Clin Exp Otorhinolaryngol.
2011 Jun;4(2):109-111.
Cavernous Hemangioma of the Tympanic Membrane
- Affiliations
-
- 1Department of Otolaryngology, Chonnam National University Medical School, Gwangju, Korea. chulsavio@hanmail.net
- 2Research Center for Resistant Cells, Chosun University, Gwangju, Korea.
Abstract
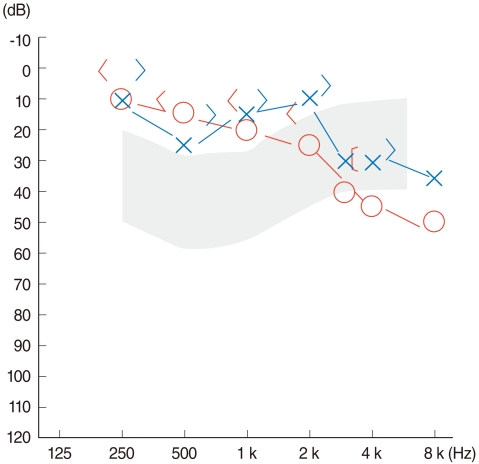
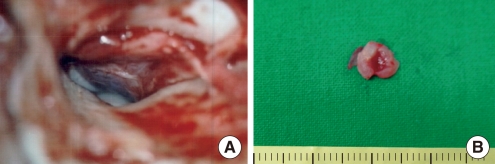
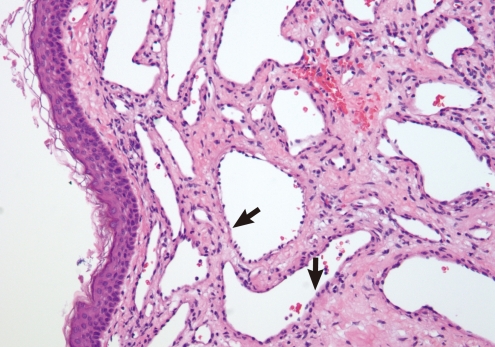
- Cavernous hemangioma seems to most frequently arise in the posterior portion of the external auditory canal. However, they rarely occur in the tympanic membrane. A 49-year-old male patient was referred for evaluation of right-sided pulsatile tinnitus that he'd experienced for the previous 2 years. Temporal bone computerized tomography showed an isolated soft tissue mass just lateral to the tympanic membrane. There was no evidence of bony erosion or middle ear invasion. The patient underwent excision of the mass using a postauricular approach. The mass was removed en bloc and the defect of the tympanic membrane was repaired by tympanoplasty type I. There was no recurrence after 1 year of follow-up.
Keyword
MeSH Terms
Figure
Reference
-
1. Batsakis JG. Tumors of the head & neck: clinical and pathological considerations. 1978. Baltimore: Willliams & Wilkins.2. Kemink JL, Graham MD, McClatchey KD. Hemangioma of the external auditory canal. Am J Otol. 1983; 10. 5(2):125–126. PMID: 6650669.3. Hawke M, van Nostrand P. Cavernous hemangioma of the external ear canal. J Otolaryngol. 1987; 2. 16(1):40–42. PMID: 3560305.4. Jackson CG, Levine SC, McKennan KX. Recurrent hemangioma of the external auditory canal. Am J Otol. 1990; 3. 11(2):117–118. PMID: 2321686.5. Limb CJ, Mabrie DC, Carey JP, Minor LB. Hemangioma of the external auditory canal. Otolaryngol Head Neck Surg. 2002; 1. 126(1):74–75. PMID: 11821770.
Article6. Reeck JB, Yen TL, Szmit A, Cheung SW. Cavernous hemangioma of the external ear canal. Laryngoscope. 2002; 10. 112(10):1750–1752. PMID: 12368608.
Article7. Yang TH, Chiang YC, Chao PZ, Lee FP. Cavernous hemangioma of the bony external auditory canal. Otolaryngol Head Neck Surg. 2006; 5. 134(5):890–891. PMID: 16647556.
Article8. Magliulo G, Parrotto D, Sardella B, Della Rocca C, Re M. Cavernous hemangioma of the tympanic membrane and external ear canal. Am J Otolaryngol. 2007; May-Jun. 28(3):180–183. PMID: 17499135.
Article9. Freedman SI, Barton S, Goodhill V. Cavernous angiomas of the tympanic membrane. Arch Otolaryngol. 1972; 8. 96(2):158–160. PMID: 4563050.
Article10. Andrade JM, Gehris CW Jr, Breitenecker R. Cavernous hemangioma of the tympanic membrane. A case report. Am J Otol. 1983; 1. 4(3):198–199. PMID: 6829733.