J Korean Med Sci.
2015 Jun;30(6):743-748. 10.3346/jkms.2015.30.6.743.
Organ Correlation in IgG4-Related Diseases
- Affiliations
-
- 1Department of Internal Medicine, Tokyo Metropolitan Komagome Hospital, Tokyo Japan. kamisawa@cick.jp
- KMID: 2160603
- DOI: http://doi.org/10.3346/jkms.2015.30.6.743
Abstract
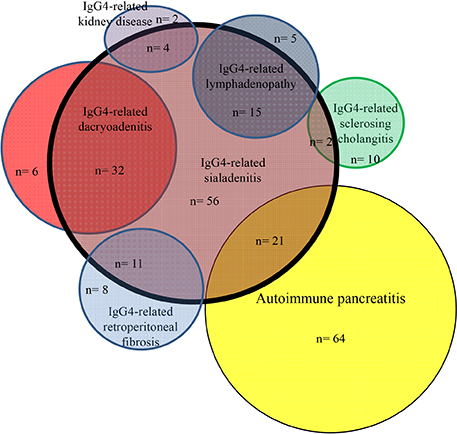
- IgG4-related disease (IgG4-RD) is a potentially multiorgan disorder. In this study, clinical and serological features from 132 IgG4-RD patients were compared about organ correlations. Underlying pathologies comprised autoimmune pancreatitis (AIP) in 85 cases, IgG4-related sclerosing cholangitis (IgG4-SC) in 12, IgG4-related sialadenitis (IgG4-SIA) in 56, IgG4-related dacryoadenitis (IgG4-DAC) in 38, IgG4-related lymphadenopathy (IgG4-LYM) in 20, IgG4-related retroperitoneal fibrosis (IgG4-RF) in 19, IgG4-related kidney disease (IgG4-KD) in 6, IgG4-related pseudotumor (IgG4-PT) in 3. Sixty-five patients (49%) had multiple IgG4-RD (two affected organs in 36 patients, three in 19, four in 8, five in 1, and six in 1). Serum IgG4 levels were significantly higher with multiple lesions than with a single lesion (P<0.001). The proportion of association with other IgG4-RD was 42% in AIP, the lowest of all IgG4-RDs. Serum IgG4 level was lower in AIP than in other IgG4-RDs. Frequently associated IgG4-RDs were SIA (25%) and DAC (12%) for AIP; AIP (75%) for IgG4-SC; DAC (57%), AIP (38%) and LYM (27%) for IgG4-SIA; AIP (26%) and LYM (26%) for IgG4-DAC; SIA (75%), DAC (50%) and AIP (45%) for IgG4-LYM; SIA (58%), AIP (42%) and LYM (32%) for IgG4-RF; AIP (100%) and SIA (67%) for IgG4-KID; and DAC (67%) and SIA (67%) for IgG4-PT. Most associated IgG4-RD lesions were diagnosed simultaneously, but IgG4-SIA and IgG4-DAC were sometimes identified before other lesions. About half of IgG4-RD patients had multiple IgG4-RD lesions, and some associations were seen between specific organs.
Keyword
MeSH Terms
Figure
Cited by 1 articles
-
Overview of IgG4-Related Tubulointerstitial Nephritis and Its Mimickers
Hyeon Joo Jeong, Su-Jin Shin, Beom Jin Lim
J Pathol Transl Med. 2016;50(1):26-36. doi: 10.4132/jptm.2015.11.09.
Reference
-
1. Stone JH, Zen Y, Deshpande V. IgG4-related disease. N Engl J Med. 2012; 366:539–551.2. Umehara H, Okazaki K, Masaki Y, Kawano M, Yamamoto M, Saeki T, Matsui S, Yoshino T, Nakamura S, Kawa S, et al. Comprehensive diagnostic criteria for IgG4-related disease (IgG4-RD), 2011. Mod Rheumatol. 2012; 22:21–30.3. Kamisawa T, Zen Y, Pillai S, Stone JH. IgG4-related disease. Lancet. 2015; 385:1460–1471.4. Kamisawa T, Funata N, Hayashi Y, Eishi Y, Koike M, Tsuruta K, Okamoto A, Egawa N, Nakajima H. A new clinicopathological entity of IgG4-related autoimmune disease. J Gastroenterol. 2003; 38:982–984.5. Kamisawa T, Takuma K, Egawa N, Tsuruta K, Sasaki T. Autoimmune pancreatitis and IgG4-related sclerosing disease. Nat Rev Gastroenterol Hepatol. 2010; 7:401–409.6. Shimosegawa T, Chari ST, Frulloni L, Kamisawa T, Kawa S, Mino-Kenudson M, Kim MH, Klöppel G, Lerch MM, Löhr M, et al. International Association of Pancreatology. International consensus diagnostic criteria for autoimmune pancreatitis: guidelines of the International Association of Pancreatology. Pancreas. 2011; 40:352–358.7. Ohara H, Okazaki K, Tsubouchi H, Inui K, Kawa S, Kamisawa T, Tazuma S, Uchida K, Hirano K, Yoshida H, et al. Research Committee of IgG4-related Diseases. Research Committee of Intractable Diseases of Liver and Biliary Tract. Ministry of Health, Labor and Welfare, Japan. Japan Biliary Association. Clinical diagnostic criteria of IgG4-related sclerosing cholangitis 2012. J Hepatobiliary Pancreat Sci. 2012; 19:536–542.8. Chiba K, Kamisawa T, Tabata T, Hara S, Kuruma S, Fujiwara T, Kuwata G, Egashira H, Koizumi K, Koizumi S, et al. Clinical features of 10 patients with IgG4-related retroperitoneal fibrosis. Intern Med. 2013; 52:1545–1551.9. Kawano M, Saeki T, Nakashima H, Nishi S, Yamaguchi Y, Hisano S, Yamanaka N, Inoue D, Yamamoto M, Takahashi H, et al. Proposal for diagnostic criteria for IgG4-related kidney disease. Clin Exp Nephrol. 