J Korean Fract Soc.
2016 Apr;29(2):121-127. 10.12671/jkfs.2016.29.2.121.
Hypoesthesia after Open Reduction and Plate Fixation of Clavicular Midshaft Fractures: Correlation with Plate Location and Clinical Features of Hypoesthesia
- Affiliations
-
- 1Department of Orthopaedic Surgery, National Health Insurance Service Ilsan Hospital, Goyang, Korea.
- 2Department of Orthopaedic Surgery, Seonam University College of Medicine Myongji Hospital, Goyang, Korea. doctoryub@naver.com
- 3Department of Orthopaedic Surgery, Inje University Ilsan Paik Hospital, Goyang, Korea.
- KMID: 2162014
- DOI: http://doi.org/10.12671/jkfs.2016.29.2.121
Abstract
- PURPOSE
The aim of this study is to evaluate the correlation between the location of the plate and the incidence of clavicular hypoesthesia and the clinical features of patients with clavicular hypoesthesia after open reduction and internal fixation of clavicular midshaft fractures.
MATERIALS AND METHODS
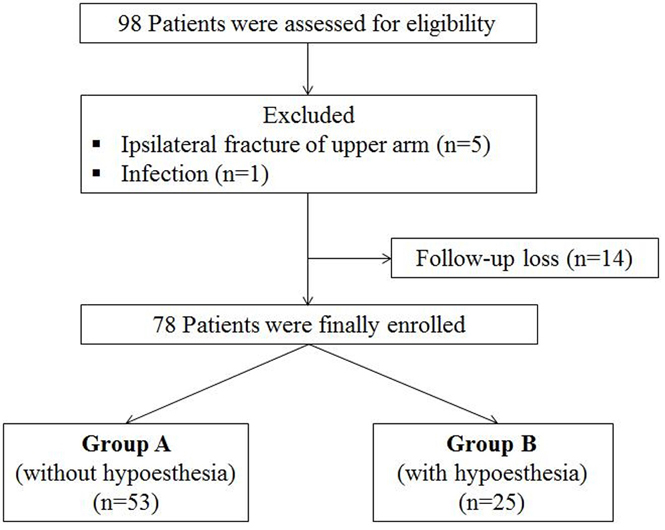
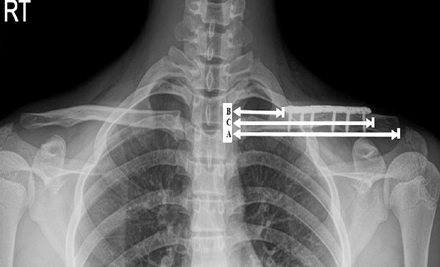
Seventy-eight patients who underwent open reduction and plate fixation for clavicle midshaft fractures between March 2013 and October 2014 were assessed for eligibility. The total clavicular length (A), the distance to the medial end of the plate from the sternoclavicular joint (B), and the distance to the lateral end of the plate from the sternoclavicular joint (C) were measured. Correlation between the location of the clavicular plate and the incidence of clavicular hypoesthesia was evaluated. In addition, the severity, and recovery of hypoesthesia were evaluated. Patient satisfaction, pain visual analogue scale were evaluated regarding hypoesthesia.
RESULTS
The incidence of hypoesthesia was 32.1% (25/78 patients). No correlation was observed with respect to the location of the clavicular plate and the incidence of clavicular hypoesthesia (p=0.666 at the medial end, p=0.369 at the lateral end). Recovery from hypoesthesia was observed in 23 out of 25 patients (p=0.008). Patient satisfaction and pain showed negative correlation with the incidence of hypoesthesia (p=0.002 and p=0.022).
CONCLUSION
There was no correlation between clavicular hypoesthesia and the plate location. Although most cases of hypoesthesia were recovered, we should try to avoid hypoesthesia due to the negative 'correlation' with patient satisfaction and pain.
Keyword
MeSH Terms
Figure
Reference
-
1. Beirer M, Postl L, Crönlein M, et al. Does a minimal invasive approach reduce anterior chest wall numbness and postoperative pain in plate fixation of clavicle fractures? BMC Musculoskelet Disord. 2015; 16:128.
Article2. Canadian Orthopaedic Trauma Society. Nonoperative treatment compared with plate fixation of displaced midshaft clavicular fractures. A multicenter, randomized clinical trial. J Bone Joint Surg Am. 2007; 89:1–10.3. Hill JM, McGuire MH, Crosby LA. Closed treatment of displaced middle-third fractures of the clavicle gives poor results. J Bone Joint Surg Br. 1997; 79:537–539.
Article4. Jeray KJ. Acute midshaft clavicular fracture. J Am Acad Orthop Surg. 2007; 15:239–248.
Article5. Khan LA, Bradnock TJ, Scott C, Robinson CM. Fractures of the clavicle. J Bone Joint Surg Am. 2009; 91:447–460.
Article6. Wang K, Dowrick A, Choi J, Rahim R, Edwards E. Post-operative numbness and patient satisfaction following plate fixation of clavicular fractures. Injury. 2010; 41:1002–1005.
Article7. Zlowodzki M, Zelle BA, Cole PA, Jeray K, McKee MD. Evidence-Based Orthopaedic Trauma Working Group. Treatment of acute midshaft clavicle fractures: systematic review of 2144 fractures: on behalf of the Evidence-Based Orthopaedic Trauma Working Group. J Orthop Trauma. 2005; 19:504–507.
Article8. McKee MD, Pedersen EM, Jones C, et al. Deficits following nonoperative treatment of displaced midshaft clavicular fractures. J Bone Joint Surg Am. 2006; 88:35–40.
Article9. Postacchini R, Gumina S, Farsetti P, Postacchini F. Long-term results of conservative management of midshaft clavicle fracture. Int Orthop. 2010; 34:731–736.
Article10. Smekal V, Oberladstaetter J, Struve P, Krappinger D. Shaft fractures of the clavicle: current concepts. Arch Orthop Trauma Surg. 2009; 129:807–815.
Article11. Christensen TJ, Horwitz DS, Kubiak EN. Natural history of anterior chest wall numbness after plating of clavicle fractures: educating patients. J Orthop Trauma. 2014; 28:642–647.
Article12. Shen WJ, Liu TJ, Shen YS. Plate fixation of fresh displaced midshaft clavicle fractures. Injury. 1999; 30:497–500.
Article13. Wang L, Ang M, Lee KT, Naidu G, Kwek E. Cutaneous hypoesthesia following plate fixation in clavicle fractures. Indian J Orthop. 2014; 48:10–13.
Article14. Nathe T, Tseng S, Yoo B. The anatomy of the supraclavicular nerve during surgical approach to the clavicular shaft. Clin Orthop Relat Res. 2011; 469:890–894.
Article15. O'Neill K, Stutz C, Duvernay M, Schoenecker J. Supraclavicular nerve entrapment and clavicular fracture. J Orthop Trauma. 2012; 26:e63–e65.
- Full Text Links
- Actions
-
Cited
- CITED
-
- Close
- Share
- Similar articles
-
- The Operative Treatment of Nonunions of Midshaft Clavicular Fractures: Reconstruction Plate Fixation and Bone Grafting
- Results of Hook Plate Fixation of Unstable Distal Clavicle Fractures
- Operative Treatment of the Clavicular Fracture with Reconstruction Plate
- Comparison of Plate Versus Threaded K-wire for Fixation of Midshaft Clavicular Fractures
- Comparison between Accurate Anatomical Reduction and Unsuccessful Reduction with a Remaining Gap after Open Reduction and Plate Fixation of Midshaft Clavicle Fracture