Korean J Gastroenterol.
2014 Aug;64(2):87-92. 10.4166/kjg.2014.64.2.87.
Prognostic Significance of Ki-67 Expression in Patients Undergoing Surgical Resection for Gastrointestinal Stromal Tumor
- Affiliations
-
- 1Department of Internal Medicine, Inje University College of Medicine, Seoul, Korea. yousunk69@korea.com
- 2Department of Surgery, Inje University College of Medicine, Seoul, Korea.
- 3Department of Pathology, Inje University College of Medicine, Seoul, Korea.
- KMID: 2164418
- DOI: http://doi.org/10.4166/kjg.2014.64.2.87
Abstract
- BACKGROUND/AIMS
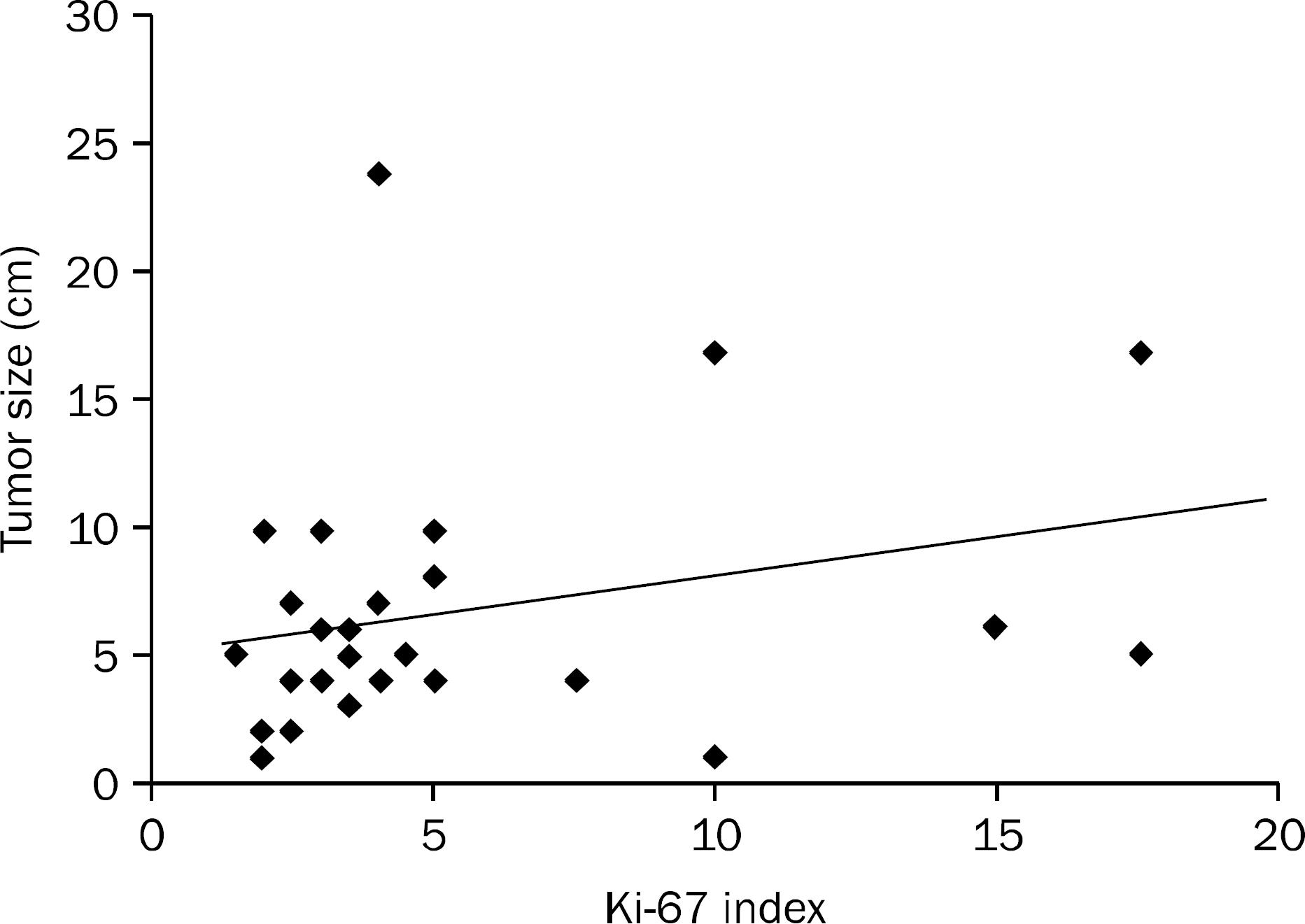
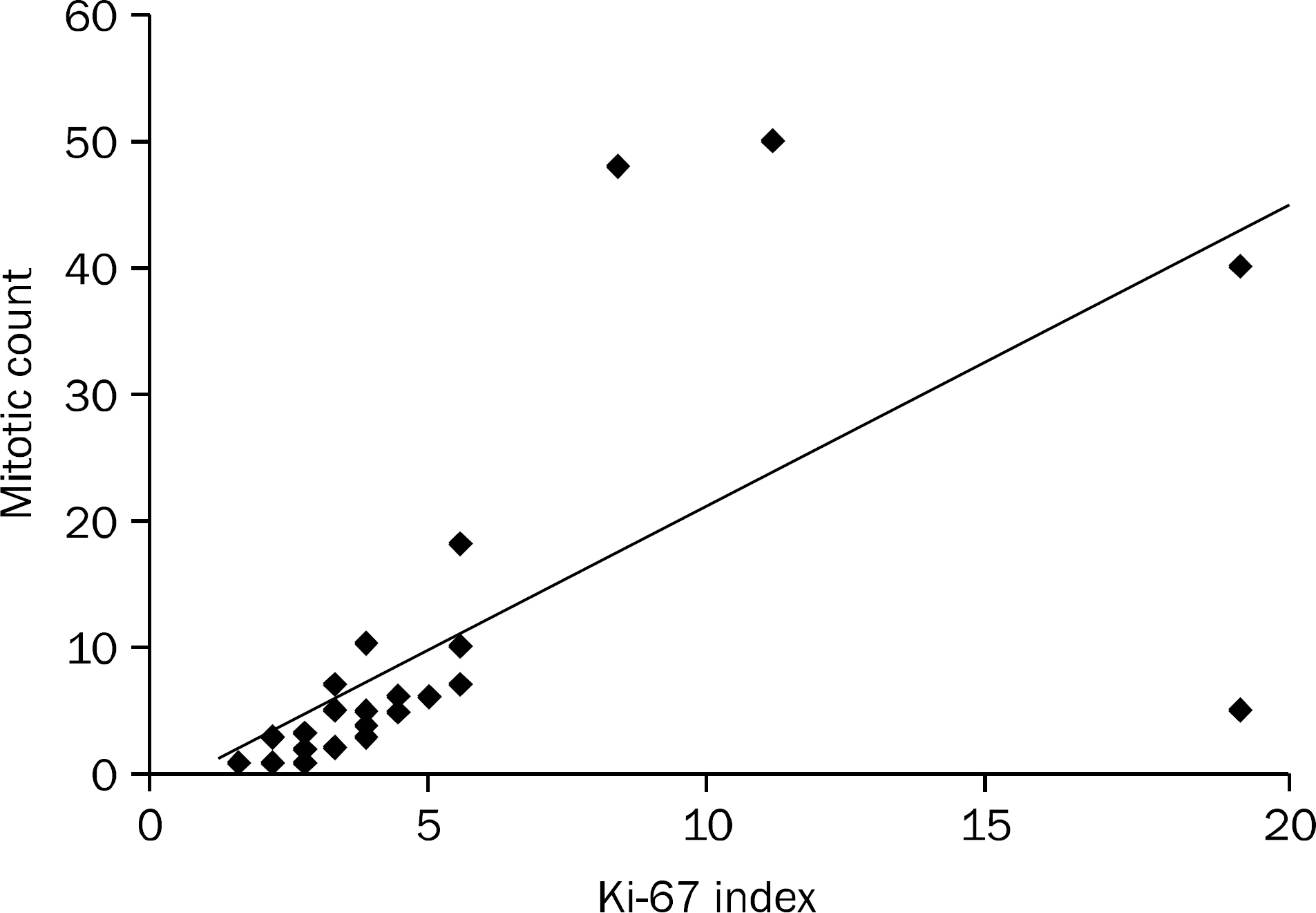
Assessment of malignant potential in gastrointestinal stromal tumor (GIST) is still problematic. The maximum tumor diameter and the mitotic index are generally used as an index of malignancy of GISTs. The Ki-67 labeling index has recently been used as an index of cell growth. The aim of this study was to investigate the prognostic value of Ki-67 in GIST.
