Imaging Sci Dent.
2012 Sep;42(3):121-127. 10.5624/isd.2012.42.3.121.
Correlation of panoramic radiographs and cone beam computed tomography in the assessment of a superimposed relationship between the mandibular canal and impacted third molars
- Affiliations
-
- 1Department of Oral and Maxillofacial Radiology, College of Dentistry, Pusan National University, Yangsan, Korea. bhjo@pusan.ac.kr
- KMID: 2167428
- DOI: http://doi.org/10.5624/isd.2012.42.3.121
Abstract
- PURPOSE
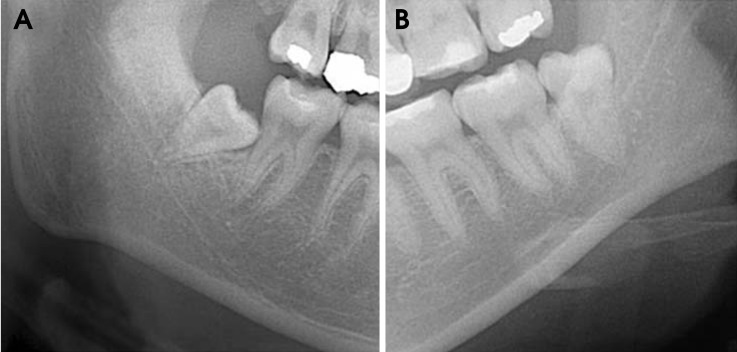
This study evaluated the association between cone beam computed tomography (CBCT) and panoramic radiographs in the assessment of a superimposed relationship between the mandibular canal and impacted third molars.
MATERIALS AND METHODS
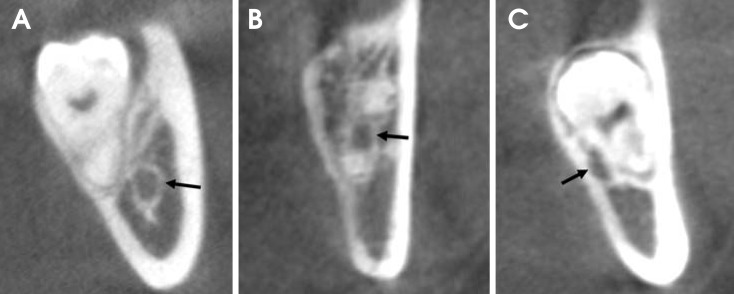
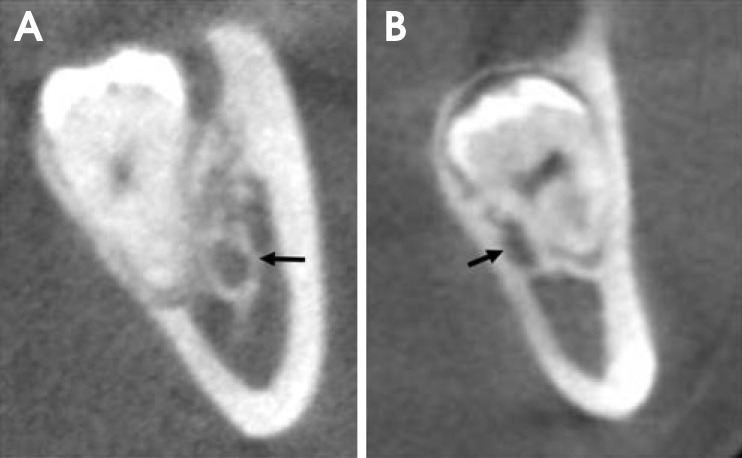
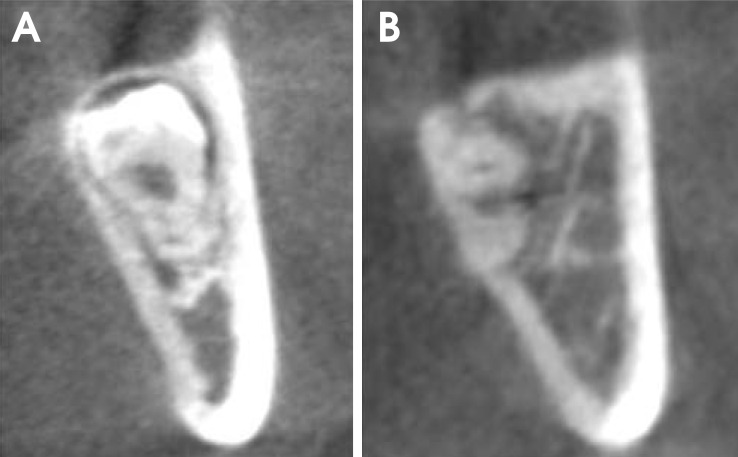
The study samples consisted of 175 impacted third molars from 131 patients who showed a superimposed relationship between the mandibular canal and third molars on panoramic radiographs and were referred for the examination of the mandibular canal with CBCT. Panoramic images were evaluated for the darkening of the root and the interruption of the mandibular canal wall. CBCT images were used to assess the buccolingual position of the mandibular canal relative to the third molar, the proximity of the roots to the canal, and lingual cortical bone loss. The association of the panoramic and CBCT findings was examined using a Chi-square test and Fisher's exact test.
