Korean J Perinatol.
2015 Dec;26(4):355-359. 10.14734/kjp.2015.26.4.355.
Early-onset Pericardial Effusion after Peripherally Inserted Central Venous Catheterization in a Preterm Infant
- Affiliations
-
- 1Department of Pediatrics, Keimyung University School of Medicine, Daegu, Korea. cskim@dsmc.or.kr
- KMID: 2164193
- DOI: http://doi.org/10.14734/kjp.2015.26.4.355
Abstract
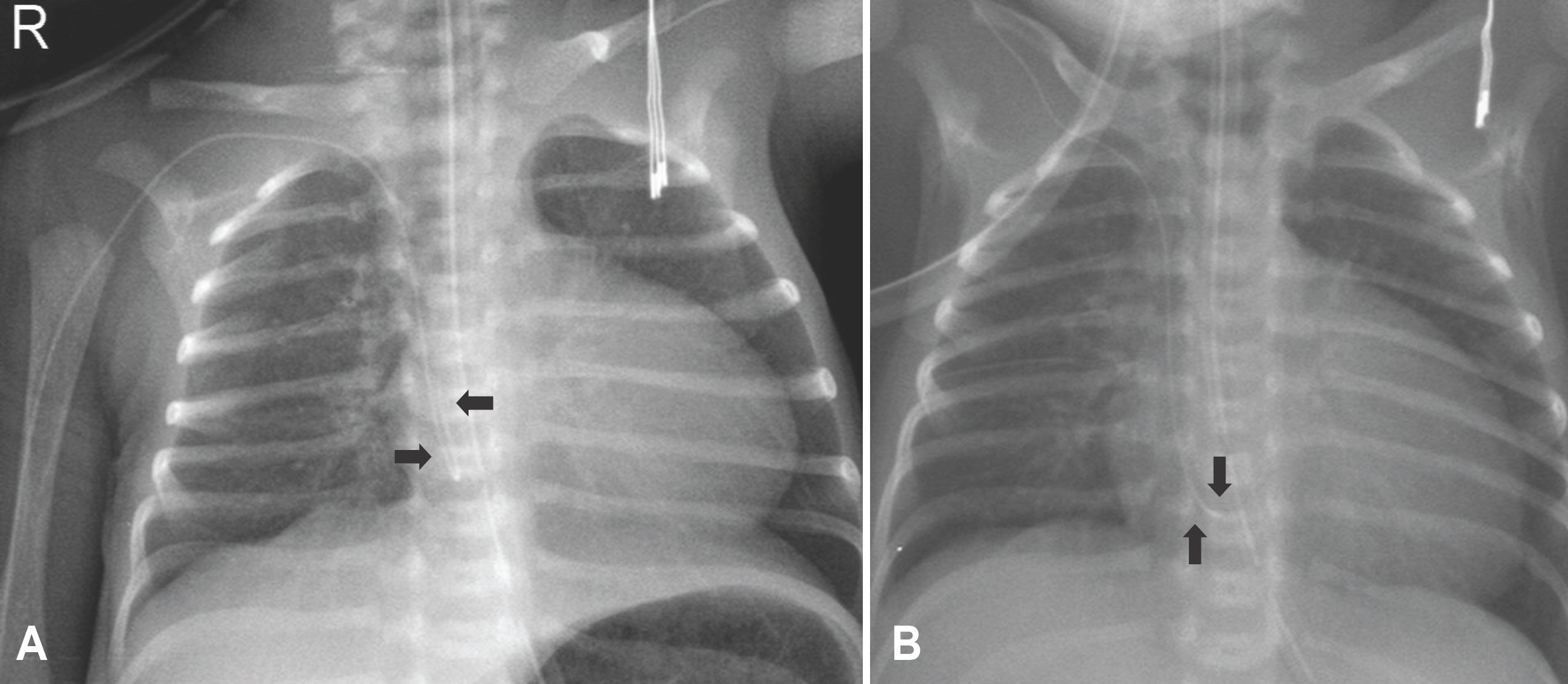
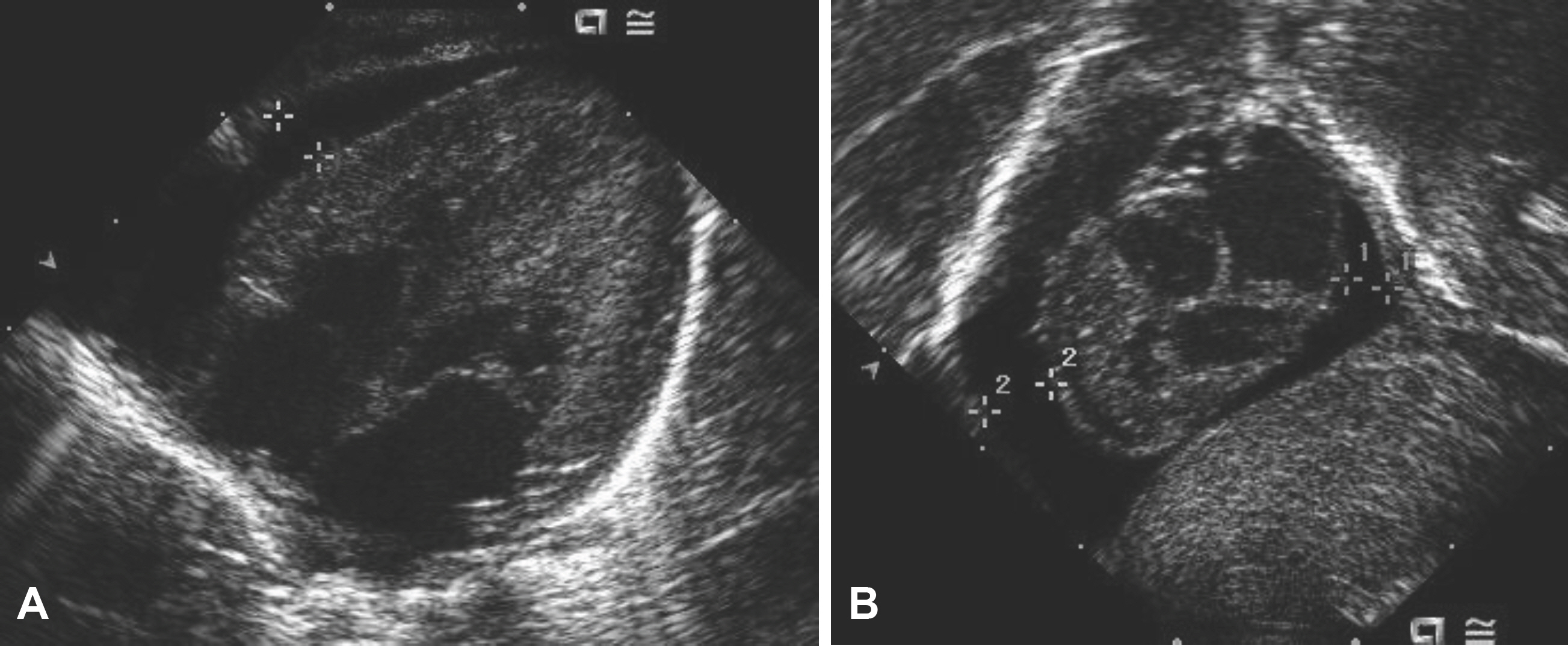
- Peripherally inserted central venous catheters (PICC) are commonly used to provide long term intravascular access for parenteral nutrition and medications in preterm infants, but rarely life-threatening complications associated with malposition of catheter tip such as pericardial effusion may be developed. We report a preterm case of early-onset pericardial effusion related to PICC of which the distal part is angulated and located in the right atrium of heart.
MeSH Terms
Figure
Reference
-
References
1. Racadio JM, Doellman DA, Johnson ND, Bean JA, Jacobs BR. Pediatric peripherally inserted central catheters: complication rates related to catheter tip location. Pediatrics. 2001; 107:e28.
Article2. Ohki Y, Maruyama K, Harigaya A, Kohno M, Arakawa H. Complications of peripherally inserted central venous catheter in Japanese neonatal intensive care units. Pediatr Int. 2013; 55:185–9.
Article3. Nowlen TT, Rosenthal GL, Johnson GL, Tom DJ, Vargo TA. Pericardial effusion and tamponade in infants with central catheters. Pediatrics. 2002; 110:137–42.
Article4. Jumani K, Advani S, Reich NG, Gosey L, Milstone AM. Risk factors for peripherally inserted central venous catheter complications in children. JAMA Pediatr. 2013; 167:429–35.
Article5. Darling JC, Newell SJ, Mohamdee O, Uzun O, Cullinane CJ, Dear PR. Central venous catheter tip in the right atrium: a risk factor for neonatal cardiac tamponade. J Perinatol. 2001; 21:461–4.
Article6. Beardsall K, White DK, Pinto EM, Kelsall AW. Pericardial effusion and cardiac tamponade as complications of neonatal long lines: are they really a problem? Arch Dis Child Fetal Neonatal Ed. 2003; 88:F292–5.
