Healthc Inform Res.
2010 Mar;16(1):60-64. 10.4258/hir.2010.16.1.60.
Ubiquitous-Severance Hospital Project: Implementation and Results
- Affiliations
-
- 1Department of Thoracic and Cardiovascular Surgery, Yonsei University College of Medicine, Seoul, Korea.
- 2Department of Biomedical Engineering, Yonsei University College of Medicine, Seoul, Korea. knh@yuhs.ac
- 3Division of Medical Information and Technology, Yonsei University Health System, Yonsei University College of Medicine, Seoul, Korea.
- 4Department of Plastic and Reconstructive Surgery, Yonsei University College of Medicine, Seoul, Korea.
- 5Department of Neurology, Yonsei University College of Medicine, Seoul, Korea.
- KMID: 2166567
- DOI: http://doi.org/10.4258/hir.2010.16.1.60
Abstract
OBJECTIVES
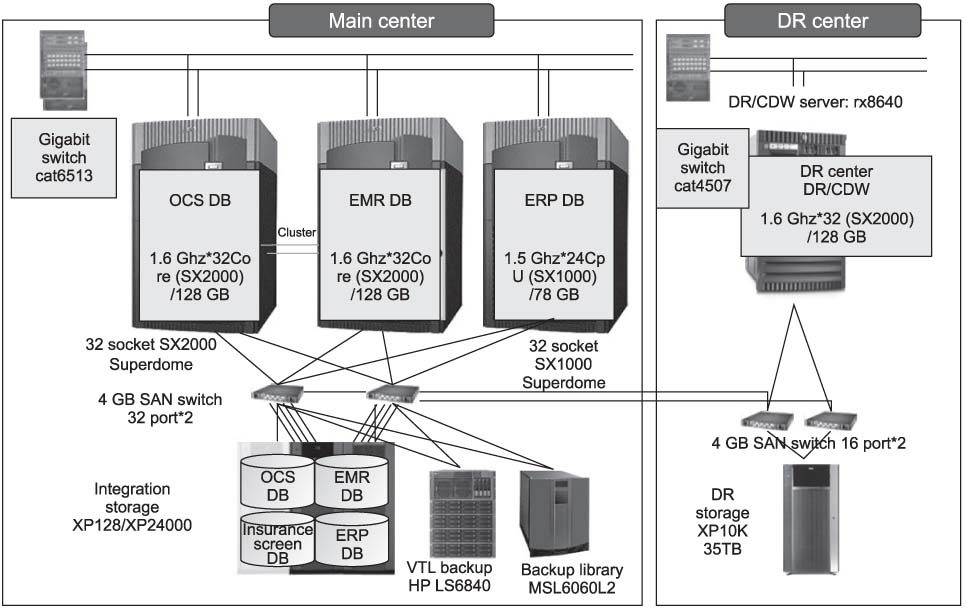
The purpose of this study was to review an implementation of u-Severance information system with focus on electronic hospital records (EHR) and to suggest future improvements. METHODS: Clinical Data Repository (CDR) of u-Severance involved implementing electronic medical records (EMR) as the basis of EHR and the management of individual health records. EHR were implemented with service enhancements extending to the clinical decision support system (CDSS) and expanding the knowledge base for research with a repository for clinical data and medical care information. RESULTS: The EMR system of Yonsei University Health Systems (YUHS) consists of HP integrity superdome servers using MS SQL as a database management system and MS Windows as its operating system. CONCLUSIONS: YUHS is a high-performing medical institution with regards to efficient management and customer satisfaction; however, after 5 years of implementation of u-Severance system, several limitations with regards to expandability and security have been identified.
Keyword
MeSH Terms
Figure
Cited by 2 articles
-
Going Abroad of Korean Health Information Systems
Young Moon Chae
Healthc Inform Res. 2014;20(3):161-162. doi: 10.4258/hir.2014.20.3.161.Implementation of Single Source Based Hospital Information System for the Catholic Medical Center Affiliated Hospitals
Inyoung Choi, Ran Choi, Jonghyun Lee, Byung Gil Choi
Healthc Inform Res. 2010;16(2):133-139. doi: 10.4258/hir.2010.16.2.133.
Reference
-
1. Yonsei University Health System [Internet]. c2009. cited 2010 Mar 1. Seoul: Yonsei University Health System;Available from: http://www.yuhs.or.kr/en/.2. Eduljee A, Rocha RA. Practical evaluation of clinical guideline document models. AMIA Annu Symp Proc. 2003. 836.3. Tully MP, Cantrill JA. Insights into creation and use of prescribing documentation in the hospital medical record. J Eval Clin Pract. 2005. 11:430–437.
Article4. Pearson SD, Goulart-Fisher D, Lee TH. Critical pathways as a strategy for improving care: problems and potential. Ann Intern Med. 1995. 123:941–948.
Article5. Coffey RJ, Richards JS, Remmert CS, LeRoy SS, Schoville RR, Baldwin PJ. An introduction to critical paths. Qual Manag Health Care. 1992. 1:45–54.
Article6. AHIMA e-HIM Personal Health Record Work Group. Practice brief. The role of the personal health record in the EHR. J AHIMA. 2005. 76:64A–64D.7. Markus ML, Tanis C. The enterprise systems experience--from adoption to success: glimpsing the future through the past. 2000. Cincinnati (OH): Pinnaflex Educational Resources, Inc.;87–100.8. Markus ML, Tanis C, Fenema PC. Enterprise resource planning: multisite ERP implementations. Commun ACM. 2000. 43:42–46.
Article
- Full Text Links
- Actions
-
Cited
- CITED
-
- Close
- Share
- Similar articles
-
- Challenges and improvement opportunities in a telemedicine pilot project
- Community-Based Home Healthcare Project for Korean Older Adults
- Effects of Dementia Friendly Community Project on Awareness of Dementia and Changes in Attitude
- Design and Implementation of RFID Application System for Hospital Information System
- Design and Implementation of Pulse-Diagnosis Ontology in Ubiquitous Computing Environment