Ann Surg Treat Res.
2015 Oct;89(4):224-227. 10.4174/astr.2015.89.4.224.
Abdominal aortic aneurysm in giant cell arteritis
- Affiliations
-
- 1Division of Vascular Surgery, Department of Surgery, Asan Medical Center, University of Ulsan College of Medicine, Seoul, Korea. twkwon2@amc.seoul.kr
- 2Department of Pathology, Asan Medical Center, University of Ulsan College of Medicine, Seoul, Korea.
- KMID: 2166900
- DOI: http://doi.org/10.4174/astr.2015.89.4.224
Abstract
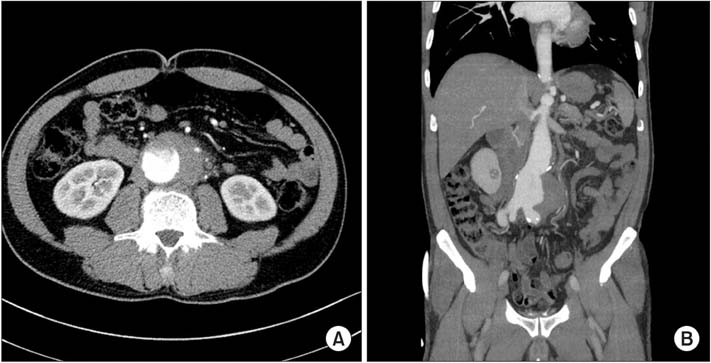
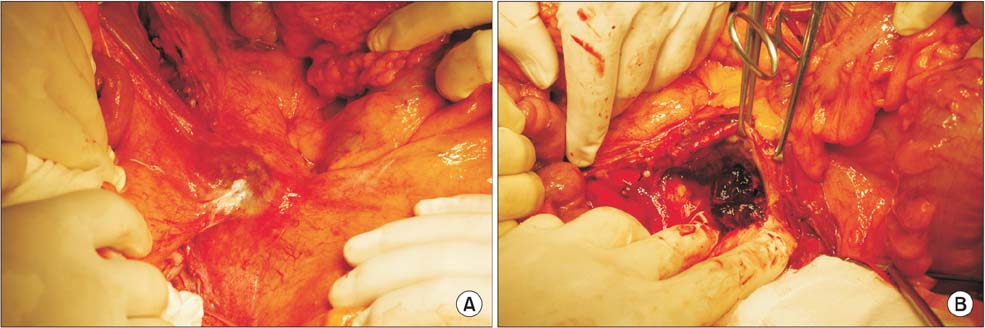
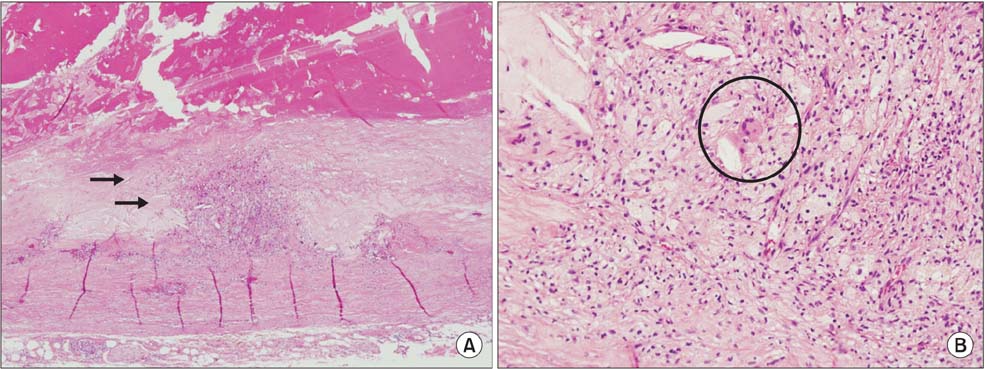
- Aortic complications of giant cell arteritis are a rare cause of abdominal aortic aneurysm. Here, we describe a case of a ruptured aortic aneurysm in a patient with giant call arteritis (GCA) who was preoperatively suspected of having an infectious aortic aneurysm. Intraoperative inspection revealed infectious granulation tissue on the anterior wall of the abdominal aorta. GCA was finally confirmed by pathological diagnosis. Our findings suggest that the surgical and postoperative treatment of nonatheromatous aortic aneurysm should be based on accurate diagnosis.
Keyword
MeSH Terms
Figure
Cited by 1 articles
-
Case of Brain Biopsy Proven Giant Cell Arteritis
Ho Hyun Park, Seung Heon Kang, Sang Hoon Park, Jae-Sung Park, Bon San Koo
J Rheum Dis. 2016;23(6):396-400. doi: 10.4078/jrd.2016.23.6.396.
Reference
-
1. Borchers AT, Gershwin ME. Giant cell arteritis: a review of classification, pathophysiology, geoepidemiology and treatment. Autoimmun Rev. 2012; 11:A544–A554.2. Marie I, Proux A, Duhaut P, Primard E, Lahaxe L, Girszyn N, et al. Long-term follow-up of aortic involvement in giant cell arteritis: a series of 48 patients. Medicine (Baltimore). 2009; 88:182–192.3. Lie JT. Illustrated histopathologic classification criteria for selected vasculitis syndromes. American College of Rheumatology Subcommittee on Classification of Vasculitis. Arthritis Rheum. 1990; 33:1074–1087.4. Breuer GS, Nesher R, Nesher G. Negative temporal artery biopsies: eventual diagnoses and features of patients with biopsynegative giant cell arteritis compared to patients without arteritis. Clin Exp Rheumatol. 2008; 26:1103–1106.5. Myklebust G, Gran JT. A prospective study of 287 patients with polymyalgia rheumatica and temporal arteritis: clinical and laboratory manifestations at onset of disease and at the time of diagnosis. Br J Rheumatol. 1996; 35:1161–1168.6. Hunder GG, Bloch DA, Michel BA, Stevens MB, Arend WP, Calabrese LH, et al. The American College of Rheumatology 1990 criteria for the classification of giant cell arteritis. Arthritis Rheum. 1990; 33:1122–1128.7. Gonzalez-Gay MA, Garcia-Porrua C, Pineiro A, Pego-Reigosa R, Llorca J, Hunder GG. Aortic aneurysm and dissection in patients with biopsy-proven giant cell arteritis from northwestern Spain: a population-based study. Medicine (Baltimore). 2004; 83:335–341.8. Fillmore AJ, Valentine RJ. Surgical mortality in patients with infected aortic aneurysms. J Am Coll Surg. 2003; 196:435–441.9. Garcia-Martinez A, Hernandez-Rodriguez J, Arguis P, Paredes P, Segarra M, Lozano E, et al. Development of aortic aneurysm/dilatation during the followup of patients with giant cell arteritis: a cross-sectional screening of fifty-four prospectively followed patients. Arthritis Rheum. 2008; 59:422–430.10. Bongartz T, Matteson EL. Large-vessel involvement in giant cell arteritis. Curr Opin Rheumatol. 2006; 18:10–17.