Hanyang Med Rev.
2011 May;31(2):63-69. 10.7599/hmr.2011.31.2.63.
Trigeminal Neuralgia and Neural Blockade
- Affiliations
-
- 1Department of Anesthesiology and Pain Medicine, Hallym University College of Medicine, Seoul, Korea. kmshin1@yahoo.co.kr
- KMID: 2168181
- DOI: http://doi.org/10.7599/hmr.2011.31.2.63
Abstract
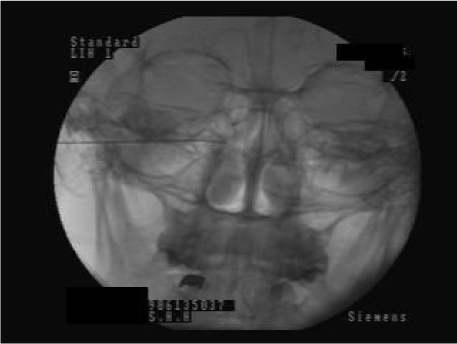
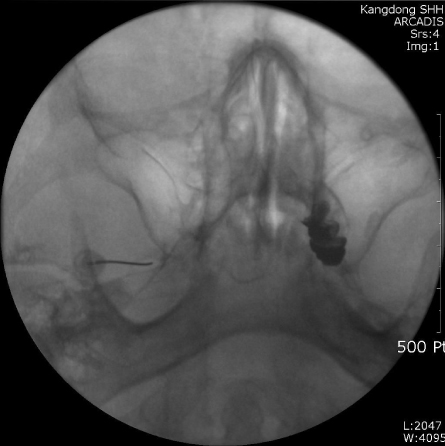
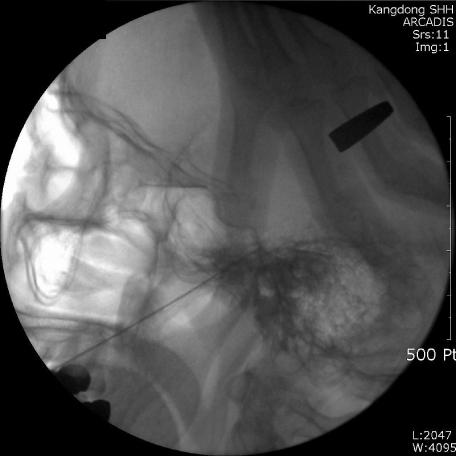
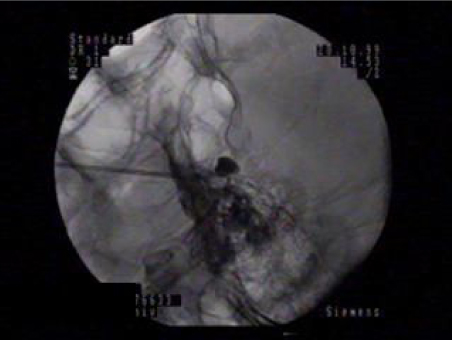
- Trigeminal neuralgia is characterized by recurrent episodes of intense lancinating pain affecting the face localized to the sensory supply areas of the trigeminal nerve. There is a lack of certainty regarding the etiology and pathophysiology of trigeminal neuralgia. The diagnosis of idiopathic typical trigeminal neuralgia requires the absence of clinically evident neurological deficit. Treatment must be individualized to each patient. Various trigeminal neural blockades can be options when medical therapy fails to relieve pain. Neural blockades include peripheral nerve branch blocks and intracranial nerve root or ganglion blocks such as RF thermocoagulation, percutaneous balloon compression and glycerol rhizolysis. Neural blockade with local anesthetics produces temporary effects, but neural blockade with neurolytics like alcohol lasts longer, around one or two years. They are very useful for patients with poor general condition or high risk. RF rhizotomy and balloon compression of trigeminal ganglion are relatively more invasive treatment options, but have more cost effectiveness with less serious complications compared to other surgical procedures. The continuous improvement of neural block techniques is necessary for better treatment of trigeminal neuralgia.
MeSH Terms
Figure
Reference
-
1. Headache Classification Subcommittee of the International Headache Society. The international classification of headache disorders. 2nd ed. Oxford, UK: Blackwell Publishing. Cephalalgia. 2004. 24:Suppl 1. 9–160.2. Rovit RL, Murali R, Jannetta PJ. Trigeminal neuralgia. 1990. 1st ed. Baltimore: Williams & Wilkins;109–136.3. Lutz J, Linn J, Mehrkens JH, Thon N, Stahl R, Seelos K, Bruckmann H, Holtmannspotter M. Trigeminal neuralgia due to neurovascular compression: high-spatial-resolution diffusion-tensor imaging reveals microstructural neural changes. Radiology. 2011. 258:524–530.
Article4. Jannetta PJ. Arterial compression of the trigeminal nerve at the pons in patients with trigeminal neuralgia. J Neurosurg. 1967. 26:159–162.
Article5. Dubner R, Sharav Y, Gracely RH, Price DD. Idiopathic trigeminal neuralgia: sensory features and pain mechanisms. Pain. 1987. 31:23–33.
Article6. Kerr FW. Pathology of trigeminal neuralgia: light and electron microscopic observations. J Neurosurg. 1967. 26:151–156.
