Healthc Inform Res.
2010 Jun;16(2):100-119. 10.4258/hir.2010.16.2.100.
Analysis of Scientific Publication Networks among Medical Schools in Korea
- Affiliations
-
- 1Department of Radiation Oncology, School of Medicine, Kyung Hee University, Seoul, Korea. kangjino@paran.com
- KMID: 2166573
- DOI: http://doi.org/10.4258/hir.2010.16.2.100
Abstract
OBJECTIVES
This research was intended to analyze the special characteristics and structure of social networks among Korean medical schools for the purpose of providing knowledge regarding medical field structure, dynamics, and potential paradigm development.
METHODS
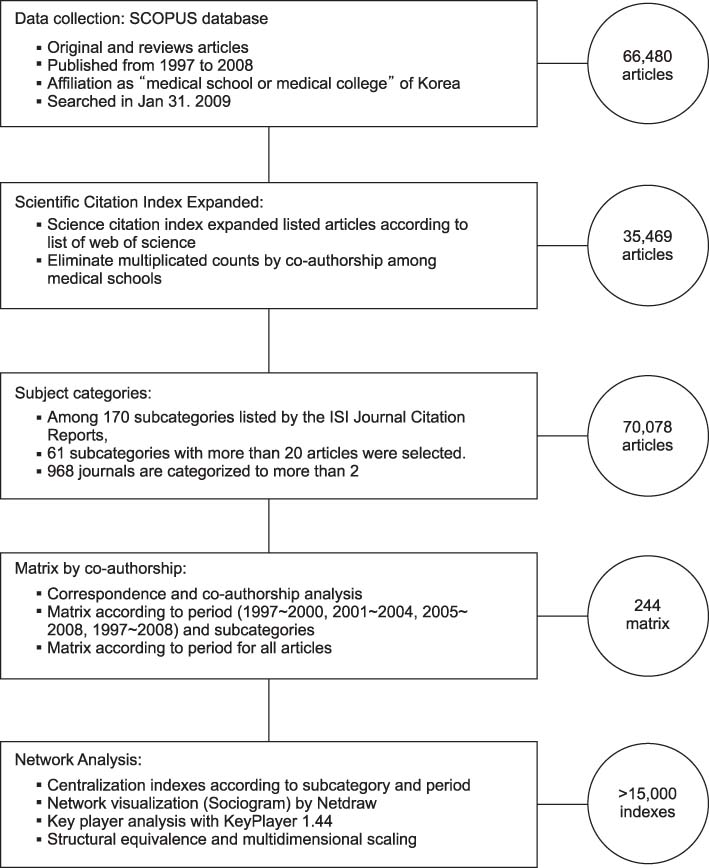
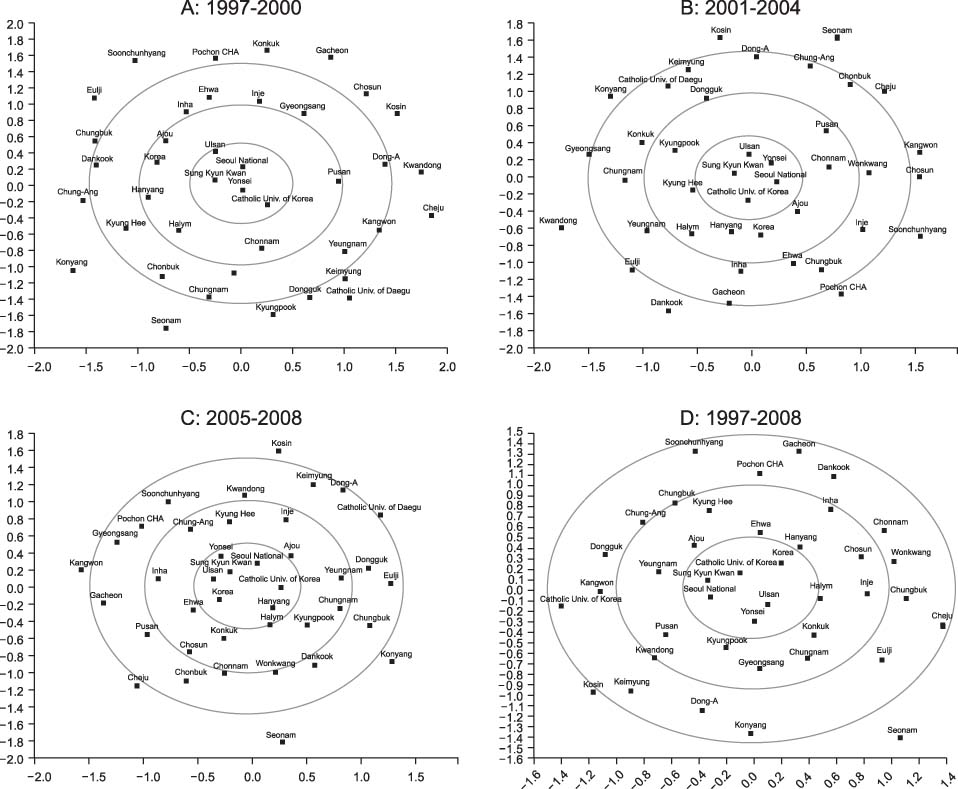
A collaborative 12-year data set of 35,469 published articles in the SCOPUS(R) database was analyzed. Among ISI subcategories, 61 having more than 20 articles were