Ann Surg Treat Res.
2014 Jun;86(6):319-324. 10.4174/astr.2014.86.6.319.
Impact of a surgical intensivist on the clinical outcomes of patients admitted to a surgical intensive care unit
- Affiliations
-
- 1Department of Critical Care Medicine, Samsung Medical Center, Sungkyunkwan University School of Medicine, Seoul, Korea.
- 2Department of Surgery, Samsung Medical Center, Sungkyunkwan University School of Medicine, Seoul, Korea.
- 3Department of Surgery, Kangbuk Samsung Medical Center, Sungkyunkwan University School of Medicine, Seoul, Korea. hkchun@skku.edu
- 4Division of Pulmonary and Critical Care Medicine, Department of Medicine, Samsung Medical Center, Sungkyunkwan University School of Medicine, Seoul, Korea.
- 5Department of Surgery, Hallym University Kangdong Sacred Heart Hospital, Hallym University School of Medicine, Seoul, Korea.
- KMID: 2167110
- DOI: http://doi.org/10.4174/astr.2014.86.6.319
Abstract
- PURPOSE
An intensivist is a key factor in the mortality of patients admitted to the intensive care unit (ICU). The aim of this study was to evaluate the effect of an intensivist on clinical outcomes of patients admitted to a surgical ICU.
METHODS
During the study period, the surgical ICU was converted from an open ICU to an intensivist-directed ICU managed by an intensivist who was board certified in both general surgery and critical care medicine. We compared consecutive patients admitted to the surgical ICU before and after implementing the intensivist-directed care. The primary outcome was ICU mortality, and secondary outcomes were hospital mortality, 90-day mortality, length of hospital stay, ICU-free days, ventilator-free days, and ICU readmission rate.
RESULTS
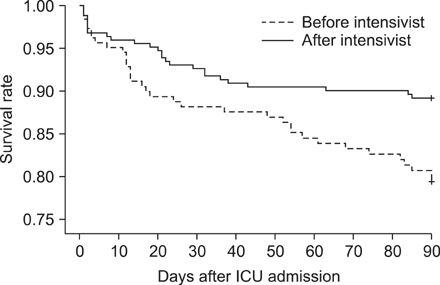
A total of 441 patients were included in this study: 188 before implementation of the intensivist and 253 after implementation. Clinical characteristics were not different between the two groups. ICU mortality decreased from 11.7% to 6.3% (P = 0.047) after implementation, and 90-day mortality also decreased significantly (P = 0.008). The adjusted hazard ratio of the intensivist for ICU mortality was 0.43 (95% confidence interval, 0.22-0.87; P = 0.020). ICU-free days (P = 0.013) and the hospital length of stay (P = 0.032) were significantly improved after implementing the intensivist-directed care. Before implementation period, 16.0% of patients were readmitted, compared with only 9.9% after implementation (P = 0.05).
CONCLUSION
Implementing intensivist-directed care in the surgical ICU was associated with significant improvements in ICU mortality and significant clinical outcomes.
MeSH Terms
Figure
Cited by 2 articles
-
Major Obstacles to Implement a Full-Time Intensivist in Korean Adult ICUs: a Questionnaire Survey
Jun Wan Lee, Jae Young Moon, Seok Wha Youn, Yong Sup Shin, Sang Il Park, Dong Chan Kim, Younsuk Koh
Korean J Crit Care Med. 2016;31(2):111-117. doi: 10.4266/kjccm.2016.31.2.111.Impact of institutional case volume on intensive care unit mortality
Christine Kang, Ho Geol Ryu
Acute Crit Care. 2023;38(2):151-159. doi: 10.4266/acc.2023.00689.
