Dement Neurocogn Disord.
2012 Jun;11(2):53-58. 10.12779/dnd.2012.11.2.53.
A Comparison on the Naming Abilities by Modality in Patients with Alzheimer's Disease
- Affiliations
-
- 1Graduate School of Rehabilitation Service, Korea Nazarene University, Cheonan, Korea.
- 2Department of Communication Disorders, Korea Nazarene University, Cheonan, Korea. hjchoi@kornu.ac.kr
- KMID: 2172234
- DOI: http://doi.org/10.12779/dnd.2012.11.2.53
Abstract
- BACKGROUND
Impairments of language function represent patients with Alzheimer's disease (AD) from the early stage and as the disease progresses the damage spreads over a much broader range of cognition and communicative functions. And, performances of the naming tasks in AD patients may reveal the gradual deterioration of their naming ability.
METHODS
In this study, naming ability was studied in patients with questionable AD (CDR 0.5, n=10), mild AD (CDR 1, n=10), moderate AD (CDR 2, n=10) and 10 healthy controls matched for age, gender and educational level using confrontation naming and naming by verbal definition tasks. The purpose of present study was 1) to investigate whether the confrontation naming and naming by verbal definition in Alzheimer's disease is different depending on the severity, 2) to examine the effects of the syllabic cue on the two naming ability for the errors questions.
RESULTS
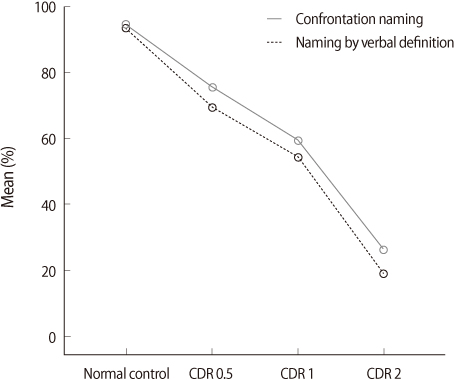
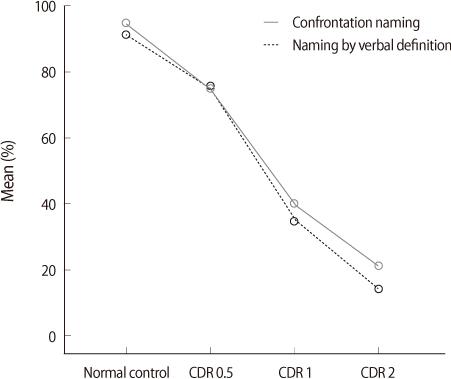
The results from this study are as follow: 1) The two naming performances of the all AD groups were lower than those of normal people and showed significant difference. 2) There were differences between the two naming tasks, significantly lower performance on confrontation naming task than naming by verbal definition. 3) The effects of syllabic cue decreased gradually as severity progressed. 4) The effects of syllabic cue were no significant differences between the two naming tasks.
CONCLUSIONS
The results suggest that anomia in patients with AD is due to various impairment including to lexico-semantic system, visual processing, phonological processing and auditory comprehension.
Figure
Reference
-
1. Balyes KA, Tomoeda CK, Trosset MW. Naming and categorical knowledge in Alzheimer's disease: The process of semantic memory deterioration. Brain Lang. 1990. 39:498–510.2. Adlam A, Bozeat S, Arnold R, Watson P, Hodges JR. Semantic knowledge in mild cognitive impairment. Cortex. 2006. 42:675–684.3. Kim H, Kim EY, Na DL. Naming deficits in patients with dementia of the Alzheimer type: Error analysis of Korean version-Boston Naming Test. J Korean Neurol Assoc. 1997. 15:1012–1021.4. Bayles K, Tomoeda CK. Confrontation naming test impairment in dementia. Brain Lang. 1983. 19:98–114.
Article5. Ellis A, Young A. Human Cognitive Neuropsychology. 1988. Hillside: LEA.
Article6. Burke D, Mackay G, Worthley J, Wade E. On the tip of tongue: What causes word finding failures in young and older adults? J Mem Lang. 1991. 30:542–579.7. Huff J, Corkin S, Growdon J. Semantic impairment and anomia in Alzheimer's disease. Brain Lang. 1986. 23:235–249.8. Hodges J, Salmon D, Butters N. Semantic memory impairment in Alzheimer's disease: Failure of access of degraded knowledge? Neuropsychologia. 1992. 30:301–314.9. Kirshner HS, Webb WG, Kelly MP. Language disturbance: An initial symptom of cortical degeneration and dementia. Arch Neurol. 1984. 41:491–496.10. Rochford MJ, Humphreys GW. A case of integrative visual agnosia. Brain. 1987. 110:1431–1462.
Article11. Lee GJ. Naming deficits in patients with dementia of the Alzheimer Type. 2002. Ewha Womans University;Unpublished master's thesis.
Article12. Lambon Ralph MA, McClelland JL, Patterson K, Galton CJ, Hodges JR. No right to speak? The relationship between object naming and semantic impairment: Neuropsychological evidence and a computational model. J Cogn Neurosci. 2001. 13:341–356.
Article13. Cummings J, Richard J, Benson D, Hill M, Read S. Aphasia in dementia of the Alzheimer type. Neurology. 1985. 35:394–397.