scrutinized. Following identification of correspondence and co-authorship, centralization indices and Key Player analysis were run for each subcategory. Medical schools were grouped into uniform clusters with convergence of iterated correlation (CONCOR) for structural equivalence. Finally, multidimensional scaling was used to visualize similarities.
RESULTS
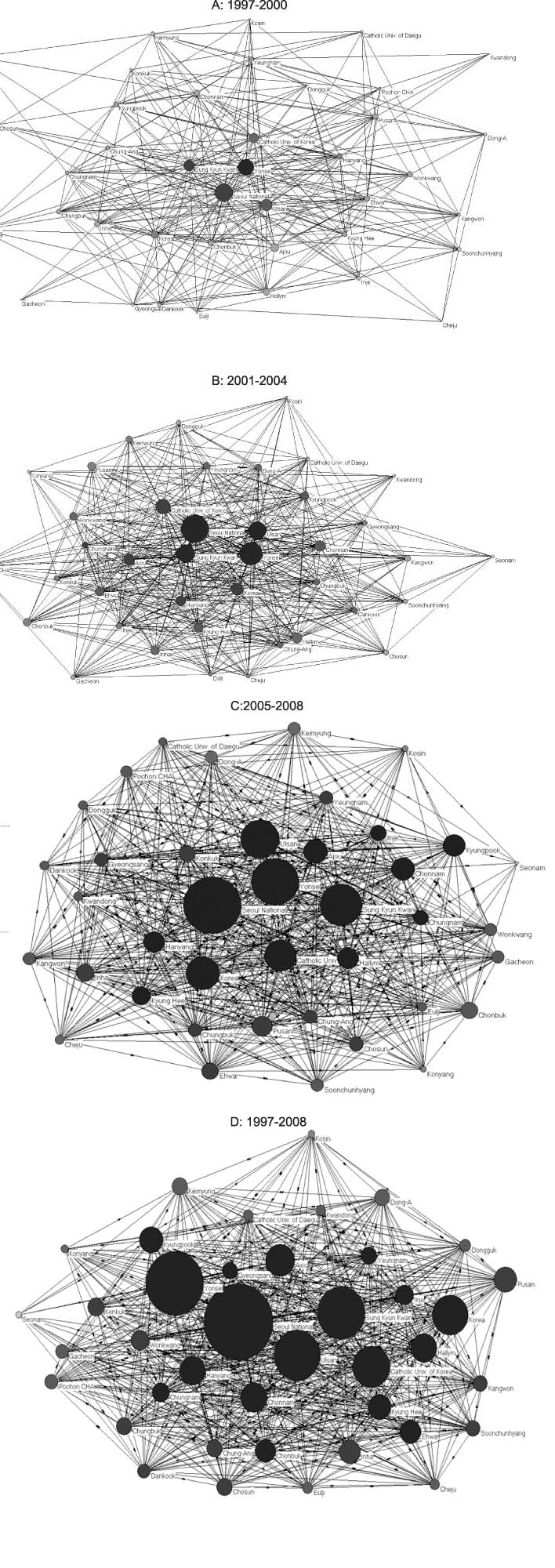
All centralization indexes analyzed demonstrated a shift in the degree of centralization in the network of medical schools throughout the period examined. Betweenness centrality and eigenvector centrality in particular revealed a dramatic change indicating minimization of the role of a specific "gatekeeper". Key Player analysis confirmed Seoul National University as a constant 'key player' throughout the period evaluated and for the subcategories examined as well.
