Anesth Pain Med.
2016 Jan;11(1):113-116. 10.17085/apm.2016.11.1.113.
Successful intubation using a specially bent lighted stylet to fit the upper airway passage of a patient with ankylosis of the temporomandibular joint and deep cervical abscesses: A case report
- Affiliations
-
- 1Department of Anesthesiology and Pain Medicine, Hallym University College of Medicine, Chuncheon, Korea. jg1229kr@hanmail.net
- 2Dongtan Sacred Heart Hospital, Hallym University College of Medicine, Hwasung, Korea.
- 3Hallym Hospital, Hallym University College of Medicine, Anyang, Korea.
- KMID: 2169086
- DOI: http://doi.org/10.17085/apm.2016.11.1.113
Abstract
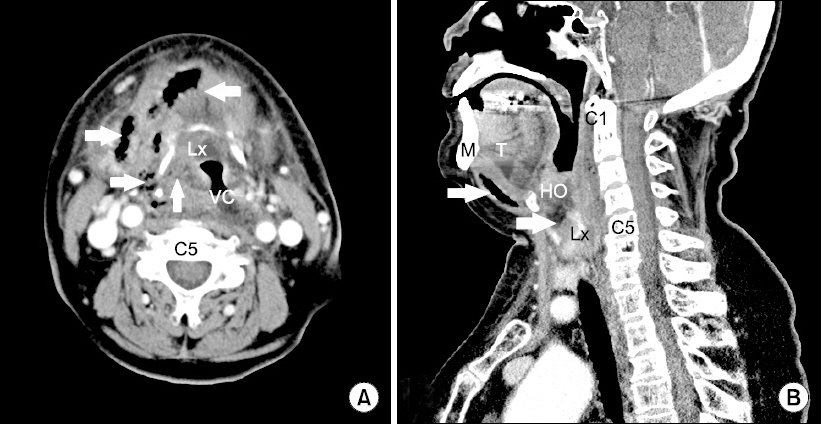
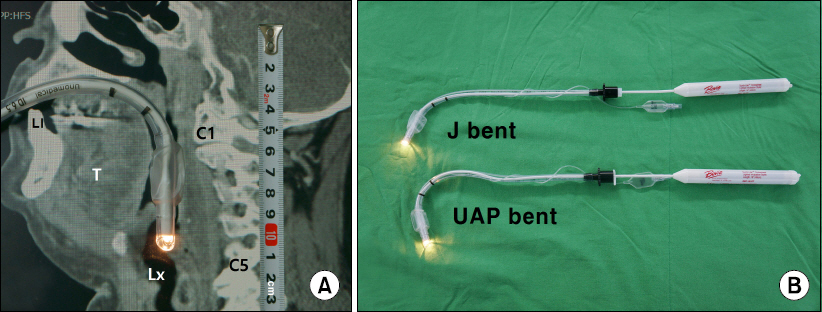
- A bent lighted stylet has demonstrated effectiveness for intubating patients with difficult airways. We report a case of successful intubation using a lighted stylet that was bent to configure the upper airway passage in a patient with ankylosis of the temporo-mandibualr joint and a small inter-incisor gap with diffuse submandibular abscesses. We suppose that lighted stylets with different bends can be used in difficult airway cases. The usefulness of a bent lighted stylet to fit the upper airway passage needs further evaluation for additional clinical application.
MeSH Terms
Figure
Reference
-
1. Davis L, Cook-Sather SD, Schneider MS. Lighted stylet tracheal intubation: a review. Anesth Analg. 2000; 90:745–56. DOI: 10.1097/00000539-200003000-00044. PMID: 10702469.
Article2. Bikramjit D. Intubation with oral lightwand with an alternative curvature in a case of temporo-mandibular joint ankylosis. Anesth Essays Res. 2014; 8:120. DOI: 10.4103/0259-1162.128932. PMID: 25886123. PMCID: PMC4173588.
Article3. Jeon YT, Lim YJ, Na HS, Park SH, Oh AY, Hwang JW, et al. A double bending lightwand can provide more successful endotracheal intubation in patients with a short thyromental distance: a prospective randomised study. Eur J Anaesthesiol. 2011; 28:651–4. DOI: 10.1097/EJA.0b013e328349a017. PMID: 21760515.4. Agrò F, Totonelli A, Gherardi S. Planned lightwand intubation in a patient with a known difficult airway. Can J Anaesth. 2004; 51:1051–2. DOI: 10.1007/BF03018502.
Article5. Hung OR, Pytka S, Morris I, Murphy M, Launcelott G, Stevens S, et al. Clinical trial of a new lightwand device (Trachlight) to intubate the trachea. Anesthesiology. 1995; 83:509–14. DOI: 10.1097/00000542-199509000-00009. PMID: 7661351.
Article6. Weis FR, Hatton MN. Intubation by use of the light wand: experience in 253 patients. J Oral Maxillofac Surg. 1989; 47:577–80. DOI: 10.1016/S0278-2391(89)80071-0.7. Kim MK, Lee JH, Kim EJ, Lee SG, Ban JS, Min BW. Comparison of the success rates of lightwand tracheal intubation on the first attempt when using the lightwand at different angles. Anesth Pain Med. 2007; 2:252–6.8. Tse JC, Rimm EB, Hussain A. Predicting difficult endotracheal intubation in surgical patients scheduled for general anesthesia: a prospective blind study. Anesth Analg. 1995; 81:254–8. DOI: 10.1097/00000539-199508000-00008. PMID: 7618711.9. Frerk CM. Predicting difficult intubation. Anaesthesia. 1991; 46:1005–8. DOI: 10.1111/j.1365-2044.1991.tb09909.x. PMID: 1781521.
Article10. Merah NA, Wong DT, Foulkes-Crabbe DJ, Kushimo OT, Bode CO. Modified Mallampati test, thyromental distance and inter-incisor gap are the best predictors of difficult laryngoscopy in West Africans. Can J Anaesth. 2005; 52:291–6. DOI: 10.1007/BF03016066. PMID: 15753502.11. Wilson ME, Spiegelhalter D, Robertson JA, Lesser P. Predicting difficult intubation. Br J Anaesth. 1988; 61:211–6. DOI: 10.1093/bja/61.2.211. PMID: 3415893.
Article
- Full Text Links
- Actions
-
Cited
- CITED
-
- Close
- Share
- Similar articles
-
- Airway Management for General Anesthesia in a Patient with Severe Trismus due to Temporomandibular Joint Ankylosis : A case report
- Difficult airway management in a case with lingual tonsil hypertrophy and temporo-mandibular joint partial ankylosis
- Successful Tracheal Intubation Using Rigid Video-Stylet in a Ptiaent with Tracheobronchopathia Osteochondroplastica
- Open Lock of the Jaw on Induction of Anesthesia: A case report
- Unrecognized Bilateral Dislocation of Temporomandibular Joint during Orotracheal Intubation