Clin Nutr Res.
2016 Jan;5(1):55-59. 10.7762/cnr.2016.5.1.55.
Effect of Salivary Reaction Time on Flow Properties of Commercial Food Thickeners Used for Dysphagic Patients
- Affiliations
-
- 1Department of Food Science and Biotechnology, Dongguk University-Seoul, Goyang, Kyunggi-do 10326, Korea. bsyoo@dongguk.edu
- 2Rheosfood Inc., Seoul 04620, Korea.
- KMID: 2162595
- DOI: http://doi.org/10.7762/cnr.2016.5.1.55
Abstract
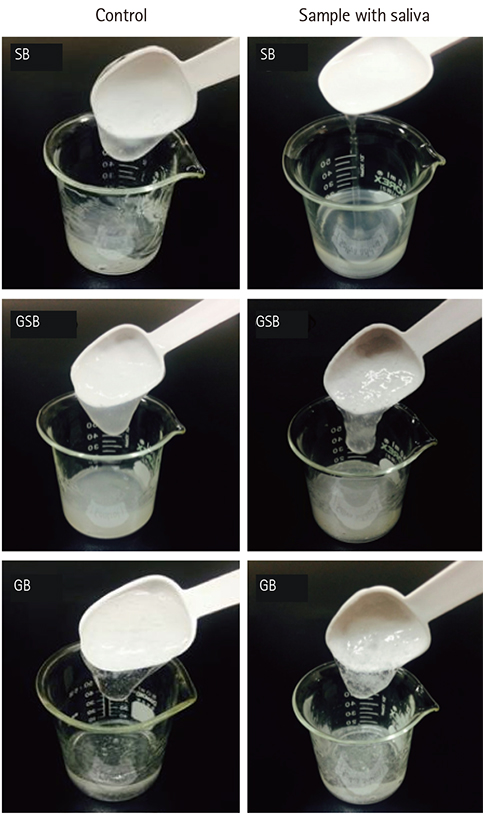
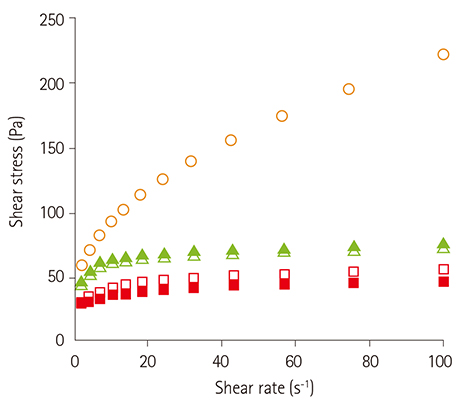
- The effect of human saliva on the flow properties of pudding-like thickened water prepared with commercial food thickeners was investigated, and their viscosity differences were also compared as a function of salivary reaction time (0-60 min after the addition of saliva). Food thickeners used in this study were starch-based (SB), gum-containing starch-based (GSB), and gumbased (GB) commercial thickeners marketed in Korea. GB showed no significant reduction in viscosity upon contact with human saliva during the salivary reaction. In contrast, SB almost completely lost its viscosity shortly after the addition of saliva, and GSB significantly reduced its viscosity after 20 min of reaction time but retained its viscosity. The results of this study indicate that GB can enhance the swallowing safety of dysphagic patients by retaining a stable viscosity level without the reduction of viscosity during consumption of thickened fluids, whereas SB may increase the possibility of aspiration owing to a rapid decrease of viscosity upon contact with human saliva.
Figure
Reference
-
1. Kim SG, Yoo B. Viscosity of dysphagia-oriented cold-thickened beverages: effect of setting time at refrigeration temperature. Int J Lang Commun Disord. 2015; 50:397–402.
Article2. Hanson B, Cox B, Kaliviotis E, Smith CH. Effects of saliva on starch-thickened drinks with acidic and neutral pH. Dysphagia. 2012; 27:427–435.
Article3. Garcia JM, Chambers E 4th, Matta Z, Clark M. Viscosity measurements of nectar- and honey-thick liquids: product, liquid, and time comparisons. Dysphagia. 2005; 20:325–335.
Article4. Glassburn DL, Deem JF. Thickener viscosity in dysphagia management: variability among speech-language pathologists. Dysphagia. 1998; 13:218–222.
Article5. Hanson B, O'Leary MT, Smith CH. The effect of saliva on the viscosity of thickened drinks. Dysphagia. 2012; 27:10–9.
Article6. Cho HM, Yoo B. Rheological characteristics of cold thickened beverages containing xanthan gum-based food thickeners used for dysphagia diets. J Acad Nutr Diet. 2015; 115:106–111.
Article7. Urlacher B, Noble O. Xanthan gum. In : Imeson AP, editor. Thickening and gelling agents for food. New York (NY): Chapman & Hall;1997. p. 284–311.8. Seo CW, Yoo B. Steady and dynamic shear rheological properties of gum-based food thickeners used for diet modification of patients with dysphagia: effect of concentration. Dysphagia. 2013; 28:205–211.
Article9. Nantanga KK, Chan E, Suleman S, Bertoft E, Seetharaman K. Differences in structures of starch hydrolysates using saliva from different individuals. Starke. 2013; 65:709–713.
Article
- Full Text Links
- Actions
-
Cited
- CITED
-
- Close
- Share
- Similar articles
-
- Factors Associated With Compliance With Viscosity-Modified Diet Among Dysphagic Patients
- Comparison of the Thickeners Used in Dysphagia Treatment
- Five Cases of Salivary Gland Swelling Developed after Upper Gastrointestiinal Endoscopy
- Comparison of Different Gum-Based Thickeners Using a Viscometer and Line Spread Test: A Preliminary Study
- Difference in Performance of Health Professionals on the Use of Food Thickeners for Dysphagia