Ann Dermatol.
2013 May;25(2):263-265. 10.5021/ad.2013.25.2.263.
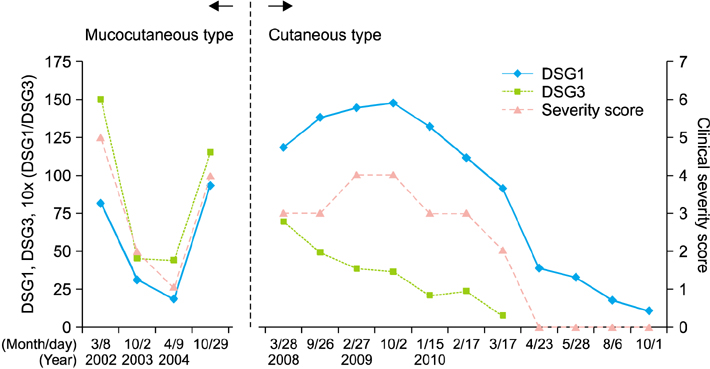
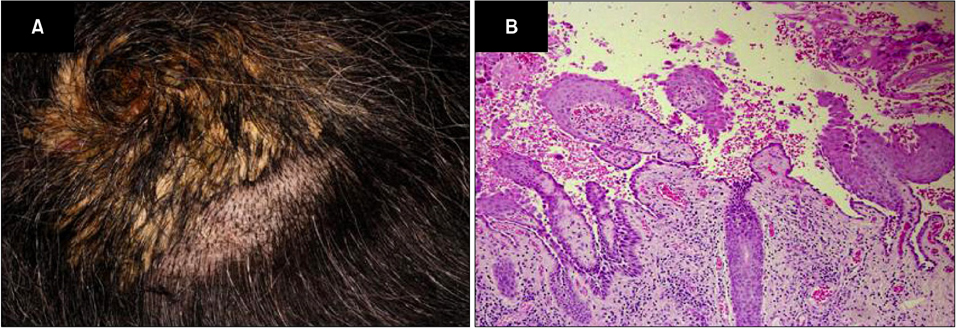
Selective Elevation of Antibodies to Desmoglein 1 during the Transition from Mucocutaneous to Cutaneous Type Pemphigus Vulgaris
- Affiliations
-
- 1Department of Dermatology, Faculty of Medicine, Oita University, Yufu, Oita, Japan. hatano@oita-u.ac.jp
- KMID: 2171808
- DOI: http://doi.org/10.5021/ad.2013.25.2.263
Abstract
- No abstract available.
Figure
Cited by 1 articles
-
A Case of Pemphigus Herpetiformis with Only Immunoglobulin G Anti-Desmocollin 3 Antibodies
Won Jin Hong, Takashi Hashimoto, Soo-Chan Kim
Ann Dermatol. 2016;28(1):102-106. doi: 10.5021/ad.2016.28.1.102.
Reference
-
1. Ding X, Aoki V, Mascaro JM Jr, Lopez-Swiderski A, Diaz LA, Fairley JA. Mucosal and mucocutaneous (generalized) pemphigus vulgaris show distinct autoantibody profiles. J Invest Dermatol. 1997. 109:592–596.
Article2. Yoshida K, Takae Y, Saito H, Oka H, Tanikawa A, Amagai M, et al. Cutaneous type pemphigus vulgaris: a rare clinical phenotype of pemphigus. J Am Acad Dermatol. 2005. 52:839–845.
Article3. Shinkuma S, Nishie W, Shibaki A, Sawamura D, Ito K, Tsuji-Abe Y, et al. Cutaneous pemphigus vulgaris with skin features similar to the classic mucocutaneous type: a case report and review of the literature. Clin Exp Dermatol. 2008. 33:724–728.
Article4. Kanwar AJ, Tsuruta D, Vinay K, Koga H, Ishii N, Dainichi T, et al. Efficacy and safety of rituximab treatment in Indian pemphigus patients. J Eur Acad Dermatol Venereol. 2013. 27:e17–e23.
Article5. Feldman RJ, Christen WG, Ahmed AR. Comparison of immunological parameters in patients with pemphigus vulgaris following rituximab and IVIG therapy. Br J Dermatol. 2012. 166:511–517.
Article
- Full Text Links
- Actions
-
Cited
- CITED
-
- Close
- Share
- Similar articles
-
- Immunolocalization of Desmoglein in Autoimmune Pemphigus
- Transition from Pemphigus Foliaceus to Pemphigus Vulgaris: Case Report with Literature Review
- A Case of Pemphigus Vulgaris
- The Neumann Type of Pemphigus Vegetans Treated with Combination of Dapsone and Steroid
- A Case of Pemphigus Vulgaris Localized on the Scalp