Clin Orthop Surg.
2015 Jun;7(2):211-216. 10.4055/cios.2015.7.2.211.
A Randomized Controlled Study to Compare the Total and Hidden Blood Loss in Computer-Assisted Surgery and Conventional Surgical Technique of Total Knee Replacement
- Affiliations
-
- 1Department of Orthopaedics, All India Institute of Medical Sciences, New Delhi, India. rmalhotra62@gmail.com
- 2Department of Anesthesiology, All India Institute of Medical Sciences, New Delhi, India.
- 3Department of Cardiology, All India Institute of Medical Sciences, New Delhi, India.
- 4Department of Cardiac Anesthesia, All India Institute of Medical Sciences, New Delhi, India.
- KMID: 2164547
- DOI: http://doi.org/10.4055/cios.2015.7.2.211
Abstract
- BACKGROUND
Total knee arthroplasty (TKA) is associated with considerable blood loss. Computer-assisted surgery (CAS) is different from conventional TKA as it avoids opening the intramedullary canal. Hence, CAS should be associated with less blood loss.
METHODS
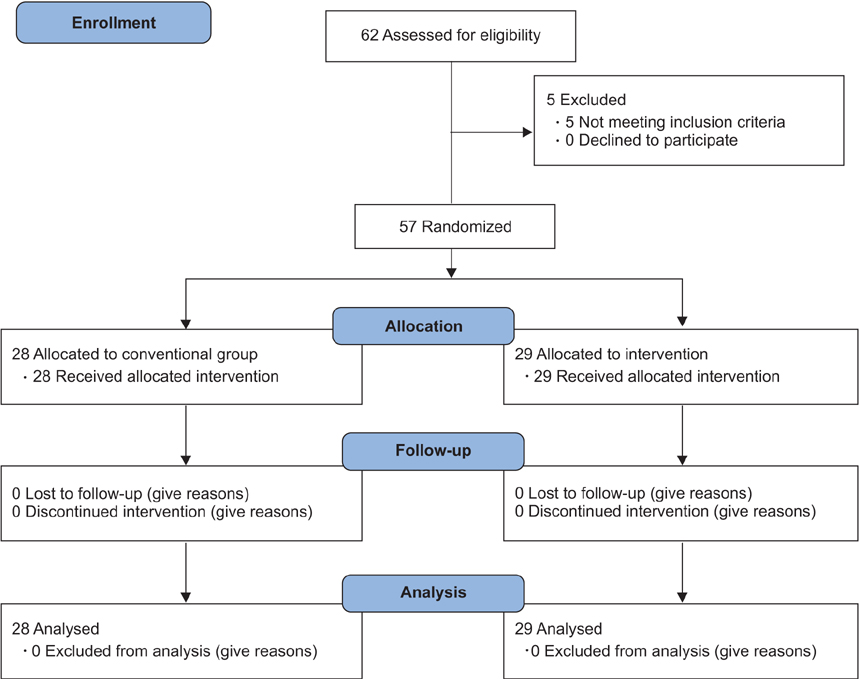
Fifty-seven patients were randomized into two groups of CAS and conventional TKA. In conventional group intramedullary femoral and extramedullary tibial jigs were used whereas in CAS group imageless navigation system was used. All surgeries were done under tourniquet. Total and hidden blood loss was calculated in both groups and compared.
RESULTS
The mean total blood loss was 980 mL in conventional group and 970 mL in CAS group with median of 1,067 mL (range, 59 to 1,791 mL) in conventional group and 863 mL (range, 111 to 2,032 mL) in CAS group. There was no significant difference in total blood loss between the two groups (p = 0.811). We have found significant hidden blood loss in both techniques, which is 54.8% of the total loss in the conventional technique and 59.5% in the computer-assisted navigation technique.
CONCLUSIONS
There is no significant difference in total and hidden blood loss in the TKA in CAS and conventional TKA. However, there is significant hidden blood loss in both techniques. There was no relation of tourniquet time with blood loss.
Keyword
MeSH Terms
Figure
Cited by 1 articles
-
Computer-Assisted Navigation in Total Knee Arthroplasty
Hwa-Jae Jeong, Yong-Beom Park, Han-Jun Lee
J Korean Orthop Assoc. 2018;53(6):478-489. doi: 10.4055/jkoa.2018.53.6.478.