Article14. Lambon Ralph MA, Howard D. Gogi aphasia or semantic dementia? Simulating and assessing poor verbal comprehension in a case of progressive fluent aphasia. Cogn Neuropsychol. 2000. 17:437–465.
Article15. McKhann G, Drachman D, Folstein M, Katzman R, Price D, Stadaln EM. Clinical diagnosis of Alzheimer's disease: Report of the NINCDS-ADRDA Work Group under the auspices of department of health and human service task force on Alzheimer's disease. Neurology. 1984. 34:939–944.
Article16. Morris JC. The Clinical Dementia Rating(CDR): Current version and scoring rules. Neurology. 1993. 43:2412–2414.17. Kang Y, Na DL, Han S. A validity study on the Korean Mini-Mental State Examination (K-MMSE) in dementia patients. J Korean Neurol Assoc. 1997. 15:300–308.18. Kim Kwang Hae. Tungguppyol kugo kyoyungnyong ohwi. 2003. Seoul: Pagijong Press.
Article19. Yonsei Institute of langage and information studies. Yonsei Primary Korean Dictionary. 2011. Seoul: Doosan Donga.
Article20. Tusan Tonga Saso Pyonjipkuk. Tonga sae Kugo sajon. 2005. Seoul: Tusan Tonga.
Article21. Balyes K, Tomoeda C, Kasznick A, Trosset M. Alzheimer's disease effects on semantic memory: Loss of structure or impaired processing? J Cogn Neurosci. 1991. 3:166–182.
Article22. Astell AJ, Harley TA. Accessing semantic knowledge in demantia: Evidence from a word definition task. Brain Lang. 2002. 82:312–327.23. Bayles K, Tomoeda CK. Cognitive-Communication Disorders of Dementia. 2007. San Diego: Plural Publishing.24. Huff J, Corkin S, Growdon J. Semantic impairment and anomia in Alzheimer's disease. Brain Lang. 1986. 23:235–249.25. Snyder LS, Holland AL, Forbes M. Lexical decisions in patients with Alzheimer's disease: Some notes on automatic versus controlled processing. J Commun Disord. 1996. 29:389–398. quiz 398-9.26. Testa JA, Ivnik RJ, Boeve R. Confrontation naming dose not incremental diagnostic utility in MCI and Alzheimer's disease. J Int Neuropsychol Soc. 2004. 10:504–512.27. Chereney H, Murdoch B, Ingram J. Conribution of perceptual and lexical-semantic errors to the naming impairments in Alzheimer's dementia as a function of disease severity. Aphasia. 1991. 5:423–441.28. Henry JD, Carwford JR, Phillips LH. Verbal fluency performance in dementia of the Alzheimer's type: A meta-analysis. Neuropsychologia. 2004. 42:1212–1222.
Article29. Kilada S, Gamaldo A, Grant EA, Moghekar A, Morris JC, O'Brien RJ. Brief screening tests for the diagnosis of dementia: Comparison with the Mini-Mental State Exam. Alzheimer Dis Assoc Disord. 2005. 19:8–16.
Article30. Duong A, Giroux F, Tardif A, Ska B. The heterogenity of pictrue-supported narratives in Alzheimer's disease. Brain Lang. 2004. 93:173–184.
Article31. Choi H. Performances in a picture description task in Japanese patients with Alzheimer's disease and with Mild Cognitive Impairment. Korean J Commun Disord. 2009. 14:326–337.
Article32. Lee EH, An SK, Oh BH, Kim K, Lee Y, Ohrr HC, Kim SM. A neurocognitive assessment: Mild dementia of the Alzheimer type, questionable dementia, and non-demented elderly. J Korean Neuropsychiatr Assoc. 2000. 39:167–182.33. Heo MJ, Ahn SW, Boo SH. Analysis of phonological awareness in patients with mild Alzheimer's disease. Educ J Phys Mult Disabl. 2008. 51:177–199.34. Rochon E. The relationship between measures of working memory and sentence comprehension in patients with Alzheimer's disease. J Speech Lang Hear Res. 2000. 43:395–413.35. Paek EJ. The effect of visual perception on confrontation naming performance: Alzheimer's disease versus Parkinson's disease with dementia. 2009. Yonsei University;Unpublished master's thesis.36. Kim MJ. Famous people naming and identification ability depeding on severeity in Alzheimer disease. 2009. Ewha Womans University;Unpublished master's thesis.
Article37. Delazer M, Semenza C, Reiner M, Hofer M, Benke T. Anomia for people names in DAT evident for semantic and post-semantic impairment. Neuropsychologia. 2003. 41:1593–1598.
Article
- Full Text Links
- Actions
-
Cited
- CITED
-
- Close
- Share
- Similar articles
-
- Priorities of Family Caregivers in Preserving Functional Abilities of Individuals with Alzheimer's Disease Living at Home: A Best-Worst Scaling Approach
- Parallel Short Forms for the Korean-Boston Naming Test (K-BNT)
- Naming deficits in patients with dementia of the Alzheimer type: Error analysis of korean version-Boston naming test
- The Homogeneity of Phenomenology of Gerstmann Syndrome: The Study in Patients with Alzheimer's Disease
- Memorials of Alois Alzheimer (June 14, 1864~December 19, 1915) and Historical Background of Alzheimer's Disease