Immune Netw.
2014 Jun;14(3):149-155. 10.4110/in.2014.14.3.149.
Insulin Resistance and Serum Levels of Interleukin-17 and Interleukin-18 in Normal Pregnancy
- Affiliations
-
- 1Research Center for Cardiovascular Atherosclerosis, Jahrom University of Medical Science, Jahrom, Iran.
- 2Department of Immunology, Jahrom University of Medical Science, Jahrom, Iran.
- 3Research Center for Social Determinants of Health, Jahrom University of Medical Science, Jahrom, Iran.
- 4Department of Student Research Committee, Jahrom University of Medical Science, Jahrom, Iran. amin_m505@yahoo.com
- KMID: 2168026
- DOI: http://doi.org/10.4110/in.2014.14.3.149
Abstract
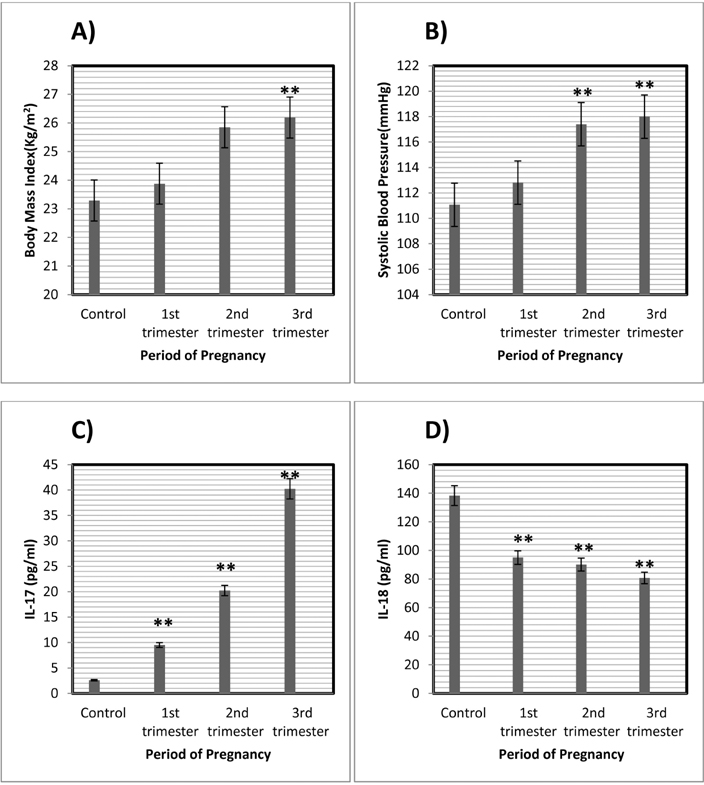
- We performed this study to evaluate the role of Interleukin-17 (IL-17) and Interleukin-18 (IL-18) in insulin resistance during normal pregnancy. This descriptive cross sectional study was carried out on 97 healthy pregnant women including 32, 25, and 40 individuals in the first, second, and third trimesters, respectively, and on 28 healthy non pregnant women between the autumn of 2012 and the spring of 2013. We analyzed the serum concentrations of IL-17 and IL-18 by using the enzyme linked immunosorbent assay (ELISA). Insulin resistance was measured by homeostasis model assessment of insulin resistance equation. No significant differences between the demographic data of the pregnant and non pregnant groups were observed. Insulin resistant in pregnant women was significantly higher than the controls (p=0.006). Serum IL-17 concentration was significantly different in non pregnant women and pregnant women in all gestational ages (p<0.05). Serum IL-18 level was significantly lower in subjects with first, second, and third trimesters of pregnancy in compared to non pregnant women (p<0.05). No significant correlations were found between serum IL-17 and IL-18 levels with insulin resistance (r=0.08, p=0.34 vs. r=0.01, p=0.91, respectively). Our data suggested that IL-17 and IL-18 do not appear to attribute greatly to pregnancy deduced insulin resistance during normal pregnancy.
