heart J. 2004. 25:859–866.
Article27. Grabowski M, Filipiak KJ, Malek LA, Karpinski G, Huczek Z, Stolarz P, et al. Admission B-type natriuretic peptide assessment improves early risk stratification by Killip classes and TIMI risk score in patients with acute ST elevation myocardial infarction treated with primary angioplasty. Int J Cardiol. 2007. 115:386–390.
Article28. Cannon CP, Weintraub WS, Demopoulos LA, Vicari R, Frey MJ, Lakkis N, et al. Comparison of early invasive and conservative strategies in patients with unstable coronary syndromes treated with the glycoprotein IIb/IIIa inhibitor tirofiban. N Engl J Med. 2001. 344:1879–1887.
Article29. Diderholm E, Andrén B, Frostfeldt G, Genberg M, Jernberg T, Lagerqvist B, et al. The prognostic and therapeutic implications of increased troponin T levels and ST depression in unstable coronary artery disease: the FRISC II invasive troponin T electrocardiogram substudy. Am Heart J. 2002. 143:760–767.
Article
- Full Text Links
- Actions
-
Cited
- CITED
-
- Close
- Share
- Similar articles
-
- Differences in the Korea Acute Myocardial Infarction Registry Compared with Western Registries
- Can time delay be shortened in the treatment of acute myocardial infarction?: Experience from Korea acute myocardial infarction registry
- In-Hospital Outcome According to the Initial Management and the "Thrombolysis in Myocardial Infarction Risk Score" of Acute Non-ST Segment Elevation Myocardial Infarction
- New Horizons of Acute Myocardial Infarction: From the Korea Acute Myocardial Infarction Registry
- Current status of acute myocardial infarction in Korea