Ann Rehabil Med.
2015 Jun;39(3):425-431. 10.5535/arm.2015.39.3.425.
Effects of Head Rotation and Head Tilt on Pharyngeal Pressure Events Using High Resolution Manometry
- Affiliations
-
- 1Department of Rehabilitation Medicine, Gangneung Asan Hospital, University of Ulsan College of Medicine, Gangneung, Korea.
- 2Department of Rehabilitation Medicine, Seoul National University Bundang Hospital, Seoul National University College of Medicine, Seongnam, Korea. jseok337@snu.ac.kr
- 3Department of Rehabilitation Medicine, CHA Bundang Medical Center, CHA University, Seongnam, Korea.
- KMID: 2165646
- DOI: http://doi.org/10.5535/arm.2015.39.3.425
Abstract
OBJECTIVE
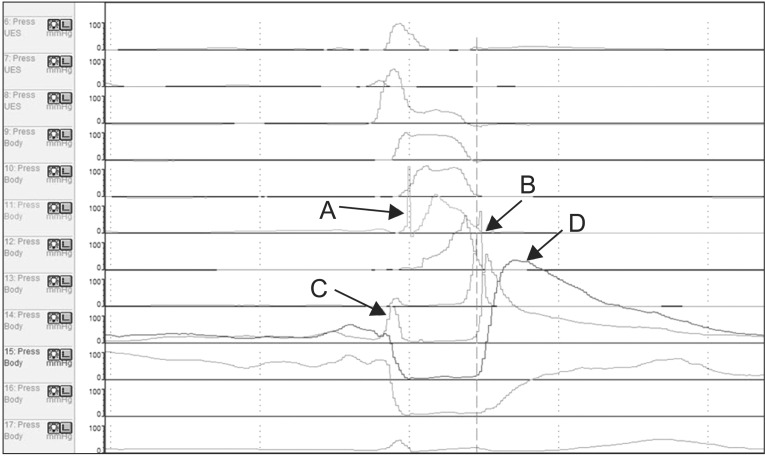
To observe changes in pharyngeal pressure during the swallowing process according to postures in normal individuals using high-resolution manometry (HRM).
METHODS
Ten healthy volunteers drank 5 mL of water twice while sitting in a neutral posture. Thereafter, they drank the same amount of water twice in the head rotation and head tilting postures. The pressure and time during the deglutition process for each posture were measured with HRM. The data obtained for these two postures were compared with those obtained from the neutral posture.
RESULTS
The maximum pressure, area, rise time, and duration in velopharynx (VP) and tongue base (TB) were not affected by changes in posture. In comparison, the maximum pressure and the pre-upper esophageal sphincter (UES) maximum pressure of the lower pharynx in the counter-catheter head rotation posture were lower than those in the neutral posture. The lower pharynx pressure in the catheter head tilting posture was higher than that in the counter-catheter head tilting. The changes in the VP peak and epiglottis, VP and TB peaks, and the VP onset and post-UES time intervals were significant in head tilting and head rotation toward the catheter postures, as compared with neutral posture.
CONCLUSION
The pharyngeal pressure and time parameter analysis using HRM determined the availability of head rotation as a compensatory technique for safe swallowing. Tilting the head smoothes the progress of food by increasing the pressure in the pharynx.
MeSH Terms
Figure
Cited by 2 articles
-
Selection of Head Turn Side on Pharyngeal Dysphagia in Hemiplegic Stroke Patients: a Preliminary Study
Hannah Lee, Hyunwoo Rho, Hee-Jung Cheon, Su Mi Oh, Yun-Hee Kim, Won Hyuk Chang
Brain Neurorehabil. 2018;11(2):. doi: 10.12786/bn.2018.11.e19.Effects of Chin-Down Maneuver on Pharyngeal Pressure Generation According to Dysphagia and Viscosity
Sun Myoung Lee, Ban Hyung Lee, Jung Woo Kim, Joon Young Jang, Eun Gyeong Jang, Ju Seok Ryu
Ann Rehabil Med. 2020;44(6):493-501. doi: 10.5535/arm.20016.
Reference
-
1. Lan Y, Xu G, Dou Z, Wan G, Yu F, Lin T. Biomechanical changes in the pharynx and upper esophageal sphincter after modified balloon dilatation in brainstem stroke patients with dysphagia. Neurogastroenterol Motil. 2013; 25:e821–e829. PMID: 23941282.