RESULTS
Panoramic radiographic signs were statistically associated with CBCT findings (P<0.01). In cases of darkening roots, lingual cortical bone loss or buccally positioned canals were more frequent. In cases in which the mandibular canal wall was interrupted on panoramic radiographs, contact or lingually positioned canals were more frequent.
CONCLUSION
The results of this study suggest that contact between the mandibular third molar and canal and a lingually positioned canal could be more frequently observed in cases of the interruption of the white line of the mandibular canal and that there could be more lingual cortical loss in cases of darkening roots.
Figure
Cited by 2 articles
-
Comparison of panoramic radiography with cone beam CT in predicting the relationship of the mandibular third molar roots to the alveolar canal
Shoaleh Shahidi, Barbod Zamiri, Pegah Bronoosh
Imaging Sci Dent. 2013;43(2):105-109. doi: 10.5624/isd.2013.43.2.105.Diversion of the mandibular canal: Is it the best predictor of inferior alveolar nerve damage during mandibular third molar surgery on panoramic radiographs?
Melek Tassoker
Imaging Sci Dent. 2019;49(3):213-218. doi: 10.5624/isd.2019.49.3.213.
Reference
-
1. Libersa P, Savignat M, Tonnel A. Neurosensory disturbances of the inferior alveolar nerve: a retrospective study of complaints in a 10-year period. J Oral Maxillofac Surg. 2007; 65:1486–1489. PMID: 17656272.
Article2. Flygare L, Ohman A. Preoperative imaging procedures for lower wisdom teeth removal. Clin Oral Investig. 2008; 12:291–302.
Article3. Jerjes W, Upile T, Shah P, Nhembe F, Gudka D, Kafas P, et al. Risk factors associated with injury to the inferior alveolar and lingual nerves following third molar surgery-revisited. Oral Surg Oral Med Oral Pathol Oral Radiol Endod. 2010; 109:335–345. PMID: 20097103.
Article4. Blaeser BF, August MA, Donoff RB, Kaban LB, Dodson TB. Panoramic radiographic risk factors for inferior alveolar nerve injury after third molar extraction. J Oral Maxillofac Surg. 2003; 61:417–421. PMID: 12684956.
Article5. Park W, Choi JW, Kim JY, Kim BC, Kim HJ, Lee SH. Cortical integrity of the inferior alveolar canal as a predictor of paresthesia after third-molar extraction. J Am Dent Assoc. 2010; 141:271–278. PMID: 20194382.
Article6. Suomalainen A, Ventä I, Mattila M, Turtola L, Vehmas T, Peltola JS. Reliability of CBCT and other radiographic methods in preoperative evaluation of lower third molars. Oral Surg Oral Med Oral Pathol Oral Radiol Endod. 2010; 109:276–284. PMID: 20123411.
Article7. Atieh MA. Diagnostic accuracy of panoramic radiography in determining relationship between inferior alveolar nerve and mandibular third molar. J Oral Maxillofac Surg. 2010; 68:74–82. PMID: 20006158.
Article8. Rood JP, Shehab BA. The radiological prediction of inferior alveolar nerve injury during third molar surgery. Br J Oral Maxillofac Surg. 1990; 28:20–25. PMID: 2322523.
Article9. Bundy MJ, Cavola CF, Dodson TB. Panoramic radiographic findings as predictors of mandibular nerve exposure following third molar extraction: digital versus conventional radiographic techniques. Oral Surg Oral Med Oral Pathol Oral Radiol Endod. 2009; 107:e36–e40. PMID: 19217011.
Article10. Gomes AC, Vasconcelos BC, Silva ED, Caldas Ade F Jr, Pita Neto IC. Sensitivity and specificity of pantomography to predict inferior alveolar nerve damage during extraction of impacted lower third molars. J Oral Maxillofac Surg. 2008; 66:256–259. PMID: 18201605.
Article11. Szalma J, Lempel E, Jeges S, Szabó G, Olasz L. The prognostic value of panoramic radiography of inferior alveolar nerve damage after mandibular third molar removal: retrospective study of 400 cases. Oral Surg Oral Med Oral Pathol Oral Radiol Endod. 2010; 109:294–302. PMID: 19846324.
Article12. Tantanapornkul W, Okochi K, Bhakdinaronk A, Ohbayashi N, Kurabayashi T. Correlation of darkening of impacted mandibular third molar root on digital panoramic images with cone beam computed tomography findings. Dentomaxillofac Radiol. 2009; 38:11–16. PMID: 19114418.
