Ann Dermatol.
2014 Apr;26(2):246-249. 10.5021/ad.2014.26.2.246.
Acute Generalized Exanthematous Pustulosis Associated with Tigecycline
- Affiliations
-
- 1Department of Dermatology, Balikesir University Medical Faculty, Balikesir, Turkey. drsozturk@gmail.com
- 2Department of Infectious Diseases and Clinical Microbiology, Ministry of Health Elazig Education and Research Hospital, Elazig, Turkey.
- 3Department of Pathology, Ministry of Health Elazig Education and Research Hospital, Elazig, Turkey.
- 4Department of Dermatology, Dicle University Medical Faculty, Diyarbakir, Turkey.
- KMID: 2171663
- DOI: http://doi.org/10.5021/ad.2014.26.2.246
Abstract
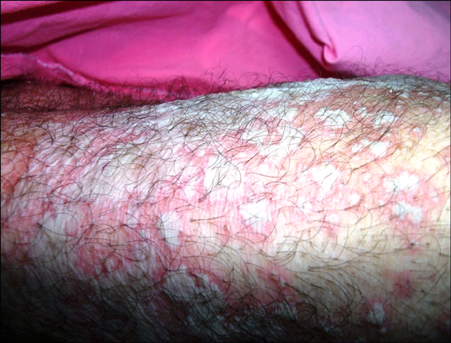
- Acute generalized exanthematous pustulosis (AGEP) is a severe and rare eruption that develops mostly from factors related to drugs. It is characterized by a fever and a pustular eruption on the erythematous skin with an acute onset and without follicular localization. Etiopathogenesis has not yet been fully explained. Although it is similar to pustular psoriasis, its clinical, historical and histopathological characteristics are different. In this article, we present a case of AGEP associated with tigecycline that developed in a patient followed up in the intensive care unit for three months with an intra-abdominal injury after a trauma and Acinetobacter baumannii infection.
MeSH Terms
Figure
Reference
-
1. Litt JZ. Drug eruptions & reactions manual. 16th ed. New York: Informa Healthcare;2010. p. 572.2. Beylot C, Bioulac P, Doutre MS. Acute generalized exanthematic pustuloses (four cases). Ann Dermatol Venereol. 1980; 107:37–48.3. Sidoroff A, Dunant A, Viboud C, Halevy S, Bavinck JN, Naldi L, et al. Risk factors for acute generalized exanthematous pustulosis (AGEP)-results of a multinational case-control study (EuroSCAR). Br J Dermatol. 2007; 157:989–996.
Article4. Sidoroff A, Halevy S, Bavinck JN, Vaillant L, Roujeau JC. Acute generalized exanthematous pustulosis (AGEP)--a clinical reaction pattern. J Cutan Pathol. 2001; 28:113–119.
Article5. Won JH, Yun SJ, Kim SJ, Lee SC, Won YH, Lee JB. A case of acute generalized exanthematous pustulosis possibly induced by ritodrine. Ann Dermatol. 2009; 21:323–325.
Article6. Stein GE, Craig WA. Tigecycline: a critical analysis. Clin Infect Dis. 2006; 43:518–524.
Article7. Nursel Ç, Murat A. Tigesiklin. ANKEM Derg. 2007; 21:29–33.8. Bassetti M, Nicolini L, Repetto E, Righi E, Del Bono V, Viscoli C. Tigecycline use in serious nosocomial infections: a drug use evaluation. BMC Infect Dis. 2010; 10:287.
Article9. Khalel MH, Fattah Saleh SA, F El-Gamal AH, Najem N. Acute generalized exanthematous pustulosis: an unusual side effect of meropenem. Indian J Dermatol. 2010; 55:176–177.
Article10. Makris M, Spanoudaki N, Giannoula F, Chliva C, Antoniadou A, Kalogeromitros D. Acute generalized exanthematous pustulosis (AGEP) triggered by a spider bite. Allergol Int. 2009; 58:301–303.
Article11. Yüksek J, Sezer E. Atypical drug eruptions: review. T Clin J Dermatol. 2008; 18:85–90.12. Wolkenstein P, Chosidow O, Fléchet ML, Robbiola O, Paul M, Dumé L, et al. Patch testing in severe cutaneous adverse drug reactions, including Stevens-Johnson syndrome and toxic epidermal necrolysis. Contact Dermatitis. 1996; 35:234–236.
Article13. Barbaud A. Drug patch testing in systemic cutaneous drug allergy. Toxicology. 2005; 209:209–216.
Article
- Full Text Links
- Actions
-
Cited
- CITED
-
- Close
- Share
- Similar articles
-
- Acute Generalized Exanthematous Pustulosis with Hemodynamic Instability Induced by Ingestion of Lacquer Chicken
- A Case of Acute Generalized Exanthematous Pustulosis Possibly Induced by Ritodrine
- Two Cases of Acute Generalized Exanthematous Pustulosis
- Acute Generalized Exanthematous Pustulosis
- A Serial Occurrence of Acute Generalized Exanthematous Pustulosis in Childhood Siblings