METHODS
We retrospectively reviewed the medical records of 32 patients with GIST who underwent surgical resection at Inje University Seoul Paik Hospital. We analyzed their Ki-67 expression, histologic finding, and prognosis.
RESULTS
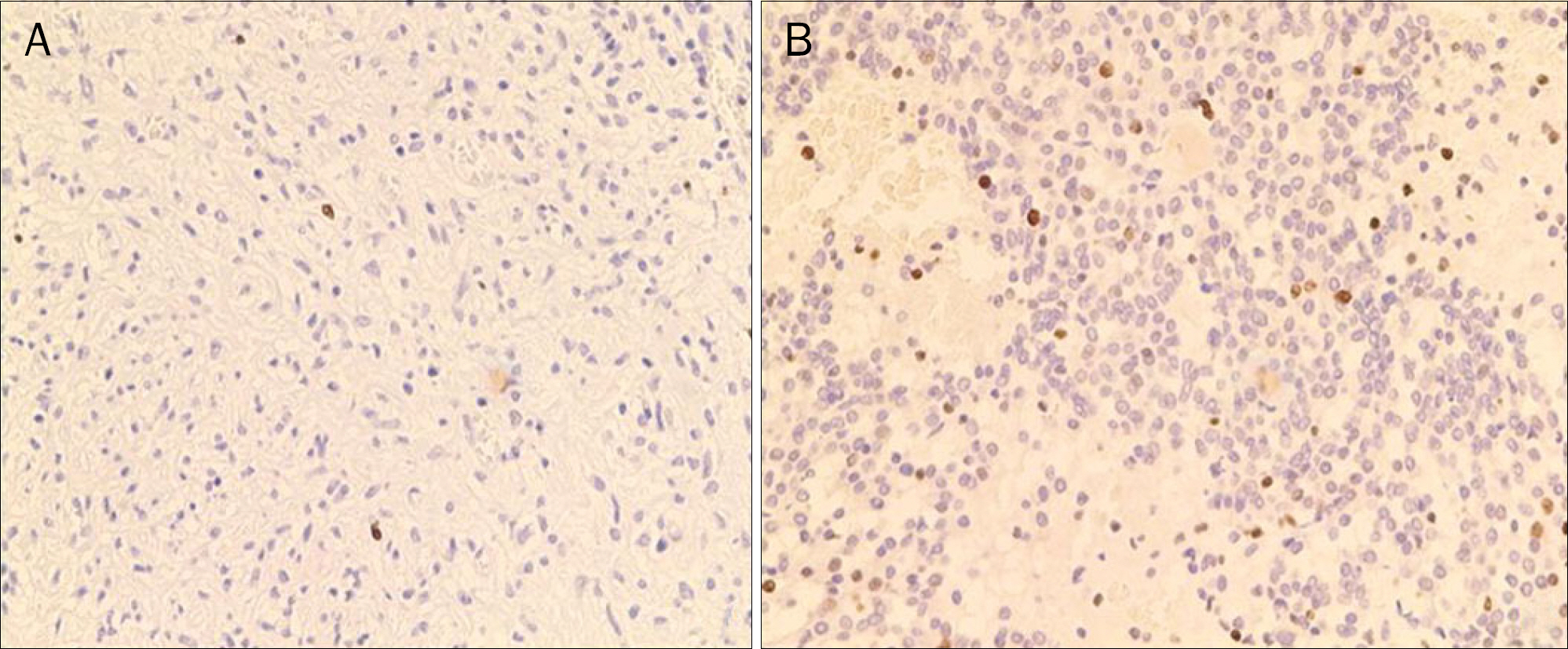
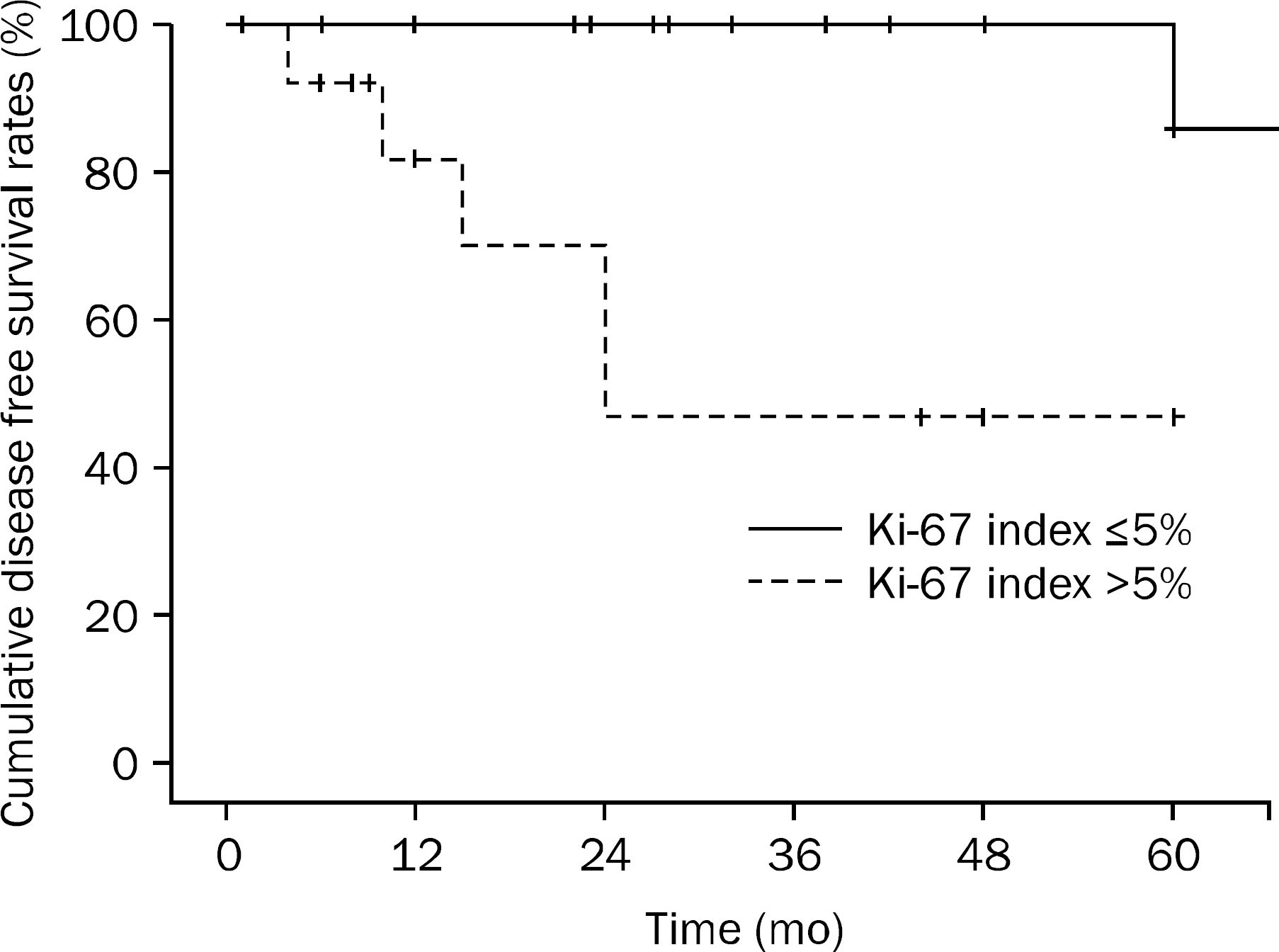
According to the tumor size and mitotic count, 4 patients were classified as very low risk, 9 patients as low risk, 14 patients as intermediate risk and 5 patients as high risk. The average Ki-67 index was 5.56+/-4.48%. The median follow-up duration was 35.72+/-29.04 months, and local/distant recurrences were observed in 6 (18.7%) patients. The overall cumulative disease free survival rates in patients with Ki-67 index < or =5% at 1 year, 2 years, and 5 years were 100%, 100%, and 86%, respectively. The overall cumulative disease free survival rates in patients with Ki-67 index >5% were at 1 year, 2 years, and 5 years were 82.1%, 70.3%, and 46.9%, respectively. There was significant relationship between elevated Ki-67 and disease free survival rate (p=0.007).
