Imaging Sci Dent.
2012 Sep;42(3):197-200. 10.5624/isd.2012.42.3.197.
Unique case of a geminated supernumerary tooth with trifid crown
- Affiliations
-
- 1Department of Conservative Dentistry and Endodontics, Manipal College of Dental Sciences, Manipal, India. amberather03@yahoo.co.in
- 2Department of Pedodontics and Preventive Dentistry, Manipal College of Dental Sciences, Manipal, India.
- KMID: 2167439
- DOI: http://doi.org/10.5624/isd.2012.42.3.197
Abstract
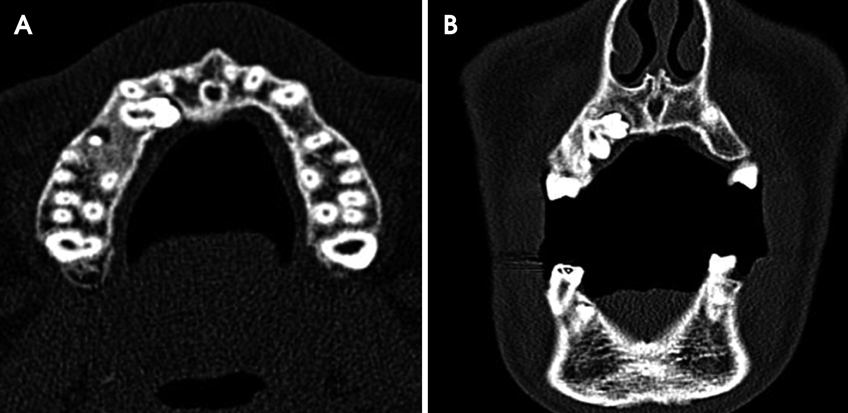
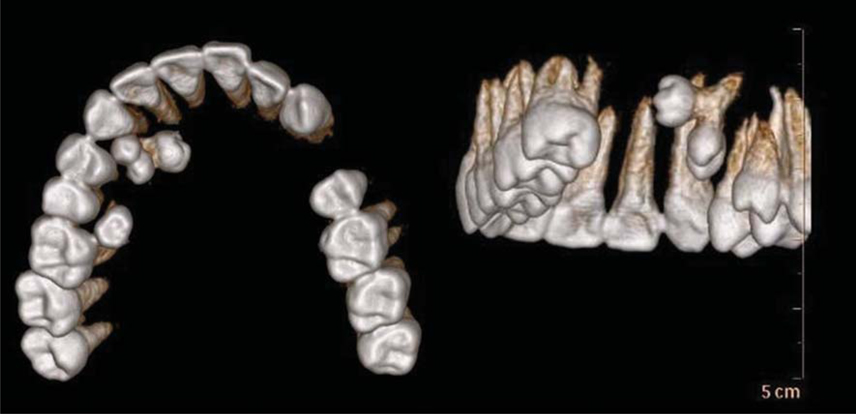
- Gemination, a relatively uncommon dental anomaly, is characterized by its peculiar representation as a tooth with a bifid crown and a common root and root canal. It usually occurs in primary dentition. To come across gemination in a supernumerary tooth is a rare phenomenon. The purpose of this paper is to present a unique case of hyperdontia wherein gemination in an impacted supernumerary tooth resulted in a trifid crown unlike the usual bifid crown. The role of conventional radiographs as well as computed tomography, to accurately determine the morphology and spatial location, and to arrive at a diagnosis, is also emphasized in this paper.
MeSH Terms
Figure
Reference
-
1. Chen RJ, Wang CC. Gemination of a maxillary premolar. Oral Surg Oral Med Oral Pathol. 1990. 69:656.
Article2. Grover PS, Lorton L. Gemination and twinning in the permanent dentition. Oral Surg Oral Med Oral Pathol. 1985. 59:313–318.
Article3. Duncan WK, Helpin ML. Bilateral fusion and gemination: a literature analysis and case report. Oral Surg Oral Med Oral Pathol. 1987. 64:82–87.
Article4. Crawford NL, North S, Davidson LE. Double permanent incisor teeth: management of three cases. Dent Update. 2006. 33:608–610.
Article5. Yague-Garcia J, Berini-Aytes L, Gay-Escoda C. Multiple supernumerary teeth not associated with complex syndromes: a retrospective study. Med Oral Patol Oral Cir Bucal. 2009. 14:E331–E336.6. Primosch RE. Anterior supernumerary teeth-assessment and surgical intervention in children. Pediatr Dent. 1981. 3:204–215.7. Nazif MM, Ruffalo RC, Zullo T. Impacted supernumerary teeth: a survey of 50 cases. J Am Dent Assoc. 1983. 106:201–204.
Article8. King NM, Lee AM, Wan PK. Multiple supernumerary premolars: their occurrence in three patients. Aust Dent J. 1993. 38:11–16.
Article9. Liu DG, Zhang WL, Zhang ZY, Wu YT, Ma XC. Three-dimensional evaluations of supernumerary teeth using cone-beam computed tomography for 487 cases. Oral Surg Oral Med Oral Pathol Oral Radiol Endod. 2007. 103:403–411.
Article10. Yang G. Supernumerary teeth and gemination. Br J Oral Maxillofac Surg. 2012. 50:e15.
Article11. Davis PJ. Hypodontia and hyperdontia of permanent teeth in Hong Kong schoolchildren. Community Dent Oral Epidemiol. 1987. 15:218–220.
Article12. Acikgoz A, Acikgoz G, Tunga U, Otan F. Characteristics and prevalence of non-syndrome multiple supernumerary teeth: a retrospective study. Dentomaxillofac Radiol. 2006. 35:185–190.13. Kim KD, Ruprecht A, Jeon KJ, Park CS. Personal computer-based three-dimensional computed tomographic images of the teeth for evaluating supernumerary or ectopically impacted teeth. Angle Orthod. 2003. 73:614–621.14. Yang Y, Xia X, Wang W, Qin M. Uncommon fusion of teeth and lateral periodontal cyst in a Chinese girl: a case report. Oral Surg Oral Med Oral Pathol Oral Radiol Endod. 2011. 112:e18–e20.
Article15. Anthonappa RP, Omer RS, King NM. Characteristics of 283 supernumerary teeth in southern Chinese children. Oral Surg Oral Med Oral Pathol Oral Radiol Endod. 2008. 105:e48–e54.
Article