2011; 15:615–626.10. Ohara H, Nakazawa T, Sano H, Ando T, Okamoto T, Takada H, Hayashi K, Kitajima Y, Nakao H, Joh T. Systemic extrapancreatic lesions associated with autoimmune pancreatitis. Pancreas. 2005; 31:232–237.11. Okazaki K. Autoimmune pancreatitis: etiology, pathogenesis, clinical findings and treatment. The Japanese experience. JOP. 2005; 6:89–96.12. Hamano H, Arakura N, Muraki T, Ozaki Y, Kiyosawa K, Kawa S. Prevalence and distribution of extrapancreatic lesions complicating autoimmune pancreatitis. J Gastroenterol. 2006; 41:1197–1205.13. Kanno A, Nishimori I, Masamune A, Kikuta K, Hirota M, Kuriyama S, Tsuji I, Shimosegawa T. Research Committee on Intractable Diseases of Pancreas. Nationwide epidemiological survey of autoimmune pancreatitis in Japan. Pancreas. 2012; 41:835–839.14. Moriyama M, Tanaka A, Maehara T, Ohyama Y, Shimizu M, Nakashima H, Hayashida JN, Shinozaki S, Kubo Y, Furukawa S, et al. Clinical characteristics of Mikulicz's disease as an IgG4-related disease. Clin Oral Investig. 2013; 17:1995–2002.15. Sato Y, Kojima M, Takata K, Morito T, Asaoku H, Takeuchi T, Mizobuchi K, Fujihara M, Kuraoka K, Nakai T, et al. Systemic IgG4-related lymphadenopathy: a clinical and pathologic comparison to multicentric Castleman's disease. Mod Pathol. 2009; 22:589–599.16. Cheuk W, Yuen HK, Chu SY, Chiu EK, Lam LK, Chan JK. Lymphadenopathy of IgG4-related sclerosing disease. Am J Surg Pathol. 2008; 32:671–681.17. Zen Y, Onodera M, Inoue D, Kitao A, Matsui O, Nohara T, Namiki M, Kasashima S, Kawashima A, Matsumoto Y, et al. Retroperitoneal fibrosis: a clinicopathologic study with respect to immunoglobulin G4. Am J Surg Pathol. 2009; 33:1833–1839.18. Saeki T, Kawano M, Mizushima I, Yamamoto M, Wada Y, Nakashima H, Homma N, Tsubata Y, Takahashi H, Ito T, et al. The clinical course of patients with IgG4-related kidney disease. Kidney Int. 2013; 84:826–833.19. Ozaki Y, Oguchi K, Hamano H, Arakura N, Muraki T, Kiyosawa K, Momose M, Kadoya M, Miyata K, Aizawa T, et al. Differentiation of autoimmune pancreatitis from suspected pancreatic cancer by fluorine-18 fluorodeoxyglucose positron emission tomography. J Gastroenterol. 2008; 43:144–151.20. Zhang J, Chen H, Ma Y, Xiao Y, Niu N, Lin W, Wang X, Liang Z, Zhang F, Li F, et al. Characterizing IgG4-related disease with 18F-FDG PET/CT: a prospective cohort study. Eur J Nucl Med Mol Imaging. 2014; 41:1624–1634.21. Yamamoto M, Takahashi H, Ohara M, Suzuki C, Naishiro Y, Yamamoto H, Shinomura Y, Imai K. A new conceptualization for Mikulicz's disease as an IgG4-related plasmacytic disease. Mod Rheumatol. 2006; 16:335–340.22. Kubota K, Wada T, Kato S, Mozaki Y, Yoneda M, Fujita K, Takahashi H, Inamori M, Abe Y, Kobayashi N, et al. Highly active state of autoimmune pancreatitis with mikulicz disease. Pancreas. 2010; 39:e6–e10.
- Full Text Links
- Actions
-
Cited
- CITED
-
- Close
- Share
- Similar articles
-
- Overview of the Immunoglobulin G4-related Disease Spectrum
- Advances in IgG4-related Hepatobiliary Disease
- Recurrent Submandibular Mass and Bilateral Periorbital Edema in IgG4-Related Disease: A Case Report
- Recent Updates of Immunoglobulin G4-related Pancreatobiliary Disease
- Classification and Diagnostic Criteria for IgG4-Related Sclerosing Cholangitis