Reference
-
1. Bierbaum BE, Callaghan JJ, Galante JO, Rubash HE, Tooms RE, Welch RB. An analysis of blood management in patients having a total hip or knee arthroplasty. J Bone Joint Surg Am. 1999; 81(1):2–10.2. Vandenbussche E, Duranthon LD, Couturier M, Pidhorz L, Augereau B. The effect of tourniquet use in total knee arthroplasty. Int Orthop. 2002; 26(5):306–309.3. Tria AJ Jr, Coon TM. Minimal incision total knee arthroplasty: early experience. Clin Orthop Relat Res. 2003; (416):185–190.4. Samama CM. A direct antifibrinolytic agent in major orthopedic surgery. Orthopedics. 2004; 27:6 Suppl. s675–s680.5. Ong SM, Taylor GJ. Can knee position save blood following total knee replacement? Knee. 2003; 10(1):81–85.6. Sehat KR, Evans R, Newman JH. How much blood is really lost in total knee arthroplasty? Correct blood loss management should take hidden loss into account. Knee. 2000; 7(3):151–155.7. Sehat KR, Evans RL, Newman JH. Hidden blood loss following hip and knee arthroplasty: correct management of blood loss should take hidden loss into account. J Bone Joint Surg Br. 2004; 86(4):561–565.8. Chauhan SK, Scott RG, Breidahl W, Beaver RJ. Computer-assisted knee arthroplasty versus a conventional jig-based technique: a randomised, prospective trial. J Bone Joint Surg Br. 2004; 86(3):372–377.9. Nadler SB, Hidalgo JH, Bloch T. Prediction of blood volume in normal human adults. Surgery. 1962; 51(2):224–232.10. Levy O, Martinowitz U, Oran A, Tauber C, Horoszowski H. The use of fibrin tissue adhesive to reduce blood loss and the need for blood transfusion after total knee arthroplasty: a prospective, randomized, multicenter study. J Bone Joint Surg Am. 1999; 81(11):1580–1588.11. Kalairajah Y, Simpson D, Cossey AJ, Verrall GM, Spriggins AJ. Blood loss after total knee replacement: effects of computer-assisted surgery. J Bone Joint Surg Br. 2005; 87(11):1480–1482.12. Millar NL, Deakin AH, Millar LL, Kinnimonth AW, Picard F. Blood loss following total knee replacement in the morbidly obese: effects of computer navigation. Knee. 2011; 18(2):108–112.13. McConnell J, Dillon J, Kinninmonth A, Sarungi M, Picard F. Blood loss following total knee replacement is reduced when using computer-assisted versus standard methods. Acta Orthop Belg. 2012; 78(1):75–79.14. Thiengwittayaporn S, Junsee D, Tanavalee A. A comparison of blood loss in minimally invasive surgery with and without electromagnetic computer navigation in total knee arthroplasty. J Med Assoc Thai. 2009; 92:Suppl 6. S27–S32.15. Mohanlal PK, Sandiford N, Skinner JA, Samsani S. Comparision of blood loss between computer assisted and conventional total knee arthroplasty. Indian J Orthop. 2013; 47(1):63–66.16. Napier RJ, Bennett D, McConway J, et al. The influence of immediate knee flexion on blood loss and other parameters following total knee replacement. Bone Joint J. 2014; 96(2):201–209.17. Murphy CG, Winter DC, Bouchier-Hayes DJ. Tourniquet injuries: pathogenesis and modalities for attenuation. Acta Orthop Belg. 2005; 71(6):635–645.18. Petaja J, Myllynen P, Myllyla G, Vahtera E. Fibrinolysis after application of a pneumatic tourniquet. Acta Chir Scand. 1987; 153(11-12):647–651.19. Tai TW, Chang CW, Lai KA, Lin CJ, Yang CY. Effects of tourniquet use on blood loss and soft-tissue damage in total knee arthroplasty: a randomized controlled trial. J Bone Joint Surg Am. 2012; 94(24):2209–2215.20. Parvizi J, Diaz-Ledezma C. Total knee replacement with the use of a tourniquet: more pros than cons. Bone Joint J. 2013; 95:11 Suppl A. 133–134.21. Li X, Yin L, Chen ZY, et al. The effect of tourniquet use in total knee arthroplasty: grading the evidence through an updated meta-analysis of randomized, controlled trials. Eur J Orthop Surg Traumatol. 2014; 24(6):973–986.22. Zhang W, Li N, Chen S, Tan Y, Al-Aidaros M, Chen L. The effects of a tourniquet used in total knee arthroplasty: a meta-analysis. J Orthop Surg Res. 2014; 9(1):13.23. Tarwala R, Dorr LD, Gilbert PK, Wan Z, Long WT. Tourniquet use during cementation only during total knee arthroplasty: a randomized trial. Clin Orthop Relat Res. 2014; 472(1):169–174.24. Irisson E, Hemon Y, Pauly V, Parratte S, Argenson JN, Kerbaul F. Tranexamic acid reduces blood loss and financial cost in primary total hip and knee replacement surgery. Orthop Traumatol Surg Res. 2012; 98(5):477–483.
- Full Text Links
- Actions
-
Cited
- CITED
-
- Close
- Share
- Similar articles
-
- Computer-Assisted Navigation in Total Knee Arthroplasty
- Blood Sparing Efficacy of Oral Tranexamic Acid in Primary Total Knee Arthroplasty: A Randomized Controlled Trial
- Computer Assisted Navigation in Knee Arthroplasty
- Comparative Analysis of Radiologic Measurement According to TKR using Computer Assisted Surgery and Conventional TKR
- The Effects of Timing of Tourniquet Release on Blood Loss in Navigation Assisted Total Knee Arthroplasty