Ann Dermatol.
2009 Feb;21(1):60-62. 10.5021/ad.2009.21.1.60.
Repeated Paradoxical Aggravation of Preexisting Psoriasis during Infliximab Treatment for Crohn's Disease
- Affiliations
-
- 1Department of Dermatology, Kyungpook National University School of Medicine, Daegu, Korea. seokjong@knu.ac.kr
- 2Department of Dermatology, Ajou University Hospital, Suwon, Korea.
- KMID: 2172069
- DOI: http://doi.org/10.5021/ad.2009.21.1.60
Abstract
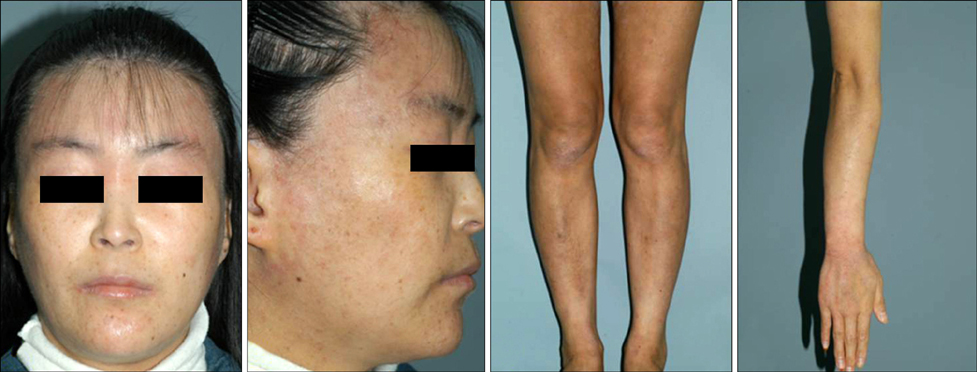
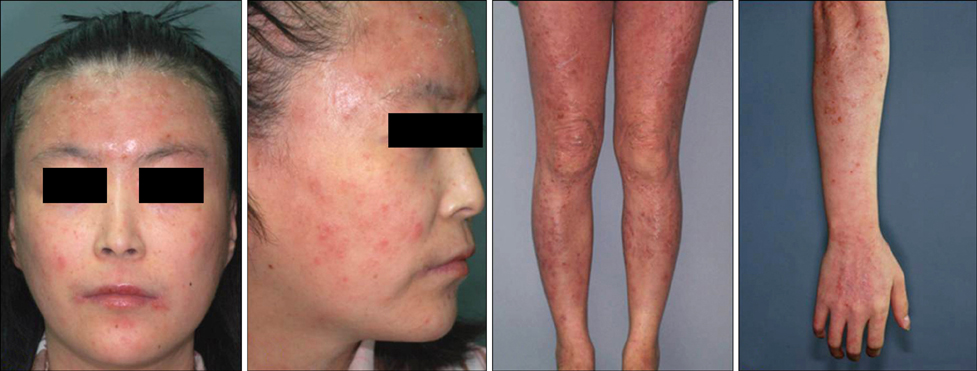
- As more rheumatologists and dermatologists have begun to use biological agents such as TNF-alpha blocker, they have confronted an unexpected complication: psoriasis was paradoxically aggravated or induced by the TNF-alpha blocker. Although it is not a common complication of TNF-alpha blocker, this aggravation may be more common than previously thought. To our knowledge, most reports about TNF-alpha blocker-induced psoriasis have been limited to western countries while only a few cases have been reported in Korea and Japan. In addition, new onset of pustular psoriasis by TNF-alpha blocker has been reported more commonly than worsening of preexisting psoriasis. Now we report a patient whose preexisting psoriasis vulgaris was aggravated repeatedly after using the TNF-alpha blocker, infliximab, to control Crohn's disease, which is a rare rheumatologic disease in Korea.
Keyword
MeSH Terms
Figure
Cited by 2 articles
-
A Case of Infliximab-induced Psoriasis in Treatment of Ankylosing Spondylitis
Min Jeong Kim, Ji Hyun Lee, Ho Joon Im, Hyun Jung Yeo, Hong Jik Lee, Ki Sup Byun
J Rheum Dis. 2014;21(5):274-277. doi: 10.4078/jrd.2014.21.5.274.A Case of Psoriasis Induced by Infliximab Treatment for Crohn's Disease
Yoon Jung Jwa, Nam-Hoon Kim, Hai Jin Park, Jun Sup Park, Won Ki Bae, Kyung-Ah Kim, June Sung Lee, Young Soo Moon
Korean J Gastroenterol. 2010;56(5):324-328. doi: 10.4166/kjg.2010.56.5.324.
Reference
-
1. Najarian DJ, Gottlieb AB. Connections between psoriasis and Crohn's disease. J Am Acad Dermatol. 2003. 48:805–821.
Article2. Peramiquel L, Puig L, Dalmau J, Ricart E, Roe E, Alomar A. Onset of flexural psoriasis during infliximab treatment for Crohn's disease. Clin Exp Dermatol. 2005. 30:713–714.
Article3. Takahashi H, Hashimoto Y, Ishida-Yamamoto A, Ashida T, Kohgo Y, Iizuka H. Psoriasiform and pustular eruption induced by infliximab. J Dermatol. 2007. 34:468–472.
Article4. Grinblat B, Scheinberg M. Unexpected onset of psoriasis during infliximab treatment: comment on the article by Beuthien et al. Arthritis Rheum. 2005. 52:1333–1334.
Article5. Flendrie M, Vissers WH, Creemers MC, de Jong EM, van de Kerkhof PC, van Riel PL. Dermatological conditions during TNF-alpha-blocking therapy in patients with rheumatoid arthritis: a prospective study. Arthritis Res Ther. 2005. 7:R666–R676.6. Choi YJ, Kim DS, Park JM, Oh SH, Park YK, Lee JH. A case of psoriasiform eruption triggered by tumor necrosis factor-alpha antagonist therapy. Korean J Dermatol. 2008. 46:721–723.7. de Gannes GC, Ghoreishi M, Pope J, Russell A, Bell D, Adams S, et al. Psoriasis and pustular dermatitis triggered by TNF-{alpha} inhibitors in patients with rheumatologic conditions. Arch Dermatol. 2007. 143:223–231.8. Heymann WR. Tumor necrosis factor inhibitor-induced pustular psoriasis? J Am Acad Dermatol. 2007. 56:327–329.
Article9. Sfikakis PP, Iliopoulos A, Elezoglou A, Kittas C, Stratigos A. Psoriasis induced by anti-tumor necrosis factor therapy: a paradoxical adverse reaction. Arthritis Rheum. 2005. 52:2513–2518.
Article
- Full Text Links
- Actions
-
Cited
- CITED
-
- Close
- Share
- Similar articles
-
- A Case of Infliximab-induced Psoriasis in Treatment of Ankylosing Spondylitis
- Development of Renal Disorder in a Patient Receiving Infliximab (Remicade(R)) for Psoriasis
- A Case of Psoriasis Induced by Infliximab Treatment for Crohn's Disease
- A Case of Pustular Psoriasis Developed during Infliximab Treatment for Crohn's Disease
- Clinical efficacy of adalimumab versus infliximab and the factors associated with recurrence or aggravation during treatment of anal fistulas in Crohn's disease