Chonnam Med J.
2014 Dec;50(3):96-101. 10.4068/cmj.2014.50.3.96.
Risk Factors for Distant Metastasis as a Primary Site of Treatment Failure in Early-Stage Breast Cancer
- Affiliations
-
- 1Department of Radiation Oncology, Presbyterian Medical Center, Jeonju, Korea.
- 2Department of Radiation Oncology, CHA Bundang Medical Center, CHA University, Seongnam, Korea. shin029@chamc.co.kr
- KMID: 2172153
- DOI: http://doi.org/10.4068/cmj.2014.50.3.96
Abstract
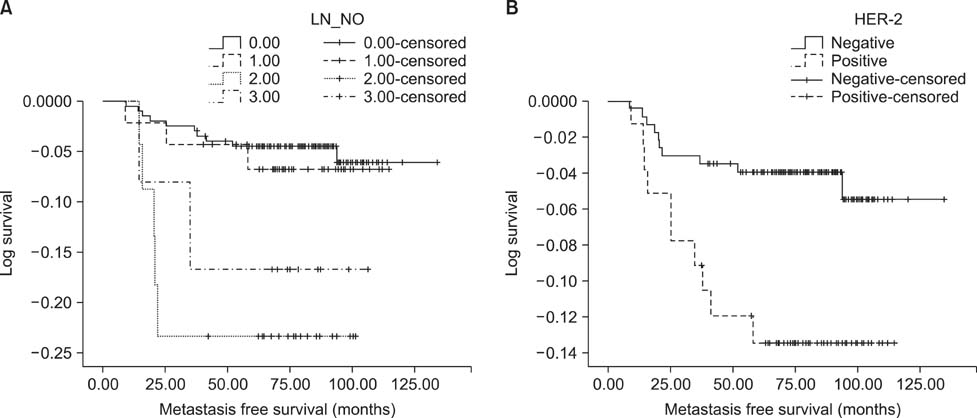
- The aim of this study was to evaluate the risk factors for distant metastasis (DM) as a primary site of failure in early-stage breast cancer. Data from 294 patients diagnosed with pathologic stage I or II breast cancer between January 2000 and December 2005 were reviewed retrospectively. Median follow-up duration was 81.0 months (range, 18-135 months). The total number of patients with DM without evidence of locoregional recurrence was 20 and the median time between surgery and DM was 29 months (range, 9-79 months). Median survival time was 38 months (range, 22-77 months) after operation. HER-2 positivity (p=0.015), T stage of tumor (p=0.012), and number of involved lymph nodes (p=0.008) were significant predictors of DM in the univariable analysis. Number of involved lymph nodes [p=0.005, hazards ratio (HR): 1.741; 95% confidence interval (CI): 1.178-2.574] and HER-2 positivity (p=0.018, HR: 2.888; 95% CI: 1.201-6.941) had a statistically significant effect on DM-free survival in the multivariable analysis. A cautious evaluation may be helpful when patients with risk factors for DM have symptoms implying the possibility of DM. To reduce DM, applying intensive therapy is needed after curative surgery for patients with high risk for DM.
Keyword
MeSH Terms
Figure
Reference
-
1. Rugo HS. The importance of distant metastases in hormone-sensitive breast cancer. Breast. 2008; 17:Suppl 1. S3–S8.
Article2. Jung KW, Park S, Kong HJ, Won YJ, Lee JY, Park EC, et al. Cancer statistics in Korea: incidence, mortality, survival, and prevalence in 2008. Cancer Res Treat. 2011; 43:1–11.
Article3. Mansell J, Monypenny IJ, Skene AI, Abram P, Carpenter R, Gattuso JM, et al. Patterns and predictors of early recurrence in postmenopausal women with estrogen receptor-positive early breast cancer. Breast Cancer Res Treat. 2009; 117:91–98.
Article4. Mell LK, Jeong JH, Nichols MA, Polite BN, Weichselbaum RR, Chmura SJ. Predictors of competing mortality in early breast cancer. Cancer. 2010; 116:5365–5373.
Article5. Fearon ER, Vogelstein B. A genetic model for colorectal tumorigenesis. Cell. 1990; 61:759–767.
Article6. Freudenberg JA, Wang Q, Katsumata M, Drebin J, Nagatomo I, Greene MI. The role of HER2 in early breast cancer metastasis and the origins of resistance to HER2-targeted therapies. Exp Mol Pathol. 2009; 87:1–11.
Article7. Pantel K, Cote RJ, Fodstad O. Detection and clinical importance of micrometastatic disease. J Natl Cancer Inst. 1999; 91:1113–1124.
