Infect Chemother.
2009 Feb;41(1):30-35. 10.3947/ic.2009.41.1.30.
Clinical Manifestation of Emphysematous Pyelonephritis and Risk Factors for Mortality
- Affiliations
-
- 1Department of Urology, College of Medicine, The Catholic University of Korea, Seoul, Korea. lee.seungju@gmail.com
- KMID: 2170246
- DOI: http://doi.org/10.3947/ic.2009.41.1.30
Abstract
-
BACKGROUND: Emphysematous pyelonephritis (EPN) is an acute gas forming necrotizing infection of the renal parenchyma with high mortality. Although its incidence is relatively low, it mostly occurs in patients wiith diabetes mellitus. The aim of the study is to identify the risk factors related to mortality and assess the outcome of managements according to the radiologic classification.
MATERIALS AND METHODS
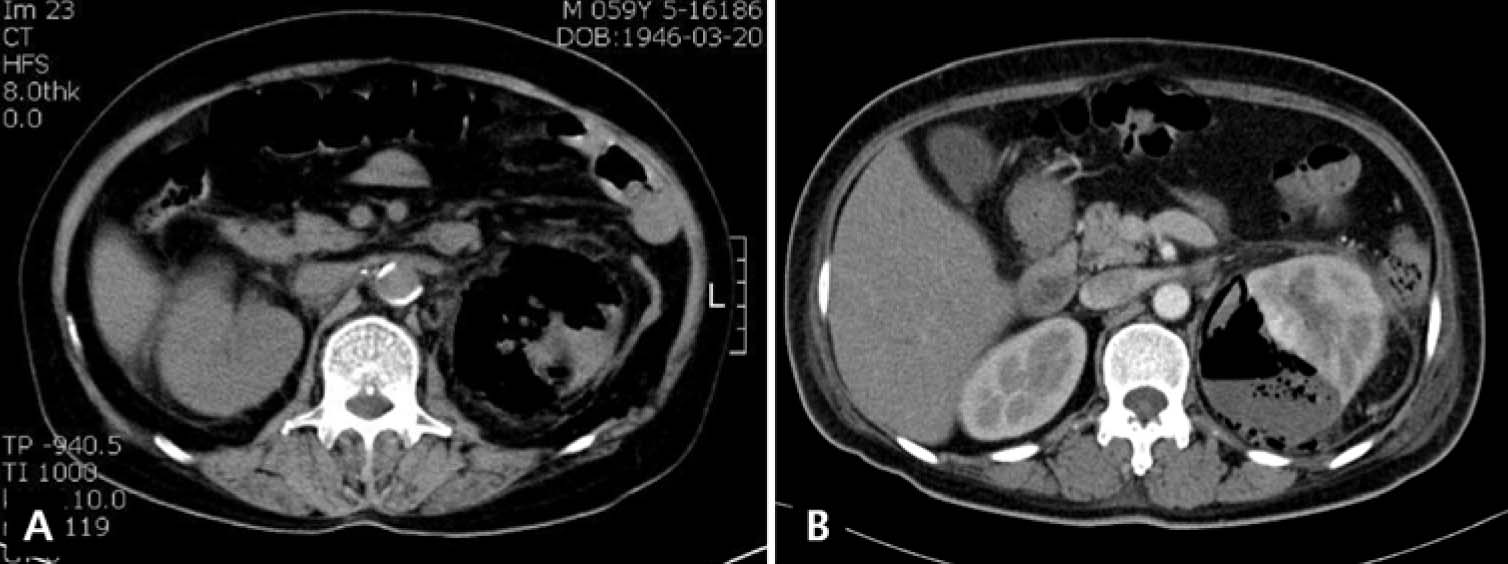
The clinical records of 23 patients diagnosed with EPN were reviewed retrospectively. The cases were grouped into two types on the basis of computed tomography scan. Type 1 EPN was defined as renal necrosis and gas formation with total absence of fluid content. Type 2 EPN was defined as the presence of renal or perirenal fluid in association with bubbly or loculated gas pattern. The patients' symptoms, performed investigations, and treatments were analyzed.
RESULTS
All patients had diabetes mellitus. Escherichia coli (78.6%) was the most common pathogen in urine and blood cultures. The factors showing statistically significant differences between survivors and non-survivors were age (P=0.013), the presence of obstructive uropathy (P= 0.008), and type 1 group (P=0.030). Multivariate logistic regression showed that factor significantly related to death was age (odds ratio=1.20, 95% confidence interval 1.01-1.38, P=0.037). Conservative treatment including antibiotics and percutaneous drainage was successful in type 2 group. Overall mortality was 26.1%; all expired patients were from type 1 group. The mortality of conservative treatment and nephrectomy in type 1 group was 83.3% and 20.0%, respectively.
CONCLUSION
These results suggest that old age is a significant risk factor for mortality in patients with EPN. Nephrectomy should be considered as the main treatment option in patients with type 1 EPN.
