Immune Netw.
2012 Jun;12(3):104-112. 10.4110/in.2012.12.3.104.
Induction of Functional Changes of Dendritic Cells by Silica Nanoparticles
- Affiliations
-
- 1Department of Biological Science and the Research Center for Women's Disease, Sookmyung Women's University, Seoul 140-742, Korea. jslim@sookmyung.ac.kr
- KMID: 2168008
- DOI: http://doi.org/10.4110/in.2012.12.3.104
Abstract
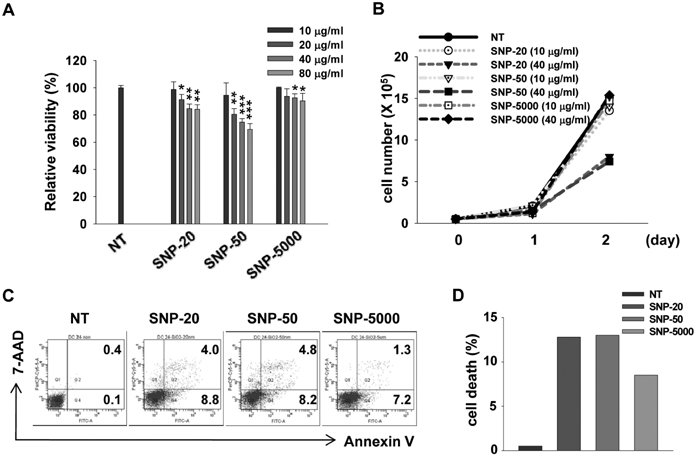
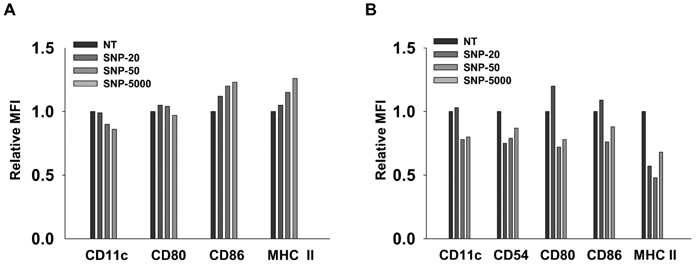
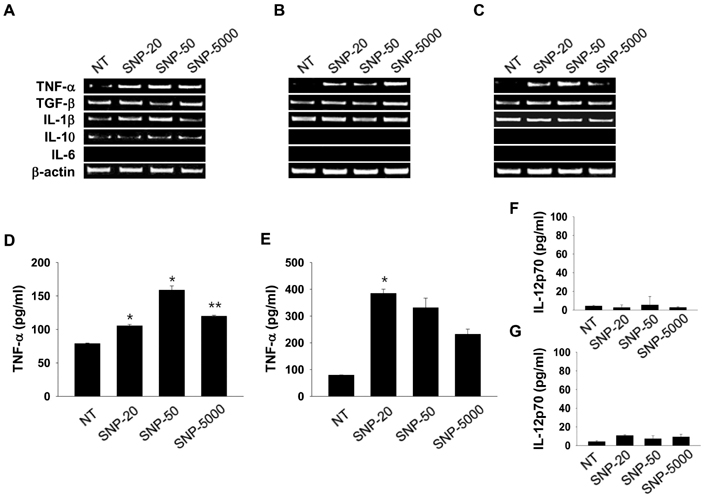
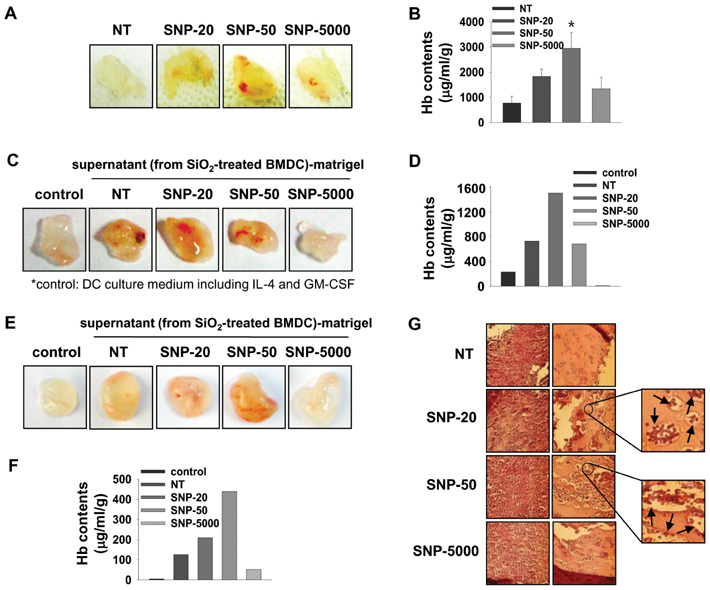
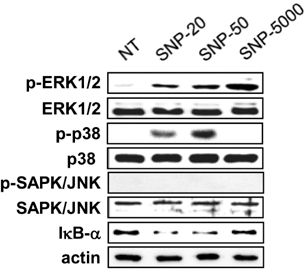
- Silica is one of the most abundant compounds found in nature. Immoderate exposure to crystalline silica has been linked to pulmonary disease and crystalline silica has been classified as a Group I carcinogen. Ultrafine (diameter <100 nm) silica particles may have different toxicological properties compared to larger particles. We evaluated the effect of ultrafine silica nanoparticles on mouse bone marrow-derived dendritic cells (BMDC) and murine dendritic cell line, DC2.4. The exposure of dendritic cells (DCs) to ultrafine silica nanoparticles showed a decrease in cell viability and an induction of cell death in size- and concentration-dependent manners. In addition, in order to examine the phenotypic changes of DCs following co-culture with silica nanoparticles, we added each sized-silica nanoparticle along with GM-CSF and IL-4 during and after DC differentiation. Expression of CD11c, a typical DC marker, and multiple surface molecules such as CD54, CD80, CD86, MHC class II, was changed by silica nanoparticles in a size-dependent manner. We also found that silica nanoparticles affect inflammatory response in DCs in vitro and in vivo. Finally, we found that p38 and NF-kappaB activation may be critical for the inflammatory response by silica nanoparticles. Our data demonstrate that ultrafine silica nanoparticles have cytotoxic effects on dendritic cells and immune modulation effects in vitro and in vivo.