Article8. Lê MG, Arriagada R, Spielmann M, Guinebretière JM, Rochard F. Prognostic factors for death after an isolated local recurrence in patients with early-stage breast carcinoma. Cancer. 2002; 94:2813–2820.
Article9. Hayes DF, Thor AD. c-erbB-2 in breast cancer: development of a clinically useful marker. Semin Oncol. 2002; 29:231–245.
Article10. Monteiro Grillo I, Jorge M, Marques Vidal P, Ortiz M, Ravasco P. The effect of locoregional recurrence on survival and distant metastasis after conservative treatment for invasive breast carcinoma. Clin Oncol (R Coll Radiol). 2005; 17:111–117.
Article11. Komoike Y, Akiyama F, Iino Y, Ikeda T, Akashi-Tanaka S, Ohsumi S, et al. Ipsilateral breast tumor recurrence (IBTR) after breast-conserving treatment for early breast cancer: risk factors and impact on distant metastases. Cancer. 2006; 106:35–41.
Article12. Touboul E, Buffat L, Belkacémi Y, Lefranc JP, Uzan S, Lhuillier P, et al. Local recurrences and distant metastases after breast-conserving surgery and radiation therapy for early breast cancer. Int J Radiat Oncol Biol Phys. 1999; 43:25–38.
Article13. Koscielny S, Tubiana M. The link between local recurrence and distant metastases in human breast cancer. Int J Radiat Oncol Biol Phys. 1999; 43:11–24.
Article14. Hynes NE. Tyrosine kinase signalling in breast cancer. Breast Cancer Res. 2000; 2:154–157.
Article15. Pietras RJ, Arboleda J, Reese DM, Wongvipat N, Pegram MD, Ramos L, et al. HER-2 tyrosine kinase pathway targets estrogen receptor and promotes hormone-independent growth in human breast cancer cells. Oncogene. 1995; 10:2435–2446.16. Tsutsui S, Ohno S, Murakami S, Hachitanda Y, Oda S. Prognostic value of c-erbB2 expression in breast cancer. J Surg Oncol. 2002; 79:216–223.
Article17. Nguyen PL, Taghian AG, Katz MS, Niemierko A, Abi Raad RF, Boon WL, et al. Breast cancer subtype approximated by estrogen receptor, progesterone receptor, and HER-2 is associated with local and distant recurrence after breast-conserving therapy. J Clin Oncol. 2008; 26:2373–2378.
Article18. Cancello G, Maisonneuve P, Rotmensz N, Viale G, Mastropasqua MG, Pruneri G, et al. Prognosis in women with small (T1mic, T1a, T1b) node-negative operable breast cancer by immunohistochemically selected subtypes. Breast Cancer Res Treat. 2011; 127:713–720.
Article19. Millar EK, Graham PH, O'Toole SA, McNeil CM, Browne L, Morey AL, et al. Prediction of local recurrence, distant metastases, and death after breast-conserving therapy in early-stage invasive breast cancer using a five-biomarker panel. J Clin Oncol. 2009; 27:4701–4708.
Article20. Noh JM, Choi DH, Huh SJ, Park W, Yang JH, Nam SJ, et al. Patterns of recurrence after breast-conserving treatment for early stage breast cancer by molecular subtype. J Breast Cancer. 2011; 14:46–51.
Article21. Kim MJ, Ro JY, Ahn SH, Kim HH, Kim SB, Gong G. Clinicopathologic significance of the basal-like subtype of breast cancer: a comparison with hormone receptor and Her2/neu-overexpressing phenotypes. Hum Pathol. 2006; 37:1217–1226.
Article22. Jatoi I, Hilsenbeck SG, Clark GM, Osborne CK. Significance of axillary lymph node metastasis in primary breast cancer. J Clin Oncol. 1999; 17:2334–2340.
Article23. Rack B, Janni W, Gerber B, Strobl B, Schindlbeck C, Klanner E, et al. Patients with recurrent breast cancer: does the primary axillary lymph node status predict more aggressive tumor progression? Breast Cancer Res Treat. 2003; 82:83–92.
Article
- Full Text Links
- Actions
-
Cited
- CITED
-
- Close
- Share
- Similar articles
-
- Breast Conservation Therapy Versus Mastectomy - Preliminary Results of Pattern of Failure and Survival Rate in Early Breast Cancer
- The Pattern of Systemic Failure and Factors Influencing on the Outcome after Distant Metastastasis in Breast Cancer
- Small bowel obstruction from distant metastasis of primary breast cancer: a case report
- The Clinical Characteristics and Predictive Factors of Stage IV Breast Cancer at the Initial Presentation: A Review of a Single Institute's Data
- Prognostic Factors for Premenopausal Women with Distant Metastatic Breast Cancer