Hanyang Med Rev.
2015 Aug;35(3):131-135. 10.7599/hmr.2015.35.3.131.
Disaster Basic Physics and Disaster Paradigm
- Affiliations
-
- 1Center for Disaster Relief Education and Research, Severance Hospital, Yonsei University College of Medicine, Seoul, Korea. drshkim@yuhs.ac
- KMID: 2168357
- DOI: http://doi.org/10.7599/hmr.2015.35.3.131
Abstract
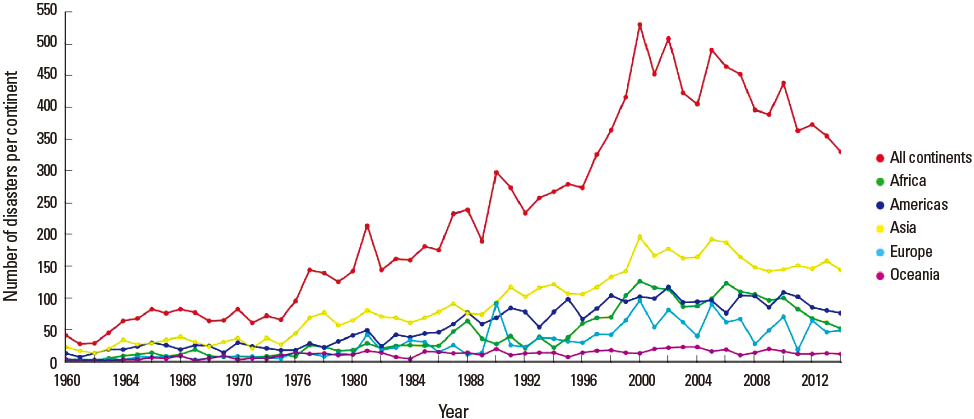
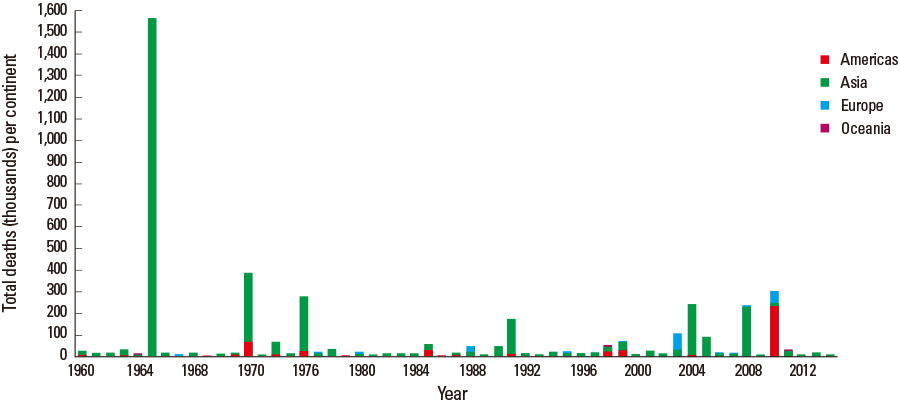
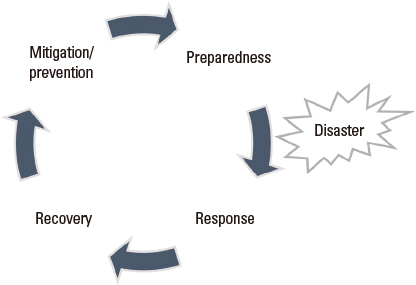
- Disasters are unpredictable and unavoidable. The definition of disaster is a serious disruption of the functioning of society, causing widespread human, material, or environmental losses that exceed the ability of affected society to cope using only its own resources. Disaster medicine is a discipline resulting from combination of emergency medicine and disaster management. The field of disaster medicine involves the study of subject matter from multiple medical disciplines, and disaster medicine presents unique ethical situations not seen in other areas of medicine. Disaster can be classified into two categories, natural disaster and manmade disaster, each type of disaster has its own characteristics. Disaster management has a cycle of 4 activities, preparedness, response, recovery, and prevention/mitigation. Disaster medicine specialists have a role in each part of this cycle. To achieve effective disaster response, the National Disaster Life Support Foundation suggests the DISASTER Paradigm(TM), which consists of detection, incident command, safety and security, assess hazards, support, triage and treatment, evacuation, and recovery.
MeSH Terms
Figure
Cited by 1 articles
-
Disaster Medicine in Korea
Taeho Lim
Hanyang Med Rev. 2015;35(3):121-123. doi: 10.7599/hmr.2015.35.3.121.
Reference
-
1. Wattanawaitunechai C, Peacock SJ, Jitpratoom P. Tsunami in Thailand--disaster management in a district hospital. N Engl J Med. 2005; 352:962–964.
Article2. Disaster preparedness for effective response: guidance and indicator package for implementing priority five of the hyogo framework [Internet]. Geneva: United Nations Office for Coordination of Humanitarian Affairs ,United Nations secretariat of the International Strategy for Disaster Reduction;c2008. cited 2015 May 31. Available from: http://www.unisdr.org/files/2909_Disasterpreparednessforeffectiveresponse.pdf/.3. Dara SI, Ashton RW, Farmer JC, Carlton PK Jr. Worldwide disaster medical response: an historical perspective. Crit Care Med. 2005; 33:S2–S6.
Article4. Centre for research on the epidemiology of disasters. EM-DAT the international disaster database [Internet]. Brussels (BE): Université Catholique de Louvain;c2015. cited 2015 May 31. Available from: http://www.emdat.be/disaster_trends/index.html/.5. Core Disaster Life Support 3.0 Course Manual. Chicago (IL): American Medical Association;2010. p. 27–31.6. Raymond E, Italo S, David S. Basic Disaster Life Support 3.0 Course Manual. 1st ed. Chicago (IL): American Medical Association;2012. p. 6–8.
- Full Text Links
- Actions
-
Cited
- CITED
-
- Close
- Share
- Similar articles
-
- Principles and system of disaster medicine
- Experiences and lessons of the disaster medical assistance in Korea
- Development of a Comprehensive Model of Disaster Management in Korea Based on the Result of Response to Sampung Building Collapse (1995): Disaster Law, and 98 Disaster Preparedness Plan of Seoul City
- A Survey on the Public Perceptions of Disaster-Related Mental Health Service
- Disaster epidemiology in Korea