MeSH Terms
-
Animals
Apoptosis
Cell Death
Cell Survival
Coculture Techniques
Crystallins
Dendritic Cells
Granulocyte-Macrophage Colony-Stimulating Factor
Interleukin-4
Lung Diseases
Mice
Nanoparticles
NF-kappa B
Silicon Dioxide
Silicones
Crystallins
Granulocyte-Macrophage Colony-Stimulating Factor
Interleukin-4
NF-kappa B
Silicon Dioxide
Silicones
Figure
Reference
-
1. Chen M, von Mikecz A. Formation of nucleoplasmic protein aggregates impairs nuclear function in response to SiO2 nanoparticles. Exp Cell Res. 2005. 305:51–62.
Article2. Pan Z, Lee W, Slutsky L, Clark RA, Pernodet N, Rafailovich MH. Adverse effects of titanium dioxide nanoparticles on human dermal fibroblasts and how to protect cells. Small. 2009. 5:511–520.
Article3. Foley S, Crowley C, Smaihi M, Bonfils C, Erlanger BF, Seta P, Larroque C. Cellular localisation of a water-soluble fullerene derivative. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 2002. 294:116–119.
Article4. Oberdörster E. Manufactured nanomaterials (fullerenes, C60) induce oxidative stress in the brain of juvenile largemouth bass. Environ Health Perspect. 2004. 112:1058–1062.
Article5. Vallhov H, Gabrielsson S, Strømme M, Scheynius A, Garcia-Bennett AE. Mesoporous silica particles induce size dependent effects on human dendritic cells. Nano Lett. 2007. 7:3576–3582.
Article6. Cho WS, Choi M, Han BS, Cho M, Oh J, Park K, Kim SJ, Kim SH, Jeong J. Inflammatory mediators induced by intratracheal instillation of ultrafine amorphous silica particles. Toxicol Lett. 2007. 175:24–33.
