Ann Dermatol.
2013 May;25(2):266-268. 10.5021/ad.2013.25.2.266.
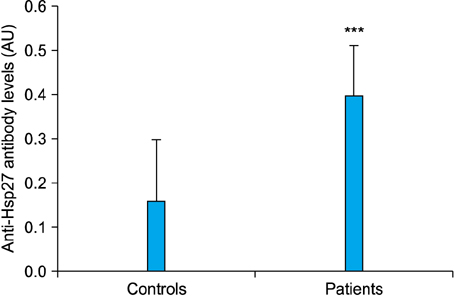
High Levels of Anti-Heat Shock Protein 27 Antibody in Pemphigus Vulgaris
- Affiliations
-
- 1Research Center for Skin Diseases and Cutaneous Leishmaniasis, Faculty of Medicine, Ghaem Hospital, Gordon Ashley Anthony Ferns, Mashhad University of Medical Science, Mashhad, Iran.
- 2Biochemistry of Nutrition Research Center, Faculty of Medicine, Mashhad University of Medical Science, Mashhad, Iran. ghayourm@mums.ac.ir
- 3Division of Medical Education, Brighton & Sussex Medical School, Mayfield House, Falmer, Brighton, Sussex, UK.
- KMID: 2171809
- DOI: http://doi.org/10.5021/ad.2013.25.2.266
Abstract
- No abstract available.
Figure
Reference
-
1. Korman N. Pemphigus. J Am Acad Dermatol. 1988. 18:1219–1238.
Article2. Amagai M, Klaus-Kovtun V, Stanley JR. Autoantibodies against a novel epithelial cadherin in pemphigus vulgaris, a disease of cell adhesion. Cell. 1991. 67:869–877.
Article3. Ghayour-Mobarhan M, Rahsepar AA, Tavallaie S, Rahsepar S, Ferns GA. The potential role of heat shock proteins in cardiovascular disease: evidence from in vitro and in vivo studies. Adv Clin Chem. 2009. 48:27–72.4. Kostenko S, Moens U. Heat shock protein 27 phosphorylation: kinases, phosphatases, functions and pathology. Cell Mol Life Sci. 2009. 66:3289–3307.
Article5. Berkowitz P, Hu P, Liu Z, Diaz LA, Enghild JJ, Chua MP, et al. Desmosome signaling. Inhibition of p38MAPK prevents pemphigus vulgaris IgG-induced cytoskeleton reorganization. J Biol Chem. 2005. 280:23778–23784.6. Rahsepar AA, Mirzaee A, Moodi F, Moohebati M, Tavallaie S, Eshraghi A, et al. Anti-heat shock protein 27 titers and oxidative stress levels are elevated in patients with valvular heart disease. Angiology. 2012. 63:609–616.
Article7. Ghayour-Mobarhan M, Sahebkar A, Parizadeh SM, Moohebati M, Tavallaie S, Rezakazemi-Bajestani SM, et al. Antibody titres to heat shock protein 27 are elevated in patients with acute coronary syndrome. Int J Exp Pathol. 2008. 89:209–215.
Article8. Seishima M, Esaki C, Osada K, Mori S, Hashimoto T, Kitajima Y. Pemphigus IgG, but not bullous pemphigoid IgG, causes a transient increase in intracellular calcium and inositol 1,4,5-triphosphate in DJM-1 cells, a squamous cell carcinoma line. J Invest Dermatol. 1995. 104:33–37.
Article9. Berkowitz P, Hu P, Warren S, Liu Z, Diaz LA, Rubenstein DS. p38MAPK inhibition prevents disease in pemphigus vulgaris mice. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA. 2006. 103:12855–12860.
Article10. Burut DF, Karim Y, Ferns GA. The role of immune complexes in atherogenesis. Angiology. 2010. 61:679–689.
Article
- Full Text Links
- Actions
-
Cited
- CITED
-
- Close
- Share
- Similar articles
-
- Lesional Expression of Heat Shock Protein 70 in Pemphigus
- Antibody response of periodontal patients to Porphyromonas gingivalis heat shock protein
- Antibody response against 65kD heat shock protein in Kawasaki disease
- Effect of Anti-CD20 Monoclonal Antibody (Rituximab) on Recalcitrant Pemphigus Vulgaris
- Expression of Heat Shock Protein 70 m-RNA in Rat Bladder Overdistended by Diuresis