CONCLUSIONS
This study provided insight into the scientific network among the medical schools of Korea. By understanding this network, a strategy to strengthen the basis of research may be developed.
Keyword
MeSH Terms
Figure
Cited by 2 articles
-
Book Review: Social Networks and Health: Models, Methods, and Applications
Ji-Young An
Healthc Inform Res. 2012;18(4):287-289. doi: 10.4258/hir.2012.18.4.287.Application of Social Network Analysis to Health Care Sectors
Hae Lan Jang, Young Sung Lee, Ji-Young An
Healthc Inform Res. 2012;18(1):44-56. doi: 10.4258/hir.2012.18.1.44.
Reference
-
1. Ministry of Education, Science and Technology. Analysis of NSI DB for SCI publications of Korea, 2007. 2008. Seoul: Ministry of Education, Science and Technology.2. Lim JK, Kim WK, Sung SY, Lee CS, Lim JH, Jeong JB, et al. Korea medical research report. KMR Report 2006. 2007. Seoul: National Academy of Medicine of Korea.3. Kang JO, Park SH. Current status of scientific citation index expanded article publications and relationship with the human resources of medical schools in Korea. J Korean Soc Med Inform. 2009. 15:321–340.
Article4. Science citation index expanded: scope notes. Thomson Reuters. c2010. cited at 2010 June 30. New York: Thomson Reuters;Available from: http://science.thomsonreuters.com/mjl/scope/scope_scie/.5. Borgatti SP, Everett MG, Freeman LC. UCINET for windows: software for social network analysis (version 6). 2002. Harvard (MA): Analytic Technologies.6. Batagelj V, Mrvar A. Pajek: program for large network analysis. cited at 2010 May 30. Available from: http://vlado.fmf.uni-lj.si/pub/networks/pajek/.7. Freeman LC. Centrality in social networks conceptual clarification. Soc Netw. 1978-1979. 1:215–239.
Article8. Borgatii SP. Identifying sets of key players in a social network. Comput Math Organ Theor. 2006. 12:21–34.
Article9. Breiger RL, Boorman SA, Arabie P. An algorithm for clustering relational data with applications to social network analysis and comparison with multidimensional scaling. J Math Psychol. 1975. 12:328–383.
Article10. Nooy WD, Mrvar A, Batagelj V. Exploratory social network analysis with Pajek: structural analysis in the social sciences. 2005. New York: Cambridge University Press.11. Newman ME. Blume LE, Durlauf SN, editors. The mathematics of networks. The new palgrave encyclopedia of economics. 2007. 2nd ed. Basingstoke (NH): Palgrave Macmillan.12. Ortiz-Arroyo D, Hussain DM. Ortiz-Arroyo D, Larsen HL, Zeng D, Hicks DL, Wagner G, editors. An information theory approach to identify sets of key players. Intelligence and security informatics. 2008. Heidelberg: Springer Berlin;15–26.
Article13. Molina JL. The informal organizational chart in organizations: an approach from the social networks analysis. Connections. 2001. 24:78–91.
- Full Text Links
- Actions
-
Cited
- CITED
-
- Close
- Share
- Similar articles
-
- Current Status of Scientific Citation Index Expanded Article Publications and Relationship with the Human Resources of Medical Schools in Korea
- Publication Ethics in the Era of Artificial Intelligence
- Ethical issues in clinical research and publication
- Fate of Abstracts Presented at the Scientific Meetings of the Korean Radiological Society
- A Scopus-Based Analysis of Publication Activity in Kazakhstan from 2010 to 2015: Positive Trends, Concerns, and Possible Solutions