Healthc Inform Res.
2013 Sep;19(3):205-214. 10.4258/hir.2013.19.3.205.
Cost-Benefit Analysis of Electronic Medical Record System at a Tertiary Care Hospital
- Affiliations
-
- 1Department of Information Strategy, Samsung Medical Center, Seoul, Korea.
- 2Department of Management, Korea National Open University, Seoul, Korea.
- 3Department of Medicine, Samsung Medical Center, Sungkyunkwan University School of Medicine, Seoul, Korea. pl.rhee@samsung.com
- KMID: 2166699
- DOI: http://doi.org/10.4258/hir.2013.19.3.205
Abstract
OBJECTIVES
Although Electronic Medical Record (EMR) systems provide various benefits, there are both advantages and disadvantages regarding its cost-effectiveness. This study analyzed the economic effects of EMR systems using a cost-benefit analysis based on the differential costs of managerial accounting.
METHODS
Samsung Medical Center (SMC) is a general hospital in Korea that developed an EMR system for outpatients from 2006 to 2008. This study measured the total costs and benefits during an 8-year period after EMR adoption. The costs include the system costs of building the EMR and the costs incurred in smoothing its adoption. The benefits included cost reductions after its adoption and additional revenues from both remodeling of paper-chart storage areas and medical transcriptionists' contribution. The measured amounts were discounted by SMC's expected interest rate to calculate the net present value (NPV), benefit-cost ratio (BCR), and discounted payback period (DPP).
RESULTS
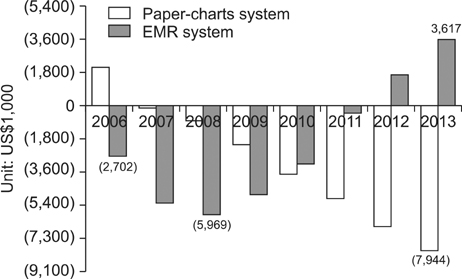
During the analysis period, the cumulative NPV and the BCR were US$3,617 thousand and 1.23, respectively. The DPP was about 6.18 years.
CONCLUSIONS
Although the adoption of an EMR resulted in overall growth in administrative costs, it is cost-effective since the cumulative NPV was positive. The positive NPV was attributed to both cost reductions and additional revenues. EMR adoption is not so attractive to management in that the DPP is longer than 5 years at 6.18 and the BCR is near 1 at 1.23. However, an EMR is a worthwhile investment, seeing that this study did not include any qualitative benefits and that the paper-chart system was cost-centric.
Keyword
MeSH Terms
Figure
Cited by 1 articles
-
Healthcare Decision Support System for Administration of Chronic Diseases
Ji-In Woo, Jung-Gi Yang, Young-Ho Lee, Un-Gu Kang
Healthc Inform Res. 2014;20(3):173-182. doi: 10.4258/hir.2014.20.3.173.
Reference
-
1. Wall Street Journal. Transcript: Health Info Tech Coordinator David Blumenthal [Internet]. New Jersey (NJ): Dow Jones & Company, Inc.;c2013. cited at 2013 Jun 8. Available from: http://online.wsj.com/article/SB124404155221081477.html.2. HealthIT.gov. Benefits of EHRs: Why Adopt EHRs? [Internet]. Washington (DC): The Office of the National Coordinator for Health Information Technology;c2013. cited at 2013 Jun 8. Available from: http://www.healthit.gov/providers-professionals/why-adopt-ehrs.3. Shea S, Hripcsak G. Accelerating the use of electronic health records in physician practices. N Engl J Med. 2010; 362(3):192–195.
Article4. Himmelstein DU, Wright A, Woolhandler S. Hospital computing and the costs and quality of care: a national study. Am J Med. 2010; 123(1):40–46.
Article5. Wang SJ, Middleton B, Prosser LA, Bardon CG, Spurr CD, Carchidi PJ, et al. A cost-benefit analysis of electronic medical records in primary care. Am J Med. 2003; 114(5):397–403.
Article6. Hillestad R, Bigelow J, Bower A, Girosi F, Meili R, Scoville R, et al. Can electronic medical record systems transform health care? Potential health benefits, savings, and costs. Health Aff (Millwood). 2005; 24(5):1103–1117.
Article7. Barlow S, Johnson J, Steck J. The economic effect of implementing an EMR in an outpatient clinical setting. J Healthc Inf Manag. 2004; 18(1):46–51.8. Kaushal R, Jha AK, Franz C, Glaser J, Shetty KD, Jaggi T, et al. Return on investment for a computerized physician order entry system. J Am Med Inform Assoc. 2006; 13(3):261–266.
Article9. Jha AK, DesRoches CM, Campbell EG, Donelan K, Rao SR, Ferris TG, et al. Use of electronic health records in U.S. hospitals. N Engl J Med. 2009; 360(16):1628–1638.
Article10. Shekelle PG, Morton SC, Keeler EB. Costs and benefits of health information technology. Evid Rep Technol Assess (Full Rep). 2006; (132):1–71.
Article11. Choi JS, Lee JH, Park JH, Nam HS, Kwon H, Kim D, et al. Design and implementation of a seamless and comprehensive integrated medical device interface system for outpatient electronic medical records in a general hospital. Int J Med Inform. 2011; 80(4):274–285.
Article12. Albrecht WS, Stice EK, Stice JD, Swain MR. Accounting: concepts and applications. 11th ed. Mason (OH): South-Western Cengage Learning;2011.13. Valancy J. How much will that EMR system really cost? Fam Pract Manag. 2002; 9(4):57–58.14. Choi JS, Lee WB. Economic analysis on the introduction of hospital mobile zone service: a case study of S hospital's communication expenses. Telecommun Rev. 2010; 20(4):683–695.15. Korea Financial Investment Association. Current price valuation of bond [Internet]. Seoul, Korea: Korea Financial Investment Association;c2013. cited at 2013 Jun 8. Available from: http://www.kofiabond.or.kr/SGPG/index.asp?id=m05_0501.16. Olazabal NG. Banking: the IT paradox. Despite much higher IT outlays by the retail-banking industry, its labor productivity growth rates have actually dropped. What went wrong? McKinsey Q. 2002; (1):47–51.17. Kaushal R, Bates DW. Information technology and medication safety: what is the benefit? Qual Saf Health Care. 2002; 11(3):261–265.
Article
- Full Text Links
- Actions
-
Cited
- CITED
-
- Close
- Share
- Similar articles
-
- Cost-Benefit Analysis of the Sharing System for Electronic Patients Records Among Healthcare Institutions
- Economic Analysis of Electronic Patient Record
- Nurses’ Experiences with the Use of Electronic Nursing Record: A Qualitative Study
- A Study on the Method to Estimate the Cost of Hospice Care
- Structure of Medical Cost in the Medical Insurance System