Korean J Urol.
2015 Jul;56(7):505-514. 10.4111/kju.2015.56.7.505.
Expression levels of heat shock protein 27 and cellular FLICE-like inhibitory protein in prostate cancer correlate with Gleason score sum and pathologic stage
- Affiliations
-
- 1Department of Urology, Hanyang University Guri Hospital, Hanyang University School of Medicine, Guri, Korea.
- 2Department of Urology, Eulji University College of Medicine, Daejeon, Korea. ytk5202@eulji.ac.kr
- 3Department of Pathology, Eulji University College of Medicine, Daejeon, Korea.
- KMID: 2160647
- DOI: http://doi.org/10.4111/kju.2015.56.7.505
Abstract
- PURPOSE
Heat shock protein (HSP) 27 protects the cell by controlling apoptosis and immune reactions, and c-FLIP (cellular-FLICE inhibitory protein) inhibits apoptosis by inhibiting caspase-8 activity. We investigated the relationship of HSP27 and c-FLIP expression to prostate-specific antigen, Gleason score sum (GSS), and pathologic stage.
MATERIALS AND METHODS
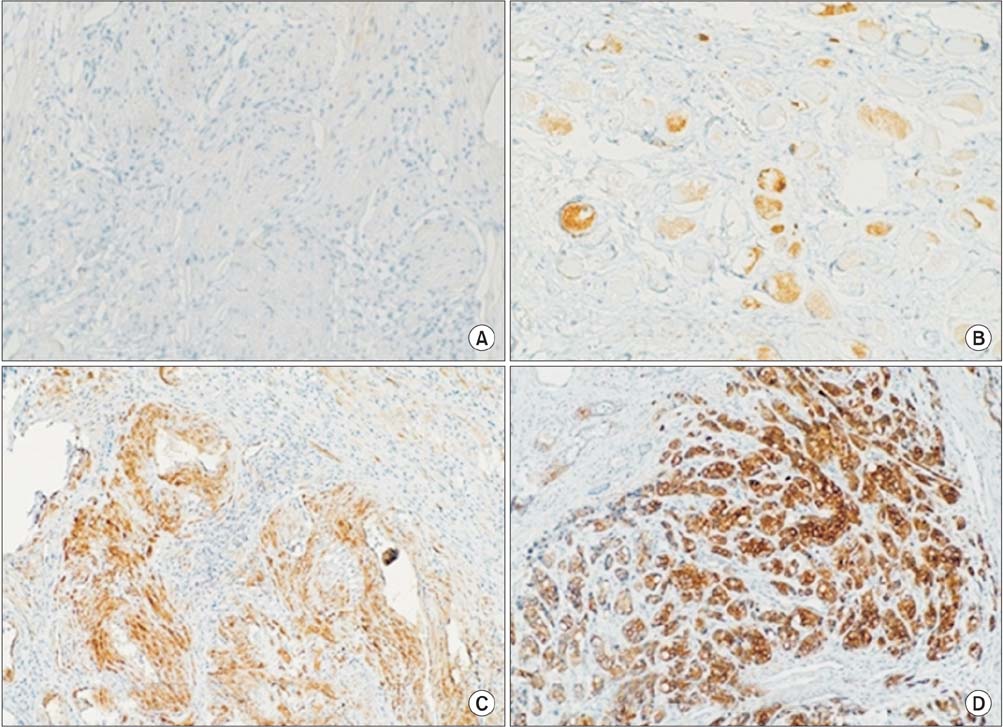
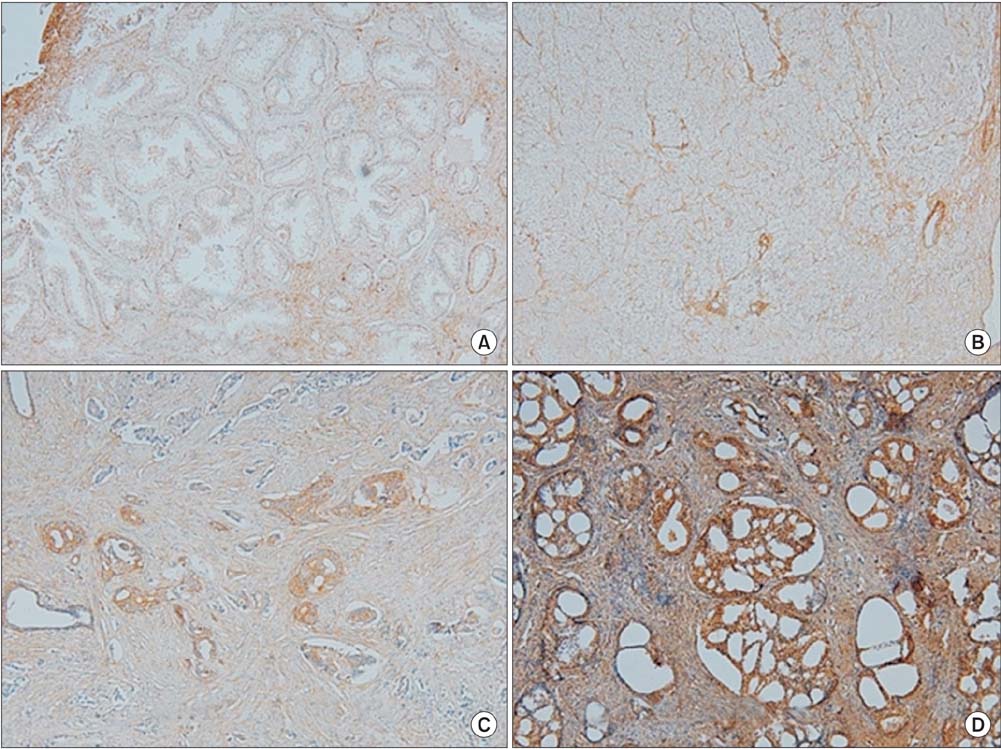
Samples from 163 patients between May 2004 and April 2010 were analyzed: 83 from patients that had underwent a radical prostatectomy, and 80 from those that underwent transurethral resection of the prostate to alleviate urinary symptoms from benign prostate hyperplasia. c-FLIP and HSP27 expression were observed by immunohistochemistry staining. Samples with less than 5% expression-positive cells were scored as 1, with 5%-50% were scored as 2, and with more than 50% were scored as 3. Local reactions were identified as 0.5 and evaluated.
RESULTS
Both the presence of HSP27 within the tumor and the number of cancer cells positive for HSP27 were significantly correlated to GSS and pathologic stage (p<0.001, p=0.001, p<0.001, p<0.001). The same was true for c-FLIP expression (p<0.001). GSS was more highly correlated to HSP27 expression than to c-FLIP expression (r=0.814 for HSP27, r=0.776 for c-FLIP), as was pathologic stage (r=0.592 for HSP27, r=0.554 for c-FLIP).
CONCLUSIONS
In prostate cancer, higher GSS and a more advanced pathologic stage were associated with a higher likelihood of having a HSP27-positive tumor and more HSP27-positive tumor cells. HSP27 expression was correlated with GSS and prostate cancer stage. A more advanced pathologic stage corresponded to a higher likelihood of having a c-FLIP-positive tumor and more c-FLIP-positive tumor cells. HSP27 expression had a higher correlation with prostate cancer stage and GSS than c-FLIP expression did.
