Clin Exp Otorhinolaryngol.
2011 Dec;4(4):184-187.
Relationship between the Korean Version of the Sniffin' Stick Test and the T&T Olfactometer in the Korean Population
- Affiliations
-
- 1Department of Otorhinolaryngology-Head and Neck Surgery, Korea University Guro Hospital, Korea University College of Medicine, Seoul, Korea. lhman@korea.ac.kr
- 2Medical Devices Clinical Trial Center, Korea University Guro Hospital, Korea University College of Medicine, Seoul, Korea.
Abstract
OBJECTIVES
The Korean version of the Sniffin' stick (KVSS) test is widely used in Korea to evaluate olfactory function. However, its validity and reliability have not been studied well. In this study, the authors administered the KVSS and the T%T olfactometer test to evaluate olfactory function and to establish relationships between these two test measures.
METHODS
Two hundred and eleven patients participated in this prospective randomized study. One hundred and nine patients with no olfactory symptoms and 102 patients with decreased olfaction participated. All participants were underwent KVSS II and T&T olfactometer testing.
RESULTS
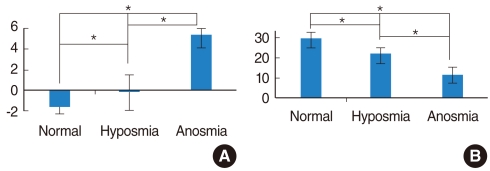
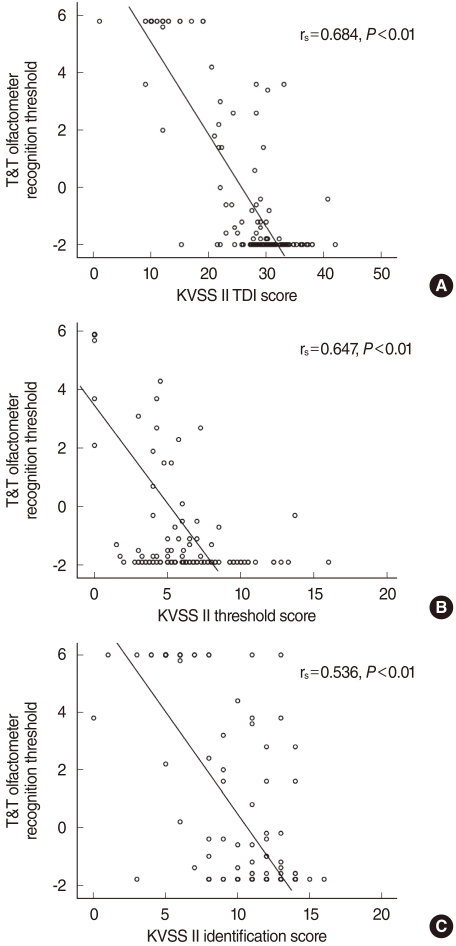
The mean recognition threshold of the T&T olfactometer was -1.8+/-0.9 for patients with normal olfaction and 4.0+/-2.6 for patients with decreased olfaction. The mean Threshold-Discrimination-Identification score of the KVSS II was 30.0+/-3.8 for patients with normal olfaction and 15.9+/-7.1 for patients with decreased olfaction. Correlation coefficient between the two tests was significantly high (r(s)=-0.725, P<0.01).
CONCLUSION
The KVSS and T&T olfactometry test are both reliable tests of olfactory function and their results are well correlated with each other.
Figure
Reference
-
1. Deems DA, Doty RL, Settle RG, Moore-Gillon V, Shaman P, Mester AF, et al. Smell and taste disorders: a study of 750 patients from the University of Pennsylvania Smell and Taste Center. Arch Otolaryngol Head Neck Surg. 1991; 5. 117(5):519–528. PMID: 2021470.
Article2. Leopold DA. Cummings CW, Fredrickson JM, Harker LA, Krause CJ, Schuller DE, editors. Physiology of olfaction. Otolaryngology Head and Neck Surgery. 1993. 2nd ed. St. Louis: Mosby Year Book;p. 640–664.
Article3. Dhong HJ, Shin DB, Rho HI, Chung SK, Chu KC. Clinical analysis of olfactory disorders. Korean J Otolaryngol-Head Neck Surg. 2001; 9. 44(9):946–950.4. Doty RL, Shaman P, Dann M. Development of the University of Pennsylvania Smell Identification Test: a standardized microencapsulated test of olfactory function. Physiol Behav. 1984; 3. 32(3):489–502. PMID: 6463130.
Article5. Doty RL, Marcus A, Lee WW. Development of the 12-item Cross-Cultural Smell Identification Test (CC-SIT). Laryngoscope. 1996; 3. 106(3 Pt 1):353–356. PMID: 8614203.6. Cain WS, Gent JF, Goodspeed RB, Leonard G. Evaluation of olfactory dysfunction in the Connecticut Chemosensory Clinical Research Center. Laryngoscope. 1988; 1. 98(1):83–88. PMID: 3336267.
Article7. Takagi SF. A standardized olfactometer in Japan. Ann NY Acad Sci. 1987; 510:113–118. PMID: 3481235.
Article8. Hong SC, Yoo YS, Kim ES, Kim SC, Park SH, Kim JK, et al. Development of KVSS Test (Korean Version of Sniffin' Sticks Test). Korean J Otolaryngol-Head Neck Surg. 1999; 7. 42(7):855–860.9. Cho JH, Jeong YS, Lee YJ, Hong SC, Yoon JH, Kim JK. The Korean version of the Sniffin' stick (KVSS) test and its validity in comparison with the cross-cultural smell identification test (CC-SIT). Auris Nasus Larynx. 2009; 6. 36(3):280–286. PMID: 18775610.
Article10. Kondo H, Matsuda T, Hashiba M, Baba S. A study of the relationship between the T&T olfactometer and the University of Pennsylvania Smell Identification Test in a Japanese population. Am J Rhinol. 1998; Sep-Oct. 12(5):353–358. PMID: 9805536.11. Tsukatani T, Reiter ER, Miwa T, Costanzo RM. Comparison of diagnostic findings using different olfactory test methods. Laryngoscope. 2005; 6. 115(6):1114–1117. PMID: 15933533.
Article12. Doty RL, Koba G. Doty RL, editor. Current trends in the measurement of olfactory function. Handbook of olfaction and gustation. 1995. New York: Marcel Dekker;p. 191–225.13. Oyama M, Furuta S, Takasaka T, Ikeda K, Moriyama H, Yanagi K, et al. Clinical evaluation of usefulness of smell identification test (International version) in Japanese elderly subjects. Jpn J Rhinol. 1995; 34(2):340–347.14. Shiokawa H. The clinical studies on the olfactory test using standard odorous substances: the change of olfactory acuity due to ageing. Nihon Jibiinkoka Gakkai Kaiho. 1975; 12. 20. 78(12):1258–1270. PMID: 1240920.
- Full Text Links
- Actions
-
Cited
- CITED
-
- Close
- Share
- Similar articles
-
- Olfactory Identification Test Using Familiar Distracters for Koreans
- Correlation between Olfactory Dysfunction Measured by T&T Olfactometer and Disease Severity Staged by CT in Chronic Rhinosinusitis
- Olfactory Dysfunction and Cognitive Impairment
- The Current Status of Evaluation Technologies for the Function of Human Olfaction
- Olfactory Function in Chromium Exposed Workers Without Nasal Septum Perforation