Keyword
MeSH Terms
Figure
Reference
-
1. Hadden DR, McLaughlin C. Normal and abnormal maternal metabolism during pregnancy. Semin Fetal Neonatal Med. 2009; 14:66–71.
Article2. Baranyi E, Winkler G. Diabetes and pregnancy. Orv Hetil. 2011; 152:1635–1640.
Article3. Kirwan JP, Hauguel-De Mouzon S, Lepercq J, Challier JC, Huston-Presley L, Friedman JE, Kalhan SC, Catalano PM. TNF-alpha is a predictor of insulin resistance in human pregnancy. Diabetes. 2002; 51:2207–2213.4. Gwozdziewiczova S, Lichnovska R, Hrebicek J. Tumor necrosis factor alfa (TNFalpha) and insulin resistance. Cesk Fysiol. 2004; 53:167–175.5. Senn JJ, Klover PJ, Nowak IA, Mooney RA. Interleukin-6 induces cellular insulin resistance in hepatocytes. Diabetes. 2002; 51(12):3391–3399.
Article6. Zinman B, Hanley AJ, Harris SB, Kwan J, Fantus IG. Circulating tumor necrosis factor-alpha concentrations in a native Canadian population with high rates of type 2 diabetes mellitus. J Clin Endocrinol Metab. 1999; 84:272–278.
Article7. Ahmed M, Gaffen SL. IL-17 in obesity and adipogenesis. Cytokine Growth Factor Rev. 2010; 21:449–453.
Article8. Roland L, Gagne A, Belanger MC, Boutet M, Julien P, Bilodeau JF. Plasma interleukin-18 (IL-18) levels are correlated with antioxidant vitamin coenzyme Q(10) in preeclampsia. Acta Obstet Gynecol Scand. 2010; 89:360–366.
Article9. Shearman AM, Cupples LA, Demissie S, Peter I, Schmid CH, Karas RH, Mendelsohn ME, Housman DE, Levy D. Association between estrogen receptor alpha gene variation and cardiovascular disease. JAMA. 2003; 290:2263–2270.
Article10. Matthews DR, Hosker JP, Rudenski AS, Naylor BA, Treacher DF, Turner RC. Homeostasis model assessment: insulin resistance and beta-cell function from fasting plasma glucose and insulin concentrations in man. Diabetologia. 1985; 28:412–419.
Article11. Jahromi AS, Zareian P, Madani A. Association of insulin resistance with serum interleukin-6 and TNF-alpha levels during normal pregnancy. Biomark Insights. 2011; 6:1–6.12. Jahromi AS, Zareian P, Madani A. Insulin resistance and interleukin-1β during normal pregnancy. Asian J Biochem. 2011; 6:366–372.
Article13. Clapp JF. Effects of Diet and Exercise on Insulin Resistance during Pregnancy. Metab Syndr Relat Disord. 2006; 4:84–90.
Article14. Manley SE, Luzio SD, Stratton IM, Wallace TM, Clark PM. Preanalytical, analytical, and computational factors affect homeostasis model assessment estimates. Diabetes Care. 2008; 31:1877–1883.
Article15. Harrington LE, Hatton RD, Mangan PR, Turner H, Murphy TL, Murphy KM, Weaver CT. Interleukin 17-producing CD4+ effector T cells develop via a lineage distinct from the T helper type 1 and 2 lineages. Nat Immunol. 2005; 6:1123–1132.
Article16. Park H, Li Z, Yang XO, Chang SH, Nurieva R, Wang YH, Wang Y, Hood L, Zhu Z, Tian Q, Dong C. A distinct lineage of CD4 T cells regulates tissue inflammation by producing interleukin 17. Nat Immunol. 2005; 6:1133–1141.
Article17. Xu S, Cao X. Interleukin-17 and its expanding biological functions. Cell Mol Immunol. 2010; 7:164–174.
