Healthc Inform Res.
2010 Jun;16(2):77-81. 10.4258/hir.2010.16.2.77.
Diagnostic Analysis of Patients with Essential Hypertension Using Association Rule Mining
- Affiliations
-
- 1Department of Medical Informatics, School of Medicine, Keimyung University, Daegu, Korea. hjpark@kmu.ac.kr
- 2Department of Internal Medicine, School of Medicine, Keimyung University, Daegu, Korea.
- 3Department of Preventive Medicine, School of Medicine, Keimyung University, Daegu, Korea.
- KMID: 2166570
- DOI: http://doi.org/10.4258/hir.2010.16.2.77
Abstract
OBJECTIVES
The purpose of this study was to analyze the records of patients diagnosed with essential hypertension using association rule mining (ARM).
METHODS
Patients with essential hypertension (ICD code, I10) were extracted from a hospital's data warehouse and a data mart constructed for analysis. Apriori modeling of the ARM method and web node in the Clementine 12.0 program were used to analyze patient data.
RESULTS
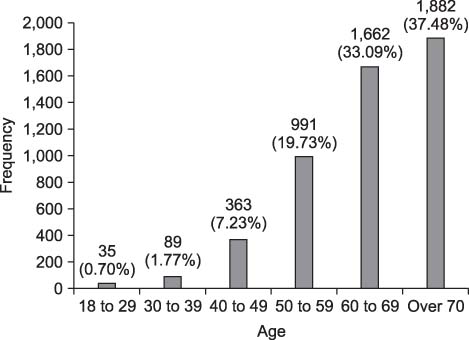
Patients diagnosed with essential hypertension totaled 5,022 and the diagnostic data extracted from those patients numbered 53,994. As a result of the web node, essential hypertension, non-insulin dependent diabetes mellitus (NIDDM), and cerebral infarction were shown to be associated. Based on the results of ARM, NIDDM (support, 35.15%; confidence, 100%) and cerebral infarction (support, 21.21%; confidence, 100%) were determined to be important diseases associated with essential hypertension.
CONCLUSIONS
Essential hypertension was strongly associated with NIDDM and cerebral infarction. This study demonstrated the practicality of ARM in co-morbidity studies using a large clinic database.
Keyword
MeSH Terms
Figure
Reference
-
1. National Statistical Office of Korea. Annual report on the cause of the death statistics 2008. 2008. Seoul: National Statistical Office of Korea;1–255.2. Lee SW, Kam S, Chun BY, Yeh MH, Kang YS, Kim KY, Lee YS, Park KS, Son JH, Oh HS, An MY, Lim PD. Therapeutic compliance and its related factors of patients with hypertension in rural area. Korean J Prev Med. 2000. 33:215–225.3. Yoon SJ, Ha BM, Kim CY. Measuring the burden of hypertension using DALY in Korea. Korean J Health Policy Adm. 2001. 11:89–101.4. Hwang EH. The study of risk factors of the disease worse due to hypertension and management aspect [dissertation]. 2003. Chuncheon: Kangwon National Univ.5. Jee SH, Suh I, Kim IS, Appel LJ. Smoking and atherosclerotic cardiovascular disease in men with low levels of serum cholesterol: the Korea Medical Insurance Corporation Study. JAMA. 1999. 282:2149–2155.
Article6. Tai YM, Chiu HW. Comorbidity study of ADHD: applying association rule mining (ARM) to National Health Insurance Database of Taiwan. Int J Med Inform. 2009. 78:e75–e83.
Article7. Kang HC, Han ST, Choi JH, Kim ES, Kim MK, Lee SK. Data mining with SAS Enterprise Miner 4.0: methodology and application. 2002. 3rd ed. Seoul: Jayuacademi;155–174.8. Heo MH, Lee YG. Data mining modeling and case. 2008. 2nd ed. Seoul: Hannarae;171–250.9. Bae HS, Cho DH, Suk KH, Kim BS, Lee JY, Noh SW, Lee SC, Chon YH. Data mining using SAS Enterprise Miner. 2008. 2nd ed. Seoul: Kyowoosa;80–86.10. Chobanian AV, Bakris GL, Black HR, Cushman WC, Green LA, Izzo JL Jr, Jones DW, Materson BJ, Oparil S, Wright JT, Roceella EJ. Seventh report of the Joint National Committee on Prevention, Detection, Evaluation, and Treatment of High Blood Pressure. Hypertension. 2003. 42:1206–1252.
Article11. Choi JW, Lee YH, Kim KJ, Kim JS, Park JS, Song JH, Lee EJ, Kim SG, Kim JD, Kim SG. The analysis of clinical information by building the clinical data warehouse. J Korean Soc Med Inform. 2001. 7:1–11.
Article12. Lee SM, Park RW. Basic concepts and principles of data mining in clinical practice. J Korean Soc Med Inform. 2009. 15:175–189.
Article13. Lee HJ. Hypertension: the role of hypertension in diabetic patients, the cause and etiology. Korean Clin Diabetes. 2004. 5:215–219.
- Full Text Links
- Actions
-
Cited
- CITED
-
- Close
- Share
- Similar articles
-
- Comorbidity Study on Type 2 Diabetes Mellitus Using Data Mining
- Association Analysis of Reactive Oxygen Species-Hypertension Genes Discovered by Literature Mining
- Association Rules to Identify Complications of Cerebral Infarction in Patients with Atrial Fibrillation
- Data Mining Application for Knowledge Management in Medical Field
- Text Mining in Biomedical Domain with Emphasis on Document Clustering