Lab Med Online.
2016 Apr;6(2):60-63. 10.3343/lmo.2016.6.2.60.
Massive Transfusion Protocols for Pediatric Patients
- Affiliations
-
- 1Department of Laboratory Medicine, Gachon University Gil Medical Center, Incheon, Korea. khkim74@gilhospital.com
- 2Department of Trauma, Gachon University Gil Medical Center, Incheon, Korea.
- KMID: 2160085
- DOI: http://doi.org/10.3343/lmo.2016.6.2.60
Abstract
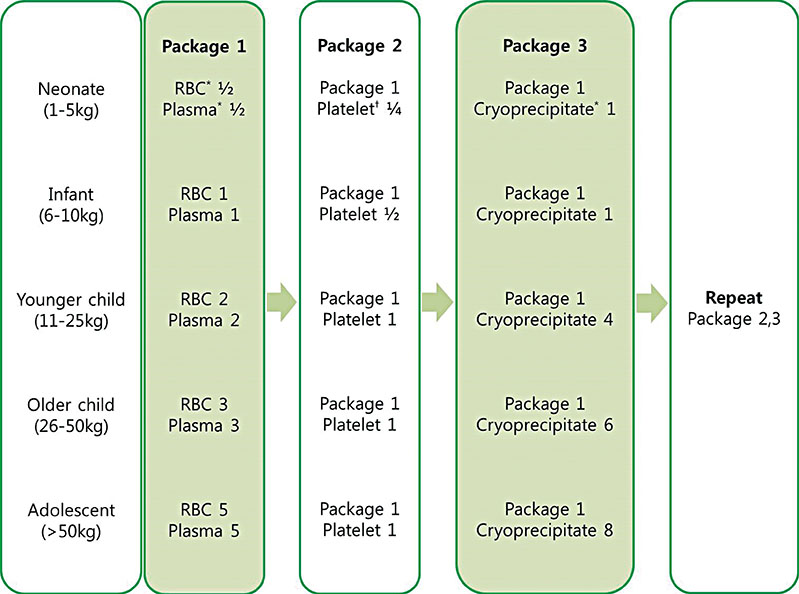
- The number of massive transfusions for pediatric patients has risen owing to the increasing number of complex surgeries and trauma centers. However, as there are only a few studies on pediatric massive transfusion, adult massive transfusion protocols are used for pediatric patients in many hospitals and institutions. Although massive transfusion protocols would improve the outcomes and reduce the received blood products during transfusion, pediatric patients differ from adults in the tolerability to transfusion, incidence of coagulopathy, and mechanisms of injuries. Therefore clinical physicians have requested for a pediatric massive transfusion protocol. Herein, we reviewed pediatric massive transfusion protocols that have been used in various clinical settings. To date, only a few single-center studies with a small number of pediatric patients have been performed. Even though these studies did not show improvement in outcomes such as mortality and side effects, they reported a short preparation time for fresh frozen plasma products and a low coagulopathy rate in pediatric massive transfusion groups. Therefore, large, prospective, multicenter studies are needed to identify the empiric ratio of blood products for improving outcomes of pediatric patients who need massive transfusion.
Figure
Reference
-
1. Han KS, Park KW, et al. Transfusion medicine. 4th ed. Seoul: Medical Book Publisher;2014. p. 94–109.2. The Korean Society of Blood Transfusion. Transfusion Guideline. 2nd ed. Updated on Feb 2013. http://www.transfusion.or.kr/file/medicine/guideline_2014.pdf.3. Yoon S, Park AJ, Kim HO. Clinical observation study of massive blood transfusion in a tertiary care hospital in Korea. Yonsei Med J. 2011; 52:469–475.
Article4. Bhananker SM, Ramaiah R. Trends in trauma transfusion. Int J Crit Illn Inj Sci. 2011; 1:51–56.
Article5. Cotton BA, Gunter OL, Isbell J, Au BK, Robertson AM, Morris JA Jr, et al. Damage control hematology: the impact of a trauma exsanguination protocol on survival and blood product utilization. J Trauma. 2008; 64:1177–1182.
Article6. Hendrickson JE, Shaz BH, Pereira G, Atkins E, Johnson KK, Bao G, et al. Coagulopathy is prevalent and associated with adverse outcomes in transfused pediatric trauma patients. J Pediatr. 2012; 160:204–209.
Article7. Transfusion Committee. Massive Transfusion Protocol. University of Michigan Hospitals and Health Centers;Updated on April 2013. https://www.pathology.med.umich.edu.8. Hendrickson JE, Shaz BH, Pereira G, Parker PM, Jessup P, Atwell F, et al. Implementation of a pediatric trauma massive transfusion protocol: one institution's experience. Transfusion. 2012; 52:1228–1236.
Article9. Chidester SJ, Williams N, Wang W, Groner JI. A pediatric massive transfusion protocol. J Trauma Acute Care Surg. 2012; 73:1273–1277.
Article10. Nosanov L, Inaba K, Okoye O, Resnick S, Upperman J, Shulman I, et al. The impact of blood product ratios in massively transfused pediatric trauma patients. Am J Surg. 2013; 206:655–660.
Article11. Dressler AM, Finck CM, Carroll CL, Bonanni CC, Spinella PC. Use of a massive transfusion protocol with hemostatic resuscitation for severe intraoperative bleeding in a child. J Pediatr Surg. 2010; 45:1530–1533.
Article12. Paterson NA. Validation of a theoretically derived model for the management of massive blood loss in pediatric patients-a case report. Paediatr Anaesth. 2009; 19:535–540.
Article
- Full Text Links
- Actions
-
Cited
- CITED
-
- Close
- Share
- Similar articles
-
- A Simple Comment of Trauma-Induced Coagulopathy and Massive Transfusion
- Analysis of Trauma Patients with Massive Transfusion in the Emergency Department
- Damage control resuscitation in children
- Suggestion to Use Optimal ABO Non-Identical but Compatible RBC Components in Emergency/Massive Transfusions: Are Type O RBC the Second Best for Type AB Patients?
- A Clinical Experience of Massive Transfusion in a Patient with Cardiac Arrest Resulting from Abdominal Aortic Aneurysm Rupture