Article13. Palma-Carrió C, García-Mira B, Larrazabal-Morón C, Peñarrocha-Diago M. Radiographic signs associated with inferior alveolar nerve damage following lower third molar extraction. Med Oral Patol Oral Cir Bucal. 2010; 15:e886–e890. PMID: 20526245.14. Maegawa H, Sano K, Kitagawa Y, Ogasawara T, Miyauchi K, Sekine J, et al. Preoperative assessment of the relationship between the mandibular third molar and the mandibular canal by axial computed tomography with coronal and sagittal reconstruction. Oral Surg Oral Med Oral Pathol Oral Radiol Endod. 2003; 96:639–646. PMID: 14600702.
Article15. Nakamori K, Fujiwara K, Miyazaki A, Tomihara K, Tsuji M, Nakai M, et al. Clinical assessment of the relationship between the third molar and the inferior alveolar canal using panoramic images and computed tomography. J Oral Maxillofac Surg. 2008; 66:2308–2313. PMID: 18940497.
Article16. Eyrich G, Seifert B, Matthews F, Matthiessen U, Heusser CK, Kruse AL, et al. 3-Dimensional imaging for lower third molars: is there an implication for surgical removal? J Oral Maxillofac Surg. 2011; 69:1867–1872. PMID: 21419547.
Article17. Jhamb A, Dolas RS, Pandilwar PK, Mohanty S. Comparative efficacy of spiral computed tomography and orthopantomography in preoperative detection of relation of inferior alveolar neurovascular bundle to the impacted mandibular third molar. J Oral Maxillofac Surg. 2009; 67:58–66. PMID: 19070749.
Article18. Ghaeminia H, Meijer GJ, Soehardi A, Borstlap WA, Mulder J, Vlijmen OJ, et al. The use of cone beam CT for the removal of wisdom teeth changes the surgical approach compared with panoramic radiography: a pilot study. Int J Oral Maxillofac Surg. 2011; 40:834–839. PMID: 21507612.
Article19. Tantanapornkul W, Okouchi K, Fujiwara Y, Yamashiro M, Maruoka Y, Ohbayashi N, et al. A comparative study of conebeam computed tomography and conventional panoramic radiography in assessing the topographic relationship between the mandibular canal and impacted third molars. Oral Surg Oral Med Oral Pathol Oral Radiol Endod. 2007; 103:253–259. PMID: 17234544.
Article20. Nakagawa Y, Ishii H, Nomura Y, Watanabe NY, Hoshiba D, Kobayashi K, et al. Third molar position: reliability of panoramic radiography. J Oral Maxillofac Surg. 2007; 65:1303–1308. PMID: 17577493.
Article21. Valmaseda-Castellón E, Berini-Aytés L, Gay-Escoda C. Inferior alveolar nerve damage after lower third molar surgical extraction: a prospective study of 1117 surgical extractions. Oral Surg Oral Med Oral Pathol Oral Radiol Endod. 2001; 92:377–383. PMID: 11598570.
Article22. Bell GW. Use of dental panoramic tomographs to predict the relation between mandibular third molar teeth and the inferior alveolar nerve. Radiological and surgical findings, and clinical outcome. Br J Oral Maxillofac Surg. 2004; 42:21–27. PMID: 14706294.23. Monaco G, Montevecchi M, Bonetti GA, Gatto MR, Checchi L. Reliability of panoramic radiography in evaluating the topographic relationship between the mandibular canal and impacted third molars. J Am Dent Assoc. 2004; 135:312–318. PMID: 15058618.
Article24. Sedaghatfar M, August MA, Dodson TB. Panoramic radiographic findings as predictors of inferior alveolar nerve exposure following third molar extraction. J Oral Maxillofac Surg. 2005; 63:3–7. PMID: 15635549.
Article25. de Melo Albert DG, Gomes AC, do Egito Vasconcelos BC, de Oliveira e Silva ED, Holanda GZ. Comparison of orthopantomographs and conventional tomography images for assessing the relationship between impacted lower third molars and the mandibular canal. J Oral Maxillofac Surg. 2006; 64:1030–1037. PMID: 16781335.
Article26. Öhman A, Kivijärvi K, Blombäck U, Flygare L. Pre-operative radiographic evaluation of lower third molars with computed tomography. Dentomaxillofac Radiol. 2006; 35:30–35. PMID: 16421261.
Article
- Full Text Links
- Actions
-
Cited
- CITED
-
- Close
- Share
- Similar articles
-
- Assessment of the relationship between the mandibular third molar and the mandibular canal using panoramic radiograph and cone beam computed tomography
- Diversion of the mandibular canal: Is it the best predictor of inferior alveolar nerve damage during mandibular third molar surgery on panoramic radiographs?
- Positional Relationship of the Mandibular Canal and Impacted Third Molars by Using Dental Cone Beam Computed Tomography
- Reliability of panoramic radiography in predicting proximity of third molars to the mandibular canal: A comparison using cone-beam computed tomography
- Comparison of panoramic radiography with cone beam CT in predicting the relationship of the mandibular third molar roots to the alveolar canal