CONCLUSIONS
Our study suggests that Ki-67 index >5% confers a higher risk of relapse in patients with GIST. Future work should focus on standardization of Ki-67 assessment and specification of its role in making treatment decisions.
MeSH Terms
-
Adult
Aged
Disease-Free Survival
Female
Gastrointestinal Neoplasms/*diagnosis/mortality/pathology
Gastrointestinal Stromal Tumors/*diagnosis/mortality/pathology
Humans
Immunohistochemistry
Kaplan-Meier Estimate
Ki-67 Antigen/*metabolism
Linear Models
Male
Middle Aged
Neoplasm Recurrence, Local
Prognosis
Retrospective Studies
Ki-67 Antigen
Figure
Reference
-
References
1. George S, Desai J. Management of gastrointestinal stromal tumors in the era of tyrosine kinase inhibitors. Curr Treat Options Oncol. 2002; 3:489–496.
Article2. Efremidou EI, Liratzopoulos N, Papageorgiou MS, Romanidis K. Perforated GIST of the small intestine as a rare cause of acute abdomen: surgical treatment and adjuvant therapy. Case report. J Gastrointestin Liver Dis. 2006; 15:297–299.3. Lee SJ, Park JK, Seo HI, et al. A clinical analysis of gastrointestinal stromal tumors in small intestine: comparison of bleeding and non-bleeding group. Intest Res. 2013; 11:113–119.
Article4. Kim SY, Kim JH, Park DS, et al. A case of perforated gastrointestinal stromal tumor in the jejunum as a rare cause of acute abdomen. Intest Res. 2013; 11:134–136.
Article5. Fletcher CD, Berman JJ, Corless C, et al. Diagnosis of gastrointestinal stromal tumors: a consensus approach. Hum Pathol. 2002; 33:459–465.
Article6. Ma Y, Longley BJ, Wang X, Blount JL, Langley K, Caughey GH. Clustering of activating mutations in c-KIT's juxtamembrane coding region in canine mast cell neoplasms. J Invest Dermatol. 1999; 112:165–170.
Article7. Tian Q, Frierson HF Jr, Krystal GW, Moskaluk CA. Activating c-kit gene mutations in human germ cell tumors. Am J Pathol. 1999; 154:1643–1647.
Article8. Natkunam Y, Rouse RV, Zhu S, Fisher C, van De Rijn M. Immunoblot analysis of CD34 expression in histologically diverse neoplasms. Am J Pathol. 2000; 156:21–27.
Article9. van de Rijn M, Hendrickson MR, Rouse RV. CD34 expression by gastrointestinal tract stromal tumors. Hum Pathol. 1994; 25:766–771.
Article10. Miettinen M, El-Rifai W, Sobin LH, Lasota J. Evaluation of malignancy and prognosis of gastrointestinal stromal tumors: a review. Hum Pathol. 2002; 33:478–483.
Article11. Mazur MT, Clark HB. Gastric stromal tumors. Reappraisal of histogenesis. Am J Surg Pathol. 1983; 7:507–519.
Article12. Ranchod M, Kempson RL. Smooth muscle tumors of the gastrointestinal tract and retroperitoneum: a pathologic analysis of 100 cases. Cancer. 1977; 39:255–262.13. Amin MB, Ma CK, Linden MD, Kubus JJ, Zarbo RJ. Prognostic value of proliferating cell nuclear antigen index in gastric stromal tumors. Correlation with mitotic count and clinical outcome. Am J Clin Pathol. 1993; 100:428–432.14. Cooper PN, Quirke P, Hardy GJ, Dixon MF. A flow cytometric, clinical, and histological study of stromal neoplasms of the gastrointestinal tract. Am J Surg Pathol. 1992; 16:163–170.
Article15. Park KJ, Kim MC. Clinical prognostic factors in malignant gastrointestinal stromal tumors. Korean J Gastroenterol. 2002; 40:307–312.16. Hornick JL, Fletcher CD. The role of KIT in the management of patients with gastrointestinal stromal tumors. Hum Pathol. 2007; 38:679–687.
Article17. Liang YM, Li XH, Li WM, Lu YY. Prognostic significance of PTEN, Ki-67 and CD44s expression patterns in gastrointestinal stromal tumors. World J Gastroenterol. 2012; 18:1664–1671.