Article2. Yoon KJ, Park JH, Park JH, Jung IS. Videofluoroscopic and manometric evaluation of pharyngeal and upper esophageal sphincter function during swallowing. J Neurogastroenterol Motil. 2014; 20:352–361. PMID: 24847841.
Article3. Savarino E, Zentilin P, Savarino V, Tenca A, Penagini R, Clarke JO, et al. Functional testing: pharyngeal pH monitoring and high-resolution manometry. Ann N Y Acad Sci. 2013; 1300:226–235. PMID: 24117645.
Article4. Clarke JO, Gyawali CP, Tatum RP. High-resolution manometry. Ann N Y Acad Sci. 2011; 1232:349–357. PMID: 21950825.
Article5. Hila A, Castell JA, Castell DO. Pharyngeal and upper esophageal sphincter manometry in the evaluation of dysphagia. J Clin Gastroenterol. 2001; 33(5):355–361. PMID: 11606849.
Article6. Takasaki K, Umeki H, Kumagami H, Takahashi H. Influence of head rotation on upper esophageal sphincter pressure evaluated by high-resolution manometry system. Otolaryngol Head Neck Surg. 2010; 142:214–217. PMID: 20115977.
Article7. Perlman AL, Schultz JG, VanDaele DJ. Effects of age, gender, bolus volume, and bolus viscosity on oropharyngeal pressure during swallowing. J Appl Physiol (1985). 1993; 75:33–37. PMID: 8376283.
Article8. Baek SS, Park SB, Lee SG, Lee KM, Kim SH. The effect of neck posture in swallowing of stroke patients. J Korean Acad Rehabil Med. 1997; 21:8–12.9. Kahrilas PJ, Logemann JA, Lin S, Ergun GA. Pharyngeal clearance during swallowing: a combined manometric and videofluoroscopic study. Gastroenterology. 1992; 103:128–136. PMID: 1612322.
Article10. Fox MR, Bredenoord AJ. Oesophageal high-resolution manometry: moving from research into clinical practice. Gut. 2008; 57:405–423. PMID: 17895358.
Article11. Mielens JD, Hoffman MR, Ciucci MR, Jiang JJ, McCulloch TM. Automated analysis of pharyngeal pressure data obtained with high-resolution manometry. Dysphagia. 2011; 26:3–12. PMID: 21264672.
Article12. McCulloch TM, Hoffman MR, Ciucci MR. High-resolution manometry of pharyngeal swallow pressure events associated with head turn and chin tuck. Ann Otol Rhinol Laryngol. 2010; 119:369–376. PMID: 20583734.
Article13. Mielens JD, Hoffman MR, Ciucci MR, McCulloch TM, Jiang JJ. Application of classification models to pharyngeal high-resolution manometry. J Speech Lang Hear Res. 2012; 55:892–902. PMID: 22232390.
Article14. Logemann JA, Kahrilas PJ, Kobara M, Vakil NB. The benefit of head rotation on pharyngoesophageal dysphagia. Arch Phys Med Rehabil. 1989; 70:767–771. PMID: 2802957.15. Ohmae Y, Ogura M, Kitahara S, Karaho T, Inouye T. Effects of head rotation on pharyngeal function during normal swallow. Ann Otol Rhinol Laryngol. 1998; 107:344–348. PMID: 9557771.
Article16. Rasley A, Logemann JA, Kahrilas PJ, Rademaker AW, Pauloski BR, Dodds WJ. Prevention of barium aspiration during videofluoroscopic swallowing studies: value of change in posture. AJR Am J Roentgenol. 1993; 160:1005–1009. PMID: 8470567.
Article17. Logemann JA. Role of the modified barium swallow in management of patients with dysphagia. Otolaryngol Head Neck Surg. 1997; 116:335–338. PMID: 9121786.
Article18. Beom J, Han TR. Treatment of dysphagia in patients with brain disorders. J Korean Med Assoc. 2013; 56:7–15.
Article
- Full Text Links
- Actions
-
Cited
- CITED
-
- Close
- Share
- Similar articles
-
- High-resolution esophageal manometry in children
- Application and Interpretation of High-resolution Manometry for Pharyngeal Dysphagia
- An Efficacy of Head Tilt Test in the Patients with Unilateral Superior Oblique Palsy
- How to Perform and Interpret Upper Esophageal Sphincter Manometry
- The Effects of Bolus Volume and Texture on Pharyngeal Pressure Events Using High-resolution Manometry and Its Comparison with Videofluoroscopic Swallowing Study