MeSH Terms
Figure
Cited by 2 articles
-
Clinical Guideline for the Diagnosis and Treatment of Urinary Tract Infections: Asymptomatic Bacteriuria, Uncomplicated & Complicated Urinary Tract Infections, Bacterial Prostatitis
, , ,
Infect Chemother. 2011;43(1):1-25. doi: 10.3947/ic.2011.43.1.1.Analysis of Treatment Modalities of 24 Cases with Emphysematous Pyelonephritis
Phil Hyun Song, Hyun Tae Kim
Infect Chemother. 2011;43(4):339-342. doi: 10.3947/ic.2011.43.4.339.
Reference
-
1. Michaeli J, Mogle S, Perlberg S, Heimen S, Caime M. Emphysematous pyelonephritis. J Urol. 1984. 131:203–208.
Article2. Klein FA, Smith MJ, Vick CW III, Schneider V. Emphysematous pyelonephritis: diagnosis and treatment. South Med J. 1986. 79:41–46.3. Al Makadma AS, Al-Akash SI. An unusual case of pyelonephritis in a paediatric renal transplant recipient. Pediatr Transplant. 2005. 9:258–260.4. Kim DS, Woesner ME, Howard TF, Olson LK. Emphysematous pyelonephritis demonstrated by computed tomography. AJR Am J Roentgenol. 1979. 132:287–288.
Article5. Chen MT, Huang CN, Chou YH, Huang CH, Chiang CP, Liu GC. Percutaneous drainage in the treatment of emphysematous pyelonephritis: 10-year experience. J Urol. 1997. 157:1569–1573.
Article6. Narlawar RS, Raut AA, Nagar A, Hira P, Hanchate V, Asrani A. Imaging features and guided drainage in emphysematous pyelonephritis: a study of 11 cases. Clin Radiol. 2004. 59:192–197.
Article7. Ramesh J, Bhansali A, Dash RJ. Diabetes, fever, and flank pain. Postgrad Med J. 1998. 74:241–243.
Article8. Wan YL, Lee TY, Bullard MJ, Tsai CC. Acute gas-producing bacterial renal infection: correlation between imaging findings and clinical outcome. Radiology. 1996. 198:433–438.
Article9. Kelly HA, MacCallum WG. Pneumaturia. JAMA. 1898. 31:375–381.
Article10. Shokeir AA, El-Azab M, Mohsen T, El-Diasty T. Emphysematous pyelonephritis: a 15-year experience with 20 cases. Urology. 1997. 49:343–346.
Article11. Tang HJ, Li CM, Yen MY, Chen YS, Wann SR, Lin HH, Lee SS, Liu YC. Clinical characteristics of emphysematous pyelonephritis. J Microbiol Immunol Infect. 2001. 34:125–130.12. Huang JJ, Tseng CC. Emphysematous pyelonephritis: clinicoradiological classification, management, prognosis, and pathogenesis. Arch Intern Med. 2000. 160:797–805.13. Ramanathan V, Nguyen PT, Van Nguyen P, Khan A, Musher D. Successful medical management of recurrent emphysematous pyelonephritis. Urology. 2006. 67:623.
Article14. Hoddick W, Jeffrey RB, Goldberg HI, Federle MP, Laing FC. CT and sonography of severe renal and perirenal infections. AJR Am J Roentgenol. 1983. 140:517–520.
Article15. Dutta P, Bhansali A, Singh SK, Gupta KL, Bhat MH, Masoodi SR, Kumar Y. Presentation and outcome of emphysematous renal tract disease in patients with diabetes mellitus. Urol Int. 2007. 78:13–22.
Article16. Ahmad M, Dakshinamurty KV. Emphysematous renal tract disease due to Aspergillus fumigatus. J Assoc Physicians India. 2004. 52:495–497.17. Wan YL, Lo SK, Bullard MJ, Chang PL, Lee TY. Predictors of outcome in emphysematous pyelonephritis. J Urol. 1998. 159:369–373.
Article18. Dutta P, Bhansali A, Singh SK, Gupta KL, Bhat MH, Masoodi SR, Kumar Y. Presentation and outcome of emphysematous renal tract disease in patients with diabetes mellitus. Urol Int. 2007. 78:13–22.
Article19. Park BS, Lee SJ, Kim YW, Huh SJ, Kim JI, Chang SG. Outcome of nephrectomy and kidney-preserving procedures for the treatment of emphysematous pyelonephritis. Scand J Urol Nephrol. 2006. 40:332–338.
Article20. Angulo JC, Dehaini A, Escribano J, Sanchez-Chapado M. Successful conservative management of emphysematous pyelonephritis, bilateral or in a solitary kidney. Scand J Urol Nephrol. 1997. 31:193–197.
Article21. Gerzof SG, Gale ME. Computed tomography and ultrasonography for diagnosis and treatment of renal and retroperitoneal abscesses. Urol Clin North Am. 1982. 9:185–193.
Article