Healthc Inform Res.
2011 Mar;17(1):67-75. 10.4258/hir.2011.17.1.67.
New Integrated Information System for Pusan National University Hospital
- Affiliations
-
- 1Pusan National University School of Medicine, Busan, Korea.
- 2Youngsan University, Busan, Korea.
- 3Dongseo University, Busan, Korea.
- 4Ministry of Health and Welfare, Gwacheon, Korea.
- 5Korea Health and Welfare Information Service, Seoul, Korea.
- 6Yonsei University Graduate School of Public Health, Seoul, Korea. ymchae@yuhs.ac.kr
- KMID: 2166597
- DOI: http://doi.org/10.4258/hir.2011.17.1.67
Abstract
OBJECTIVES
This study presents the information system for Pusan National University Hospital (PNUH), evaluates its performance qualitatively, and conducts economic analysis.
METHODS
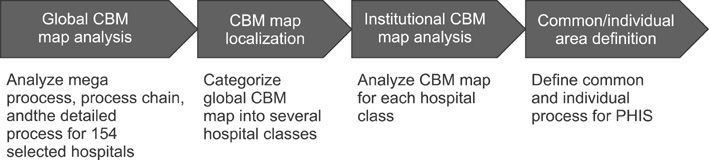
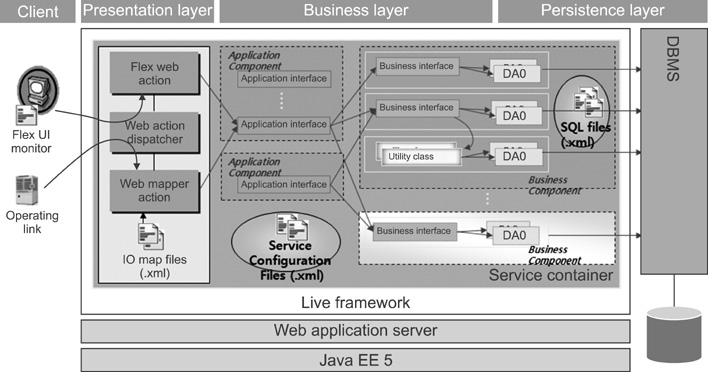
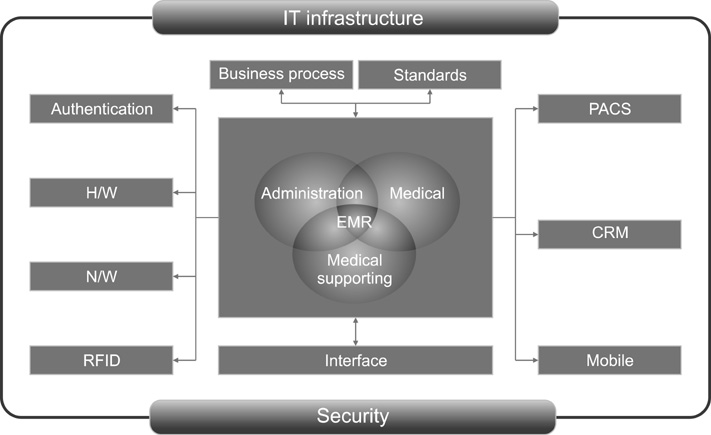
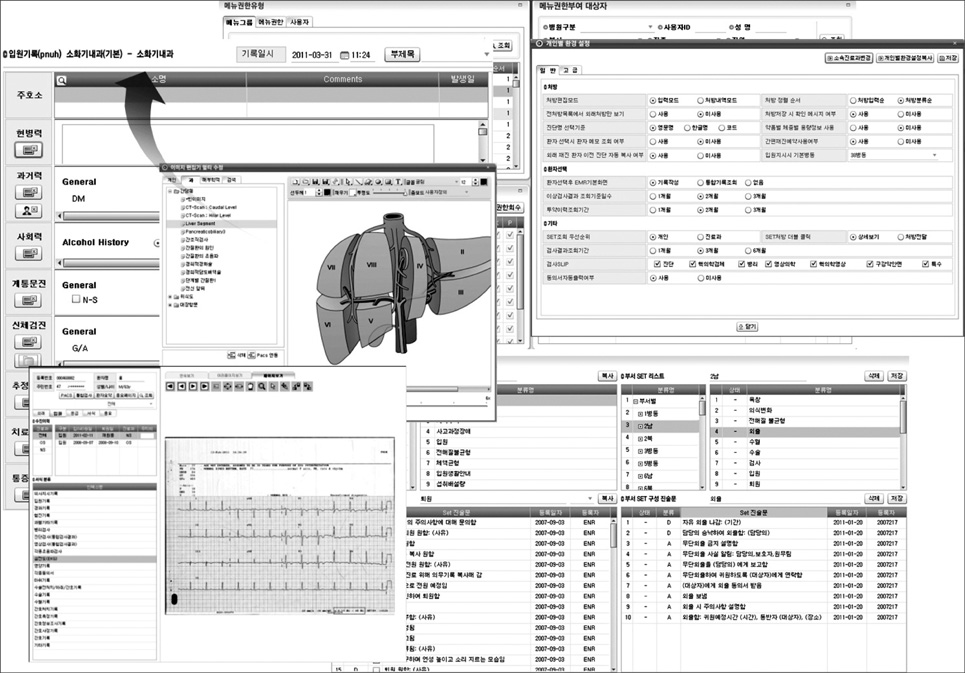
Information system for PNUH was designed by component-based development and developed by internet technologies. Order Communication System, Electronic Medical Record, and Clinical Decision Support System were newly developed. The performance of the hospital information system was qualitatively evaluated based on the performance reference model in order to identify problem areas for the old system. The Information Economics approach was used to analyze the economic feasibility of hospital information system in order to account for the intangible benefits.