Reference
-
1. Pronovost P, Thompson DA, Holzmueller CG, Dorman T, Morlock LL. Impact of the Leapfrog Group's intensive care unit physician staffing standard. J Crit Care. 2007; 22:89–96.2. Pronovost PJ, Angus DC, Dorman T, Robinson KA, Dremsizov TT, Young TL. Physician staffing patterns and clinical outcomes in critically ill patients: a systematic review. JAMA. 2002; 288:2151–2162.3. Carson SS, Stocking C, Podsadecki T, Christenson J, Pohlman A, MacRae S, et al. Effects of organizational change in the medical intensive care unit of a teaching hospital: a comparison of 'open' and 'closed' formats. JAMA. 1996; 276:322–328.4. Ghorra S, Reinert SE, Cioffi W, Buczko G, Simms HH. Analysis of the effect of conversion from open to closed surgical intensive care unit. Ann Surg. 1999; 229:163–171.5. Nathens AB, Rivara FP, MacKenzie EJ, Maier RV, Wang J, Egleston B, et al. The impact of an intensivist-model ICU on trauma-related mortality. Ann Surg. 2006; 244:545–554.6. Dimick JB, Pronovost PJ, Heitmiller RF, Lipsett PA. Intensive care unit physician staffing is associated with decreased length of stay, hospital cost, and complications after esophageal resection. Crit Care Med. 2001; 29:753–758.7. Kumar K, Zarychanski R, Bell DD, Manji R, Zivot J, Menkis AH, et al. Impact of 24-hour in-house intensivists on a dedicated cardiac surgery intensive care unit. Ann Thorac Surg. 2009; 88:1153–1161.8. Mirski MA, Chang CW, Cowan R. Impact of a neuroscience intensive care unit on neurosurgical patient outcomes and cost of care: evidence-based support for an intensivist-directed specialty ICU model of care. J Neurosurg Anesthesiol. 2001; 13:83–92.9. Pronovost PJ, Jenckes MW, Dorman T, Garrett E, Breslow MJ, Rosenfeld BA, et al. Organizational characteristics of intensive care units related to outcomes of abdominal aortic surgery. JAMA. 1999; 281:1310–1317.10. Angus DC, Shorr AF, White A, Dremsizov TT, Schmitz RJ, Kelley MA, et al. Critical care delivery in the United States: distribution of services and compliance with Leapfrog recommendations. Crit Care Med. 2006; 34:1016–1024.11. Nathens AB, Maier RV, Jurkovich GJ, Monary D, Rivara FP, Mackenzie EJ. The delivery of critical care services in US trauma centers: is the standard being met? J Trauma. 2006; 60:773–783.12. Levy MM, Rapoport J, Lemeshow S, Chalfin DB, Phillips G, Danis M. Association between critical care physician management and patient mortality in the intensive care unit. Ann Intern Med. 2008; 148:801–809.13. Schoenfeld DA, Bernard GR. ARDS Network. Statistical evaluation of ventilator-free days as an efficacy measure in clinical trials of treatments for acute respiratory distress syndrome. Crit Care Med. 2002; 30:1772–1777.14. Gajic O, Afessa B. Physician staffing models and patient safety in the ICU. Chest. 2009; 135:1038–1044.15. Kahn JM, Brake H, Steinberg KP. Intensivist physician staffing and the process of care in academic medical centres. Qual Saf Health Care. 2007; 16:329–333.16. Hawari FI, Al Najjar TI, Zaru L, Al Fayoumee W, Salah SH, Mukhaimar MZ. The effect of implementing high-intensity intensive care unit staffing model on outcome of critically ill oncology patients. Crit Care Med. 2009; 37:1967–1971.17. Ewart GW, Marcus L, Gaba MM, Bradner RH, Medina JL, Chandler EB. The critical care medicine crisis: a call for federal action: a white paper from the critical care professional societies. Chest. 2004; 125:1518–1521.18. Gutsche JT, Kohl BA. Who should care for intensive care unit patients? Crit Care Med. 2007; 35:2 Suppl. S18–S23.19. Stawicki SP, Pryor JP, Hyams ES, Gupta R, Gracias VH, Schwab CW. The surgeon and the intensivist: reaching consensus in intensive care triage. J Surg Educ. 2007; 64:289–293.20. Johnson JL, Moore EE, Aasen AO, Rogy MA, Wang JE, Alsanea O, et al. The role of the surgeon as intensivist: an international perspective. Curr Opin Crit Care. 2006; 12:357–369.21. Korean Society of Critical Care Medicine. 1st White paper from Korean Society of Critical Care Medicine. Seoul. Korean Society of Critical Care Medicine: 2009.
- Full Text Links
- Actions
-
Cited
- CITED
-
- Close
- Share
- Similar articles
-
- The Impact of an Attending Intensivist on the Clinical Outcomes of Patients Admitted to the Cardiac Surgical Intensive Care Unit after Coronary Artery Bypass Grafting
- Feasibility of Percutaneous Dilatational Tracheostomy with a Light Source in the Surgical Intensive Care Unit
- The efficacy of intensivist-led closed-system intensive care units in improving outcomes for cancer patients requiring emergent surgical intervention
- Analysis of Medical Consultation Patterns in Medical and Surgical Intensive Care Units: Changes in the Pattern of Consultation after the Implementation of Intensivist-Directed Care
- Critical emergency medicine and the resuscitative care unit