Article7. Huang DM, Chung TH, Hung Y, Lu F, Wu SH, Mou CY, Yao M, Chen YC. Internalization of mesoporous silica nanoparticles induces transient but not sufficient osteogenic signals in human mesenchymal stem cells. Toxicol Appl Pharmacol. 2008. 231:208–215.
Article8. Wang JJ, Sanderson BJ, Wang H. Cytotoxicity and genotoxicity of ultrafine crystalline SiO2 particulate in cultured human lymphoblastoid cells. Environ Mol Mutagen. 2007. 48:151–157.
Article9. Park EJ, Park K. Oxidative stress and pro-inflammatory responses induced by silica nanoparticles in vivo and in vitro. Toxicol Lett. 2009. 184:18–25.
Article10. Fubini B, Hubbard A. Reactive oxygen species (ROS) and reactive nitrogen species (RNS) generation by silica in inflammation and fibrosis. Free Radic Biol Med. 2003. 34:1507–1516.
Article11. Warheit DB, McHugh TA, Hartsky MA. Differential pulmonary responses in rats inhaling crystalline, colloidal or amorphous silica dusts. Scand J Work Environ Health. 1995. 21:Suppl 2. 19–21.12. Leigh J, Wang H, Bonin A, Peters M, Ruan X. Silica-induced apoptosis in alveolar and granulomatous cells in vivo. Environ Health Perspect. 1997. 105:Suppl 5. 1241–1245.13. Banchereau J, Steinman RM. Dendritic cells and the control of immunity. Nature. 1998. 392:245–252.
Article14. Banchereau J, Briere F, Caux C, Davoust J, Lebecque S, Liu YJ, Pulendran B, Palucka K. Immunobiology of dendritic cells. Annu Rev Immunol. 2000. 18:767–811.
Article15. Blanco P, Palucka AK, Pascual V, Banchereau J. Dendritic cells and cytokines in human inflammatory and autoimmune diseases. Cytokine Growth Factor Rev. 2008. 19:41–52.
Article16. Kang K, Kim H, Kim KI, Yang Y, Yoon DY, Kim JH, Ryu JH, Noh EJ, Jeon SD, Lim JS. SK-126, a synthetic compound, regulates the production of inflammatory cytokines induced by LPS in antigen-presenting cells. Biochem Pharmacol. 2008. 75:1054–1064.
Article17. Heath WR, Belz GT, Behrens GM, Smith CM, Forehan SP, Parish IA, Davey GM, Wilson NS, Carbone FR, Villadangos JA. Cross-presentation, dendritic cell subsets, and the generation of immunity to cellular antigens. Immunol Rev. 2004. 199:9–26.
Article18. Reis e Sousa C. Dendritic cells in a mature age. Nat Rev Immunol. 2006. 6:476–483.
Article19. Shen Z, Reznikoff G, Dranoff G, Rock KL. Cloned dendritic cells can present exogenous antigens on both MHC class I and class II molecules. J Immunol. 1997. 158:2723–2730.20. Inaba K, Inaba M, Romani N, Aya H, Deguchi M, Ikehara S, Muramatsu S, Steinman RM. Generation of large numbers of dendritic cells from mouse bone marrow cultures supplemented with granulocyte/macrophage colony-stimulating factor. J Exp Med. 1992. 176:1693–1702.
Article21. Wörle-Knirsch JM, Pulskamp K, Krug HF. Oops they did it again! Carbon nanotubes hoax scientists in viability assays. Nano Lett. 2006. 6:1261–1268.
Article22. Laaksonen T, Santos H, Vihola H, Salonen J, Riikonen J, Heikkilä T, Peltonen L, Kumar N, Murzin DY, Lehto VP, Hirvonen J. Failure of MTT as a toxicity testing agent for mesoporous silicon microparticles. Chem Res Toxicol. 2007. 20:1913–1918.
Article23. Kowalczyk DW, Wlazlo AP, Blaszczyk-Thurin M, Xiang ZQ, Giles-Davis W, Ertl HC. A method that allows easy characterization of tumor-infiltrating lymphocytes. J Immunol Methods. 2001. 253:163–175.