MeSH Terms
-
Aged
Biomarkers, Tumor/*metabolism
CASP8 and FADD-Like Apoptosis Regulating Protein/*metabolism
HSP27 Heat-Shock Proteins/*metabolism
Humans
Lymphatic Metastasis
Male
Middle Aged
Neoplasm Grading
Neoplasm Proteins/metabolism
Neoplasm Staging
Prostatectomy/methods
Prostatic Hyperplasia/metabolism/surgery
Prostatic Neoplasms/*metabolism/pathology/surgery
Transurethral Resection of Prostate
Biomarkers, Tumor
CASP8 and FADD-Like Apoptosis Regulating Protein
HSP27 Heat-Shock Proteins
Neoplasm Proteins
Figure
Reference
-
1. Rocchi P, Beraldi E, Ettinger S, Fazli L, Vessella RL, Nelson C, et al. Increased Hsp27 after androgen ablation facilitates androgen-independent progression in prostate cancer via signal transducers and activators of transcription 3-mediated suppression of apoptosis. Cancer Res. 2005; 65:11083–11093.2. Atkins D, Lichtenfels R, Seliger B. Heat shock proteins in renal cell carcinomas. Contrib Nephrol. 2005; 148:35–56.3. Rocchi P, So A, Kojima S, Signaevsky M, Beraldi E, Fazli L, et al. Heat shock protein 27 increases after androgen ablation and plays a cytoprotective role in hormone-refractory prostate cancer. Cancer Res. 2004; 64:6595–6602.4. Hyer ML, Sudarshan S, Kim Y, Reed JC, Dong JY, Schwartz DA, et al. Downregulation of c-FLIP sensitizes DU145 prostate cancer cells to Fas-mediated apoptosis. Cancer Biol Ther. 2002; 1:401–406.5. Korkolopoulou P, Goudopoulou A, Voutsinas G, Thomas-Tsagli E, Kapralos P, Patsouris E, et al. c-FLIP expression in bladder urothelial carcinomas: its role in resistance to Fasmediated apoptosis and clinicopathologic correlations. Urology. 2004; 63:1198–1204.6. Lee SH, Kim HS, Kim SY, Lee YS, Park WS, Kim SH, et al. Increased expression of FLIP, an inhibitor of Fas-mediated apoptosis, in stomach cancer. APMIS. 2003; 111:309–314.7. Kaulfuss S, Burfeind P, Gaedcke J, Scharf JG. Dual silencing of insulin-like growth factor-I receptor and epidermal growth factor receptor in colorectal cancer cells is associated with decreased proliferation and enhanced apoptosis. Mol Cancer Ther. 2009; 8:821–833.8. Day TW, Sinn AL, Huang S, Pollok KE, Sandusky GE, Safa AR. c-FLIP gene silencing eliminates tumor cells in breast cancer xenografts without affecting stromal cells. Anticancer Res. 2009; 29:3883–3886.9. Lanneau D, de Thonel A, Maurel S, Didelot C, Garrido C. Apoptosis versus cell differentiation: role of heat shock proteins HSP90, HSP70 and HSP27. Prion. 2007; 1:53–60.10. Cornford PA, Dodson AR, Parsons KF, Desmond AD, Woolfenden A, Fordham M, et al. Heat shock protein expression independently predicts clinical outcome in prostate cancer. Cancer Res. 2000; 60:7099–7105.11. Lee SW, Kim EK, Kim SS, Uh HS, Cha KS, Yoo TK. Expression of Heat Shock Protein 27 according to Gleason Score and Pathologic Stage of Prostate Cancer. Korean J Urol. 2009; 50:547–552.12. Kim SS, Cho HJ, Kang JY, Kang HK, Yoo TK. Inhibition of androgen receptor expression with small interfering RNA enhances cancer cell apoptosis by suppressing survival factors in androgen insensitive, late stage LNCaP cells. ScientificWorldJournal. 2013; 2013:519397.13. Nakajima A, Komazawa-Sakon S, Takekawa M, Sasazuki T, Yeh WC, Yagita H, et al. An antiapoptotic protein, c-FLIPL, directly binds to MKK7 and inhibits the JNK pathway. EMBO J. 2006; 25:5549–5559.14. Xu L, Chen S, Bergan RC. MAPKAPK2 and HSP27 are downstream effectors of p38 MAP kinase-mediated matrix metalloproteinase type 2 activation and cell invasion in human prostate cancer. Oncogene. 2006; 25:2987–2998.15. Lotan TL, Lyon M, Huo D, Taxy JB, Brendler C, Foster BA, et al. Up-regulation of MKK4, MKK6 and MKK7 during prostate cancer progression: an important role for SAPK signalling in prostatic neoplasia. J Pathol. 