Korean J Gastroenterol.
2014 Aug;64(2):119-122. 10.4166/kjg.2014.64.2.119.
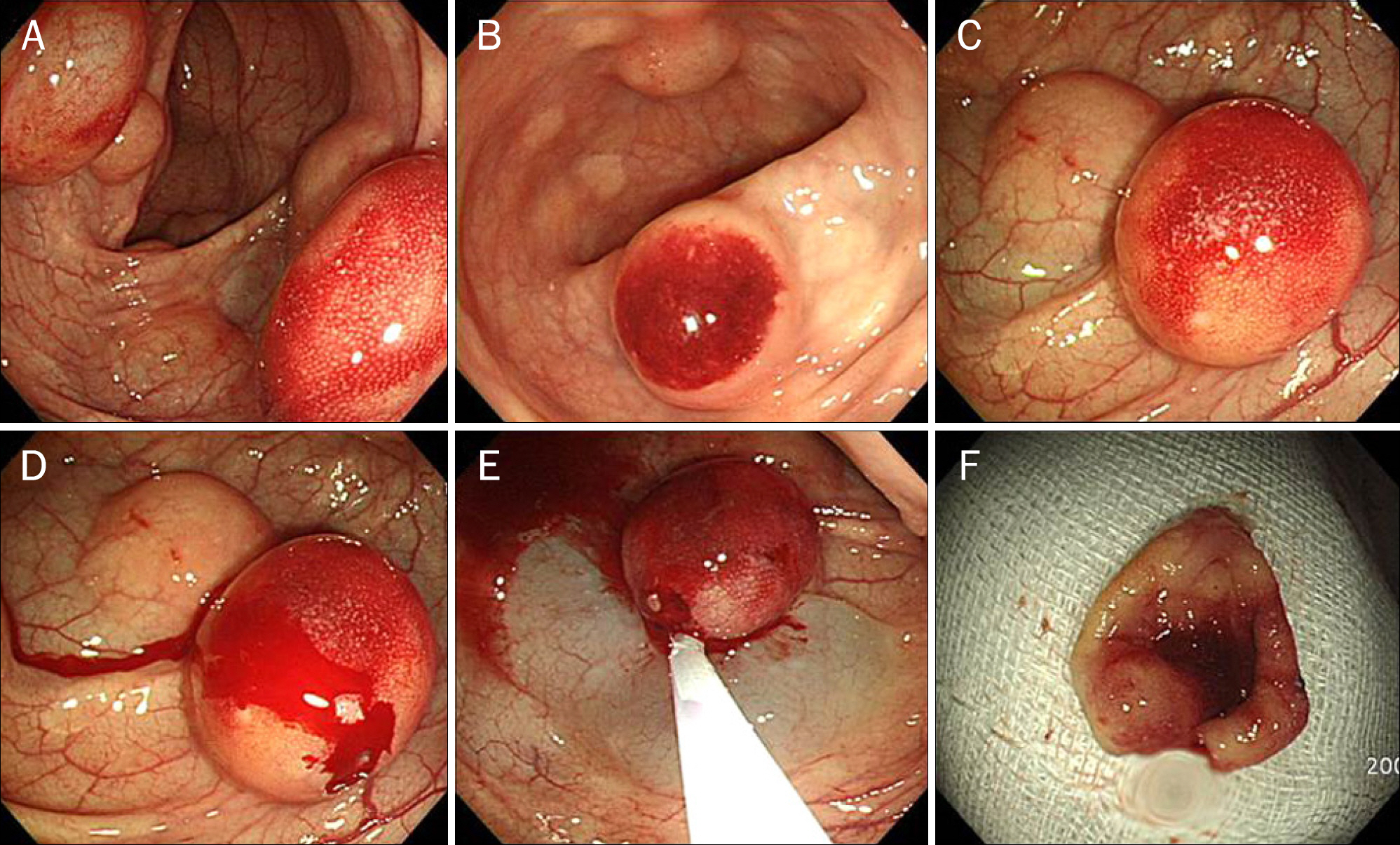
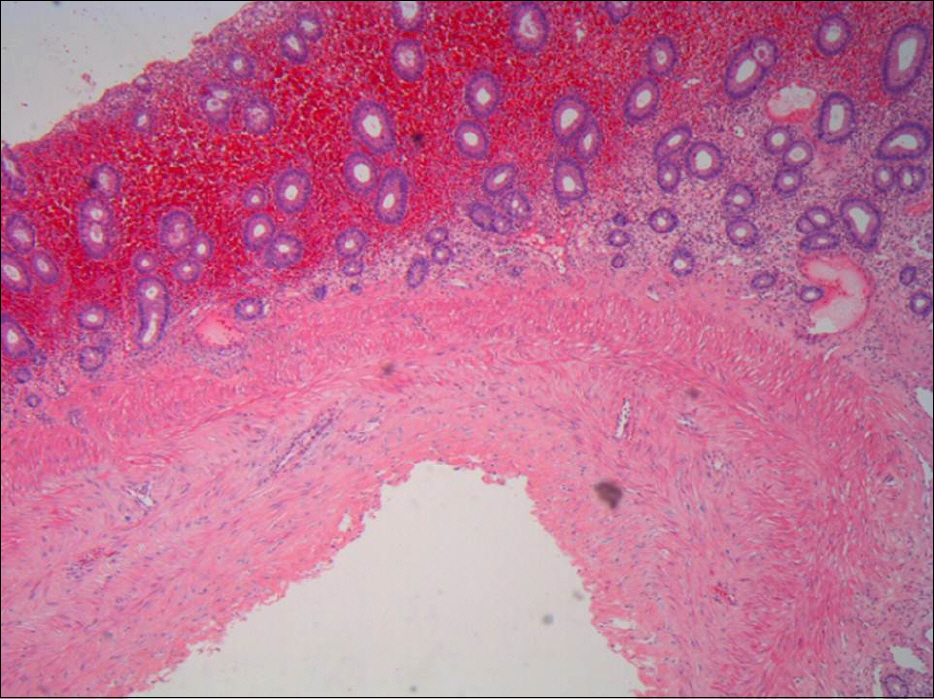
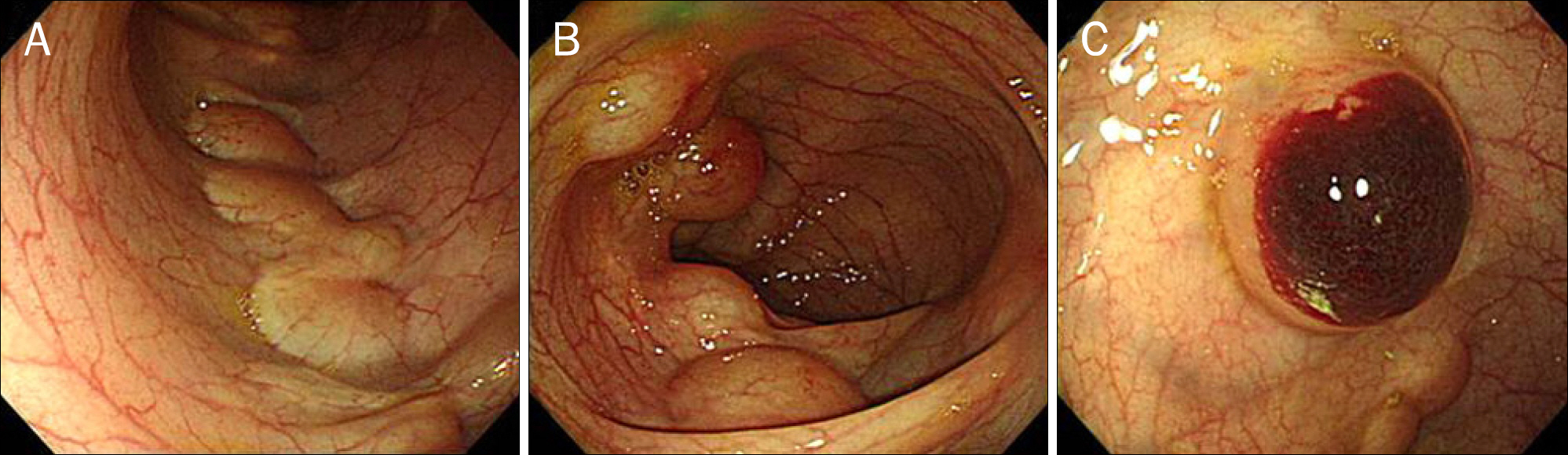
A Case with Primary Pneumatosis Cystoides Treated after Colonoscopic Endoscopic Mucosal Resection
- Affiliations
-
- 1Department of Internal Medicine, Dongguk University Ilsan Hospital, Dongguk University College of Medicine, Goyang, Korea. gangmali@naver.com
- KMID: 2164424
- DOI: http://doi.org/10.4166/kjg.2014.64.2.119
Abstract
- No abstract available.
MeSH Terms
Figure
Reference
-
References
1. Ho LM, Paulson EK, Thompson WM. Pneumatosis intestinalis in the adult: benign to life-threatening causes. AJR Am J Roentgenol. 2007; 188:1604–1613.
Article2. Galandiuk S, Fazio VW. Pneumatosis cystoides intestinalis. A review of the literature. Dis Colon Rectum. 1986; 29:358–363.3. Kim JS, Kwon SB, Kim W, et al. A case of primary pneumatosis cystoides intestinalis in a patient with chronic abdominal pain. Intest Res. 2011; 9:40–45.
Article4. Heng Y, Schuffler MD, Haggitt RC, Rohrmann CA. Pneumatosis intestinalis: a review. Am J Gastroenterol. 1995; 90:1747–1758.
- Full Text Links
- Actions
-
Cited
- CITED
-
- Close
- Share
- Similar articles
-
- A Case of Primary Pneumatosis Cystoides Intestinalis in a Patient with Chronic Abdominal Pain
- A Case of Pneumatosis Cystoides Intestinalis in a Patient with Chronic Diarrhea and Abdominal Pain
- A Case of Pneumatosis Cystoides Intestinalis in a Patient with Systemic Lupus Erythematosus
- Pneumatosis Cystoides Intestinalis of Adult Ileum: A Case Report
- Pneumatosis Cystoides Intestinalis With Portal Venous Gas: Two Case Reports