Article24. Curiel TJ, Cheng P, Mottram P, Alvarez X, Moons L, Evdemon-Hogan M, Wei S, Zou L, Kryczek I, Hoyle G, Lackner A, Carmeliet P, Zou W. Dendritic cell subsets differentially regulate angiogenesis in human ovarian cancer. Cancer Res. 2004. 64:5535–5538.
Article25. Saudemont A, Jouy N, Hetuin D, Quesnel B. NK cells that are activated by CXCL10 can kill dormant tumor cells that resist CTL-mediated lysis and can express B7-H1 that stimulates T cells. Blood. 2005. 105:2428–2435.
Article26. Kang K, Lim DH, Choi IH, Kang T, Lee K, Moon EY, Yang Y, Lee MS, Lim JS. Vascular tube formation and angiogenesis induced by polyvinylpyrrolidone-coated silver nanoparticles. Toxicol Lett. 2011. 205:227–234.
Article27. Hansen SF, Michelson ES, Kamper A, Borling P, Stuer-Lauridsen F, Baun A. Categorization framework to aid exposure assessment of nanomaterials in consumer products. Ecotoxicology. 2008. 17:438–447.
Article28. Passagne I, Morille M, Rousset M, Pujalté I, L'azou B. Implication of oxidative stress in size-dependent toxicity of silica nanoparticles in kidney cells. Toxicology. 2012. 299:112–124.
Article29. Napierska D, Thomassen LC, Rabolli V, Lison D, Gonzalez L, Kirsch-Volders M, Martens JA, Hoet PH. Size-dependent cytotoxicity of monodisperse silica nanoparticles in human endothelial cells. Small. 2009. 5:846–853.
Article30. Waters KM, Masiello LM, Zangar RC, Tarasevich BJ, Karin NJ, Quesenberry RD, Bandyopadhyay S, Teeguarden JG, Pounds JG, Thrall BD. Macrophage responses to silica nanoparticles are highly conserved across particle sizes. Toxicol Sci. 2009. 107:553–569.
Article31. Lin W, Huang YW, Zhou XD, Ma Y. In vitro toxicity of silica nanoparticles in human lung cancer cells. Toxicol Appl Pharmacol. 2006. 217:252–259.
Article32. Cha KE, Myung H. Cytotoxic effects of nanoparticles assessed in vitro and in vivo. J Microbiol Biotechnol. 2007. 17:1573–1578.33. Choi SJ, Oh JM, Choy JH. Toxicological effects of inorganic nanoparticles on human lung cancer A549 cells. J Inorg Biochem. 2009. 103:463–471.
Article34. Carlson C, Hussain SM, Schrand AM, Braydich-Stolle LK, Hess KL, Jones RL, Schlager JJ. Unique cellular interaction of silver nanoparticles: size-dependent generation of reactive oxygen species. J Phys Chem B. 2008. 112:13608–13619.
Article35. Park EJ, Yi J, Chung KH, Ryu DY, Choi J, Park K. Oxidative stress and apoptosis induced by titanium dioxide nanoparticles in cultured BEAS-2B cells. Toxicol Lett. 2008. 180:222–229.
Article36. Herzog E, Byrne HJ, Casey A, Davoren M, Lenz AG, Maier KL, Duschl A, Oostingh GJ. SWCNT suppress inflammatory mediator responses in human lung epithelium in vitro. Toxicol Appl Pharmacol. 2009. 234:378–390.
Article
- Full Text Links
- Actions
-
Cited
- CITED
-
- Close
- Share
- Similar articles
-
- Immunostimulatory Effects of Silica Nanoparticles in Human Monocytes
- The Effects of Silica Nanoparticles in Macrophage Cells
- Induction of Potent Antigen-specific Cytotoxic T Cell Response by PLGA-nanoparticles Containing Antigen and TLR Agonist
- Silica-Capped and Gold-Decorated Silica Nanoparticles for Enhancing Effect of Gold Nanoparticle-Based Photothermal Therapy
- Silica-Based Advanced Nanoparticles For Treating Ischemic Disease