Article18. Louten J, Boniface K, de Waal Malefyt R. Development and function of TH17 cells in health and disease. J Allergy Clin Immunol. 2009; 123:1004–1011.
Article19. Peck A, Mellins ED. Breaking old paradigms: Th17 cells in autoimmune arthritis. Clin Immunol. 2009; 132:295–304.
Article20. Sallusto F, Lanzavecchia A. Human Th17 cells in infection and autoimmunity. Microbes Infect. 2009; 11:620–624.
Article21. Marzi M, Vigano A, Trabattoni D, Villa ML, Salvaggio A, Clerici E, Clerici M. Characterization of type 1 and type 2 cytokine production profile in physiologic and pathologic human pregnancy. Clin Exp Immunol. 1996; 106:127–133.
Article22. Saito S, Nakashima A, Shima T, Ito M. Th1/Th2/Th17 and regulatory T-cell paradigm in pregnancy. Am J Reprod Immunol. 2010; 63:601–610.
Article23. Saito S, Nakashima A, Ito M, Shima T. Clinical implication of recent advances in our understanding of IL-17 and reproductive immunology. Expert Rev Clin Immunol. 2011; 7:649–657.
Article24. Okamura H, Kashiwamura S, Tsutsui H, Yoshimoto T, Nakanishi K. Regulation of interferon-gamma production by IL-12 and IL-18. Curr Opin Immunol. 1998; 10:259–264.25. Nakanishi K, Yoshimoto T, Tsutsui H, Okamura H. Interleukin-18 is a unique cytokine that stimulates both Th1 and Th2 responses depending on its cytokine milieu. Cytokine Growth Factor Rev. 2001; 12:53–72.
Article26. Ekelund CK, Vogel I, Skogstrand K, Thorsen P, Hougaard DM, Langhoff-Roos J, Jacobsson B. Interleukin-18 and interleukin-12 in maternal serum and spontaneous preterm delivery. J Reprod Immunol. 2008; 77:179–185.
Article27. Sakai M, Shiozaki A, Sasaki Y, Yoneda S, Saito S. The ratio of interleukin (IL)-18 to IL-12 secreted by peripheral blood mononuclear cells is increased in normal pregnant subjects and decreased in pre-eclamptic patients. J Reprod Immunol. 2004; 61:133–143.
Article28. Jagannathan-Bogdan M, McDonnell ME, Shin H, Rehman Q, Hasturk H, Apovian CM, Nikolajczyk BS. Elevated proinflammatory cytokine production by a skewed T cell compartment requires monocytes and promotes inflammation in type 2 diabetes. J Immunol. 2011; 186:1162–1172.
Article29. Esposito K, Pontillo A, Ciotola M, Di Palo C, Grella E, Nicoletti G, Giugliano D. Weight loss reduces interleukin-18 levels in obese women. J Clin Endocrinol Metab. 2002; 87:3864–3866.
Article30. Gaffen SL. Structure and signalling in the IL-17 receptor family. Nat Rev Immunol. 2009; 9:556–567.
Article31. Escobar-Morreale HF, Botella-Carretero JI, Villuendas G, Sancho J, San Millan JL. Serum interleukin-18 concentrations are increased in the polycystic ovary syndrome: relationship to insulin resistance and to obesity. J Clin Endocrinol Metab. 2004; 89:806–811.
Article
- Full Text Links
- Actions
-
Cited
- CITED
-
- Close
- Share
- Similar articles
-
- Role of Interleukin-6 in Human Obesity and Insulin Resistance
- Combined effect of hyperglycemia and interleukin-1 beta on the insulin secretion of isolated rat islets
- A Study of correlation of fetal and maternal serum interleukin-1beta and interleukin-6 with histologic placental inflammation
- Change of cytokine expression in normal pregnancy and the puerperium
- Serum Interleukin-10 Levels in Rheumatoid Arthritis Patients