2007; 212:386–394.16. Pavese JM, Ogden IM, Voll EA, Huang X, Xu L, Jovanovic B, et al. Mitogen-activated protein kinase kinase 4 (MAP2K4) promotes human prostate cancer metastasis. PLoS One. 2014; 9:e102289.17. Charafe-Jauffret E, Tarpin C, Bardou VJ, Bertucci F, Ginestier C, Braud AC, et al. Immunophenotypic analysis of inflammatory breast cancers: identification of an 'inflammatory signature'. J Pathol. 2004; 202:265–273.18. Sarto C, Valsecchi C, Magni F, Tremolada L, Arizzi C, Cordani N, et al. Expression of heat shock protein 27 in human renal cell carcinoma. Proteomics. 2004; 4:2252–2260.19. Concannon CG, Orrenius S, Samali A. Hsp27 inhibits cytochrome c-mediated caspase activation by sequestering both pro-caspase-3 and cytochrome c. Gene Expr. 2001; 9:195–201.20. Erkizan O, Kirkali G, Yorukoglu K, Kirkali Z. Significance of heat shock protein-27 expression in patients with renal cell carcinoma. Urology. 2004; 64:474–478.21. Miyake H, Muramaki M, Kurahashi T, Takenaka A, Fujisawa M. Expression of potential molecular markers in prostate cancer: correlation with clinicopathological outcomes in patients undergoing radical prostatectomy. Urol Oncol. 2010; 28:145–151.22. Teimourian S, Jalal R, Sohrabpour M, Goliaei B. Down-regulation of Hsp27 radiosensitizes human prostate cancer cells. Int J Urol. 2006; 13:1221–1225.23. Day TW, Huang S, Safa AR. c-FLIP knockdown induces ligand-independent DR5-, FADD-, caspase-8-, and caspase-9-dependent apoptosis in breast cancer cells. Biochem Pharmacol. 2008; 76:1694–1704.24. Longley DB, Wilson TR, McEwan M, Allen WL, McDermott U, Galligan L, et al. c-FLIP inhibits chemotherapy-induced colorectal cancer cell death. Oncogene. 2006; 25:838–848.25. Zhang X, Jin TG, Yang H, DeWolf WC, Khosravi-Far R, Olumi AF. Persistent c-FLIP(L) expression is necessary and sufficient to maintain resistance to tumor necrosis factor-related apoptosis-inducing ligand-mediated apoptosis in prostate cancer. Cancer Res. 2004; 64:7086–7091.26. Ye H, Li Y, Melamed J, Pearce P, Wei J, Chiriboga L, et al. Stromal anti-apoptotic androgen receptor target gene c-FLIP in prostate cancer. J Urol. 2009; 181:872–877.27. Wilson C, Wilson T, Johnston PG, Longley DB, Waugh DJ. Interleukin-8 signaling attenuates TRAIL- and chemotherapy-induced apoptosis through transcriptional regulation of c-FLIP in prostate cancer cells. Mol Cancer Ther. 2008; 7:2649–2661.28. Gao S, Lee P, Wang H, Gerald W, Adler M, Zhang L, et al. The androgen receptor directly targets the cellular Fas/FasL-associated death domain protein-like inhibitory protein gene to promote the androgen-independent growth of prostate cancer cells. Mol Endocrinol. 2005; 19:1792–1802.29. Kao CJ, Martiniez A, Shi XB, Yang J, Evans CP, Dobi A, et al. miR-30 as a tumor suppressor connects EGF/Src signal to ERG and EMT. Oncogene. 2014; 33:2495–2503.30. Roe K, Bratland A, Vlatkovic L, Ragnum HB, Saelen MG, Olsen DR, et al. Hypoxic tumor kinase signaling mediated by STAT5A in development of castration-resistant prostate cancer. PLoS One. 2013; 8:e63723.
- Full Text Links
- Actions
-
Cited
- CITED
-
- Close
- Share
- Similar articles
-
- Expression of Heat Shock Protein 27 according to Gleason Score and Pathologic Stage of Prostate Cancer
- Environmental factors regulating the expression of Porphyromonas gingivalis heat shock protein
- Silencing of Heat Shock Protein 27 Expression Accelerates Doxazosin-induced Apoptosis in Prostate Cancer Cell Line PC-3
- Expression of Heat Shock Protein 70 m-RNA in Rat Bladder Overdistended by Diuresis
- The Protective Effect of Induced Heat Shock Protein in Human Corneal Epithelial Cells