Article7. Kerr FW, Miller RH. The pathology of trigeminal neuralgia. Electron microscopic studies. Arch Neurol. 1966. 15:308–319.8. Beaver DL, Moses HL, Ganote CE. Electron microscopy of the trigeminal ganglion, 3, trigenminal neuralgia. Arch Pathol. 1965. 79:571–582.9. Beaver DL, Moses HL, Ganote CE. Electron microscopy of the trigeminal ganglion, 2, autopsy study of human ganglia. Arch Pathol. 1965. 79:557–570.10. Seltzer Z, Devor M. Ephaptic transmission in chronically damaged peripheral nerves. Neurology. 1979. 29:1061–1064.
Article11. Calvin WH, Loeser JD, Howe JF. A neurophysiological theory for the pain mechanism of tic douloureux. Pain. 1977. 3:147–154.
Article12. Fromm GH, Chattha AS, Terrence CF, Glass JD. Role of inhibitory mechanisms in trigeminal neuralgia. Neurology. 1981. 31:683–687.
Article13. Fromm GH, Terrence CF, Maroon JC. Trigeminal neuralgia. Current concepts regarding etiology and pathogenesis. Arch Neurol. 1984. 41:1204–1207.
Article14. Loeser JD. Wall PD, Melzack R, editors. Tic douloureux and atypical face pain. Textbook of pain. 1989. 2nd ed. New York: Churchill Livingstone;535–542.15. Loeser JD. Bonica JJ, editor. Cranial neuralgias. The management of pain. 1990. 2nd ed. Philadelphia: Lea & Febiger;676–682.16. Schmidek HH, Sweet WH. Current techniques in operative neurosurgery. 1977. New York: Grune & Stratton;469–490.17. Sweet WH, Mark VH. Unipolar anodal electrolytic lesions in the brain of man and cat; report of five human cases with electrically produced bulbar or mesencephalic tractotomies. AMA Arch Neurol Psychiatry. 1953. 70:224–234.18. Vervest ACM, Stolker RJ, Groen GJ. Radiofrequency lesioning for pain treatment: a review. Pain Clinic. 1995. 8:175–189.19. Letcher FS, Goldring S. The effect of radiofrequency current and heat on peripheral nerve action potential in the cat. J Neurosurg. 1968. 29:42–47.
Article20. Shin KM, Shin SC, Cho YR, Lim SY, Hong SY, Choi YR. Stereotactic radiofrequency gasserian ganglionotomy. J Korean Pain Soc. 1996. 9:183–186.21. Sweet WH, Poletti CE. Problems with retrogasserian glycerol in the treatment of trigeminal neuralgia. Appl Neurophysiol. 1985. 48:252–257.
Article22. Burchiel KJ. Percutaneous retrogasserian glycerol rhizolysis in the management of trigeminal neuralgia. J Neurosurg. 1988. 69:361–366.
Article23. Young RF. Glycerol rhizolysis for treatment of trigeminal neuralgia. J Neurosurg. 1988. 69:39–45.
Article24. Mullan S, Lichtor T. Percutaneous microcompression of the trigeminal ganglion for trigeminal neuralgia. J Neurosurg. 1983. 59:1007–1012.
Article25. Lobato RD, Rivas JJ, Sarabia R, Lamas E. Percutaneous microcompression of the gasserian ganglion for trigeminal neuralgia. J Neurosurg. 1990. 72:546–553.
Article26. Brown JA, Preul MC. Percutaneous trigeminal ganglion compression for trigeminal neuralgia. Experience in 22 patients and review of the literature. J Neurosurg. 1989. 70:900–904.27. Shin KM, Ahn CS, Choi YR, Jung IS. Effect of percutaneous microcompression in trigeminal neuralgia: case report. Korean J Anesthesiol. 1997. 32:845–849.
Article28. Fraioli B, Esposito V, Guidetti B, Cruccu G, Manfredi M. Treatment of trigeminal neuralgia by thermocoagulation, glycerolization, and percutaneous compression of the gasserian ganglion and/or retrogasserian rootlets: long-term results and therapeutic protocol. Neurosurgery. 1989. 24:239–245.
Article29. Kang HK, Park YO, Shin KM, Kim YM, Kim HJ, Yoon YJ. Nasociliary nerve radiofrequency thermocoagulation for trigeminal neuralgia: a case report. J Korean Pain Soc. 2003. 16:92–96.30. Kline MT. Stereotactic radiofrequency lesions as part of the management of pain. 1992. Orlando: Deutsch press;72–76.31. Shin KM. Stereotactic sphenopalatine ganglionotomy using radiofrequency thermocoagulation: case reports. J Korean Pain Soc. 1999. 12:227–230.32. Beckmann JS. Genetic studies and molecular structures: the dystrophin associated complex. Hum Mol Genet. 1996. 5:865–867.
Article33. Jung SW, Lee JB, Hong SJ, Shin KM. The clinical effectiveness and selectivity of radiofrequency trigeminal rhizotomy using a 2 mm active tip electrode for the treatment of trigeminal neuralgia. Korean J Anesthesiol. 2005. 48:619–623.
Article34. Shin KM. Analysis of ballon volumes used during percutaneous microcompression of the gasserian ganglion for trigeminal neuralgia in Korean patients. Korean J Anesthesiol. 2000. 38:301–306.
Article
- Full Text Links
- Actions
-
Cited
- CITED
-
- Close
- Share
- Similar articles
-
- A Case of Atypical Trigeminal Neuralgia Mistaken as Glossopharyngeal Neuralgia: A case report
- Bilateral Trigeminal Neuralgia
- Differentiation of Neurological Disorders in Orbital Pain: Focusing on Primary Headache and Trigeminal Neuralgia
- Treatment of Trigeminal Neuralgia with Low-frequency Electrical Acupuncture
- Isolated Trigeminal Neuralgia Presented Due to Cerebellopontine Angle Epidermoid Cyst