Article18. Belev B, Brč ić I, Prejac J, et al. Role of Ki-67 as a prognostic factor in gastrointestinal stromal tumors. World J Gastroenterol. 2013; 19:523–527.
Article19. Nishimura R, Osako T, Okumura Y, Hayashi M, Arima N. Clinical significance of Ki-67 in neoadjuvant chemotherapy for primary breast cancer as a predictor for chemosensitivity and for prognosis. Breast Cancer. 2010; 17:269–275.
Article20. Fisher G, Yang ZH, Kudahetti S, et al. Transatlantic Prostate Group. Prognostic value of Ki-67 for prostate cancer death in a conservatively managed cohort. Br J Cancer. 2013; 108:271–277.
Article21. Hong SM, Kim YS, Moon JS, et al. Prognostic significance of Ki-67 expression in rectal carcinoid tumors. Korean J Gastroenterol. 2013; 61:82–87.
Article22. Rudolph P, Peters J, Lorenz D, Schmidt D, Parwaresch R. Correlation between mitotic and Ki-67 labeling indices in paraf-fin-embedded carcinoma specimens. Hum Pathol. 1998; 29:1216–1222.
Article23. Ando N, Goto H, Niwa Y, et al. The diagnosis of GI stromal tumors with EUS-guided fine needle aspiration with immunohistochemical analysis. Gastrointest Endosc. 2002; 55:37–43.
Article24. Okubo K, Yamao K, Nakamura T, et al. Endoscopic ultrasound-guided fine-needle aspiration biopsy for the diagnosis of gastrointestinal stromal tumors in the stomach. J Gastroenterol. 2004; 39:747–753.
Article25. Jahng AW, Reicher S, Chung D, et al. Staining for p53 and Ki-67 increases the sensitivity of EUS-FNA to detect pancreatic malignancy. World J Gastrointest Endosc. 2010; 2:362–368.
Article26. Moon JS. Endoscopic ultrasound-guided fine needle aspiration in submucosal lesion. Clin Endosc. 2012; 45:117–123.
Article27. Dematteo RP, Ballman KV, Antonescu CR, et al. American College of Surgeons Oncology Group (ACOSOG) Intergroup Adjuvant GIST Study Team. Adjuvant imatinib mesylate after resection of lo-calised, primary gastrointestinal stromal tumour: a randomised, double-blind, placebo-controlled trial. Lancet. 2009; 373:1097–1104.
Article28. Demetri GD, Benjamin RS, Blanke CD, et al. NCCN Task Force. NCCN Task Force report: management of patients with gastrointestinal stromal tumor (GIST)–update of the NCCN clinical practice guidelines. J Natl Compr Canc Netw. 2007; 5(Suppl 2):S1–S29.
Article29. The ESMO/European Sarcoma Network Working Group. Gastrointestinal stromal tumors: ESMO Clinical Practice Guidelines for diagnosis, treatment and follow-up. Ann Oncol. 2012; 23(Suppl 7):vii49–vii55.30. Sakurai S, Fukayama M, Kaizaki Y, et al. Telomerase activity in gastrointestinal stromal tumors. Cancer. 1998; 83:2060–2066.
Article31. Schneider-Stock R, Boltze C, Lasota J, et al. High prognostic value of p16INK4 alterations in gastrointestinal stromal tumors. J Clin Oncol. 2003; 21:1688–1697.
Article32. Sohn BS, Jeon HM, Sung GY, et al. Value of elevated Ki67 index (>10%) and p53 protein expression as prognostic factors in GISTs. J Korean Surg Soc. 2004; 66:98–102.
- Full Text Links
- Actions
-
Cited
- CITED
-
- Close
- Share
- Similar articles
-
- The Expression of c-erbB-2, EGFR, p53 and Ki-67 in Ovarian Borderline Tumors and Carcinomas of the Ovary
- The Expressions of E2F1 and p53 in Gastrointestinal Stromal Tumors and Their Prognostic Significance
- The Prognostic Value of the S-phase Fraction and Ki-67 Expression in Early Breast Cancer
- Prognostic Significance of Ki-67 Expression in Rectal Carcinoid Tumors
- Expression of Topoisomerase II alpha and Ki-67 in Invasive Mammary Carcinoma and Their Clinicopathologic Implication