Ann Dermatol.
2016 Jun;28(3):385-387. 10.5021/ad.2016.28.3.385.
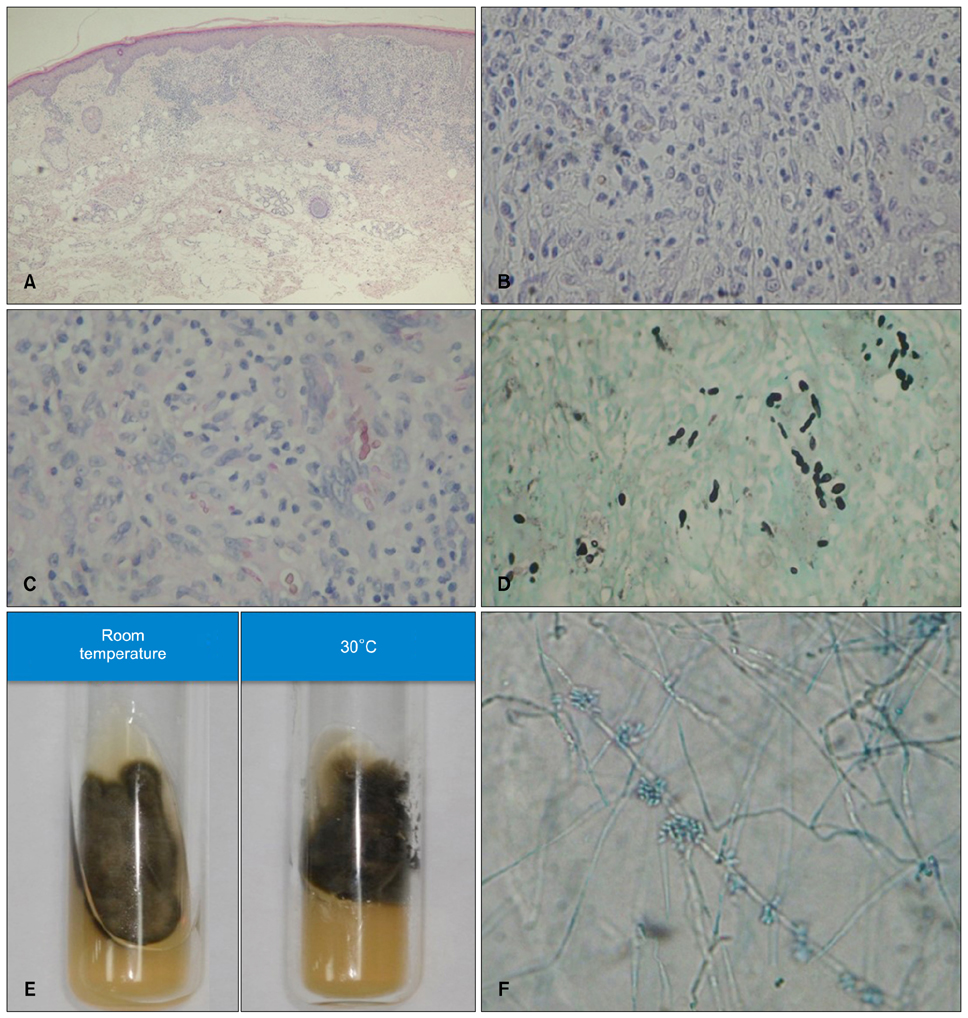
A Case of Phaeohyphomycosis Caused by Exophiala lecanii-corni
- Affiliations
-
- 1Department of Dermatology, Kyungpook National University School of Medicine, Daegu, Korea. weonju@knu.ac.kr
- KMID: 2164650
- DOI: http://doi.org/10.5021/ad.2016.28.3.385
Abstract
- No abstract available.
MeSH Terms
Figure
Cited by 1 articles
-
A Case of Subcutaneous and Intranasal Phaeohyphomycosis Caused by Microsphaeropsis arundinis in an Immunocompromised Patient Misdiagnosed with Mucormycosis
Hoon Choi, Choong Jae Kim, Min Sung Kim, Bong Seok Shin, Chan Ho Na
Ann Dermatol. 2019;31(5):571-575. doi: 10.5021/ad.2019.31.5.571.
Reference
-
1. Kim DS, Yoon YM, Kim SW. Phaeohyphomycosis due to Exophiala dermatitidis successfully treated with itraconazole. Korean J Med Mycol. 1999; 4:79–83.2. Ben-Ami R, Lewis RE, Raad II, Kontoyiannis DP. Phaeohyphomycosis in a tertiary care cancer center. Clin Infect Dis. 2009; 48:1033–1041.
Article3. Ajello L, Georg LK, Steigbigel RT, Wang CJ. A case of phaeohyphomycosis caused by a new species of Phialophora. Mycologia. 1974; 66:490–498.
Article4. Suh MK, Kwon SW, Kim TH, Sun YW, Lim JW, Ha GY, et al. A case of subcutaneous phaeohyphomycosis caused by Exophiala jeanselmei. Korean J Dermatol. 2005; 43:124–127.5. Clancy CJ, Wingard JR, Hong Nguyen M. Subcutaneous phaeohyphomycosis in transplant recipients: review of the literature and demonstration of in vitro synergy between antifungal agents. Med Mycol. 2000; 38:169–175.
Article
- Full Text Links
- Actions
-
Cited
- CITED
-
- Close
- Share
- Similar articles
-
- Phaeohyphomycosis Due to Exophiala dermatitidis Successfully Treated with Itraconazole
- A Case of Subcutaneous Phaeohyphomycosis Caused by Exophiala oligosperma Showing Multiple Cysts
- A Case of Phaeohyphomycosis from Exophiala Species Mimicking Facial Cutaneous Tumor
- The First Case of Phaeohyphomycosis Caused by Exophiala xenobiotica in an Immunocompetent Patient in Korea
- A Case of Subcutaneous Phaeohyphomycosis Caused by Exophiala jeanselmei