Article7. Nadroo AM, Lin J, Green RS, Magid MS, Holzman IR. Death as a complication of peripherally inserted central catheters in neonates. J Pediatr. 2001; 138:599–601.
Article8. Pizzuti A, Parodi E, Abbondi P, Frigerio M. Cardiac tamponade and successful pericardiocentesis in an extremely low birth weight neonate with percutaneously inserted central venous line: a case report. Cases J. 2010; 3:15.
Article9. Warren M, Thompson KS, Popek EJ, Vogel H, Hicks J. Pericardial effusion and cardiac tamponade in neonates: sudden unexpected death associated with total parenteral nutrition via central venous catheterization. Ann Clin Lab Sci. 2013; 43:163–71.10. Pezzati M, Filippi L, Chiti G, Dani C, Rossi S, Bertini G, et al. Central venous catheters and cardiac tamponade in preterm infants. Intens Care Med. 2004; 30:2253–6.
Article11. Giacoia GP. Cardiac tamponade and hydrothorax as complications of central venous parenteral nutrition in infants. J Parenter Enteral Nutr. 1991; 15:110–3.
Article12. Kim JS, Park HG, Go KH, Kim ER. A case of pericardial effusion complicating a percutaneous central venous catheterization in premature infant. J Korean Soc Neonatol. 1996; 3:100–4.13. Kabra NS, Kluckow MR. Survival after an acute pericardial tamponade as a result of percutaneously inserted central venous catheter in a preterm neonate. Indian J Pediatr. 2001; 68:677–80.
Article14. Neubauer AP. Percutaneous central i.v. access in the neonate: experience with 535 silastic catheters. Acta Paediatr. 1995; 84:756–60.
Article
- Full Text Links
- Actions
-
Cited
- CITED
-
- Close
- Share
- Similar articles
-
- Pleural Effusion and Diaphragmatic Palsy Associated with Peripherally Inserted Central Venous Catheter in a Preterm Infant
- A Case of Unilateral Pleural Effusion Due to Percutaneously Inserted Central Venous Catheterization
- Pericardial Effusion after Central Venous Catheterization of Subclavian Vein
- Removal of a Peripherally Inserted Central Catheter Remnant using Cardiac Catheterization in Preterm Infant
- Perforation of azygos vein and right-sided hydrothorax caused by peripherally inserted central catheter in extremely low birth weight infant