RESULTS
Average performance scores were 3.16 for input layer, 3.35 for process layer, and 3.57 for business layer. In addition, the cumulative benefit to cost ratio was 0.50 in 2011, 1.73 in 2012, 1.76 in 2013, 1.71 in 2014, and 1.71 in 2015. The B/C ratios steadily increase as value items are added.
CONCLUSIONS
While overall performance scores were reasonably high, doctors were less satisfied with the system, perhaps due to the weak clinical function in the systems. The information economics analysis demonstrated the economic profitability of the information systems if all intangible benefits were included. The second qualitative evaluation survey and economic analysis were proposed to evaluate the changes in performance of the new system.
MeSH Terms
Figure
Reference
-
1. Healthcare Information Management and Systems Society. Essentials of the US hospital IT market. 2010. 5th ed. Chicago: Healthcare Information Management and Systems Society;vii.2. Yu KB. Effects of EMR and CDSS on hospital performance [dissertaion]. 2011. Seoul: Yonsei University Graduate School of Public Health;26.3. Choi J, Kim JW, Seo JW, Chung CK, Kim KH, Kim JH, Kim JH, Chie EK, Cho HJ, Goo JM, Lee HJ, Wee WR, Nam SM, Lim MS, Kim YA, Yang SH, Jo EM, Hwang MA, Kim WS, Lee EH, Choi SH. Implementation of consolidated HIS: improving quality and efficiency of healthcare. Healthc Inform Res. 2010. 16:299–304.
Article4. National Health Insurance Corporation. 2007 National Health Insurance statistical yearbook. 2007. Seoul: National Health Insurance Corporation;40–41.5. Chung KH. Methodology for performance evaluation of public information systems. 2008. Gwacheon: Korea Information System Development Institute;47–56.6. Chung WJ, Lee SH. Cost-benefit analysis of internet-based prescription delivery system. Korean J Health Policy Adm. 2002. 12:54–83.7. Korea Development Institute. Pre-evaluation of public health information systems. 2008. Seoul: Korea Development Institute;79–183.8. Parker MM, Trainor HE, Benson RJ. Information strategy and economics: linking information systems strategy to business performance. 1990. Englewood Cliffs, NJ: Prentice Hall.9. Chae YM, Lee HJ, Park CR. Economic analysis of order communication system for hospitals. Korean J Prev Med. 1991. 24:473–484.10. Kang SH, Chung YI, Chae YM. Economic analysis of electronic patient record. J Korean Soc Med Inform. 1997. 3:37–47.
Article11. IBM. Information strategy plan for public hospitals [unpublished report]. 2007. IBM.12. Chae YM, Cho KW, Kim HS, Park CB. Evaluation of hospital information system based on the performance reference model. Korean J Health Serv Manag. Forthcoming 2011.
Article13. Chae YM, Kim S, Cho KW, Kim HS, Kang SH, Kim HH, Park CB. Economic analysis of hospital information system by information economics approach. J Korean Soc Health Inf Health Stat. 2010. 35:195–205.
- Full Text Links
- Actions
-
Cited
- CITED
-
- Close
- Share
- Similar articles
-
- National Computerized Leprosy Information System
- A Study on The Integrated Interface Implementation for Medical Treatment Examination Equipment
- Development of a Integrated Healthcare Information System in Standardized Environment
- Development of Hospital DrWin PACS Integrated with HIS
- An Integrated Database and Web Service for Microbial Resources at KACC