Ann Clin Microbiol.
2016 Mar;19(1):20-23. 10.5145/ACM.2016.19.1.20.
An Effective Method of RNA Extraction from Mycobacterium tuberculosis
- Affiliations
-
- 1Department of Biomedical Science, Graduate School, Kyung Hee University, Seoul, Korea.
- 2Department of Laboratory Medicine, Kyung Hee University School of Medicine, Seoul, Korea. leehejo@khmc.or.kr
- KMID: 2160081
- DOI: http://doi.org/10.5145/ACM.2016.19.1.20
Abstract
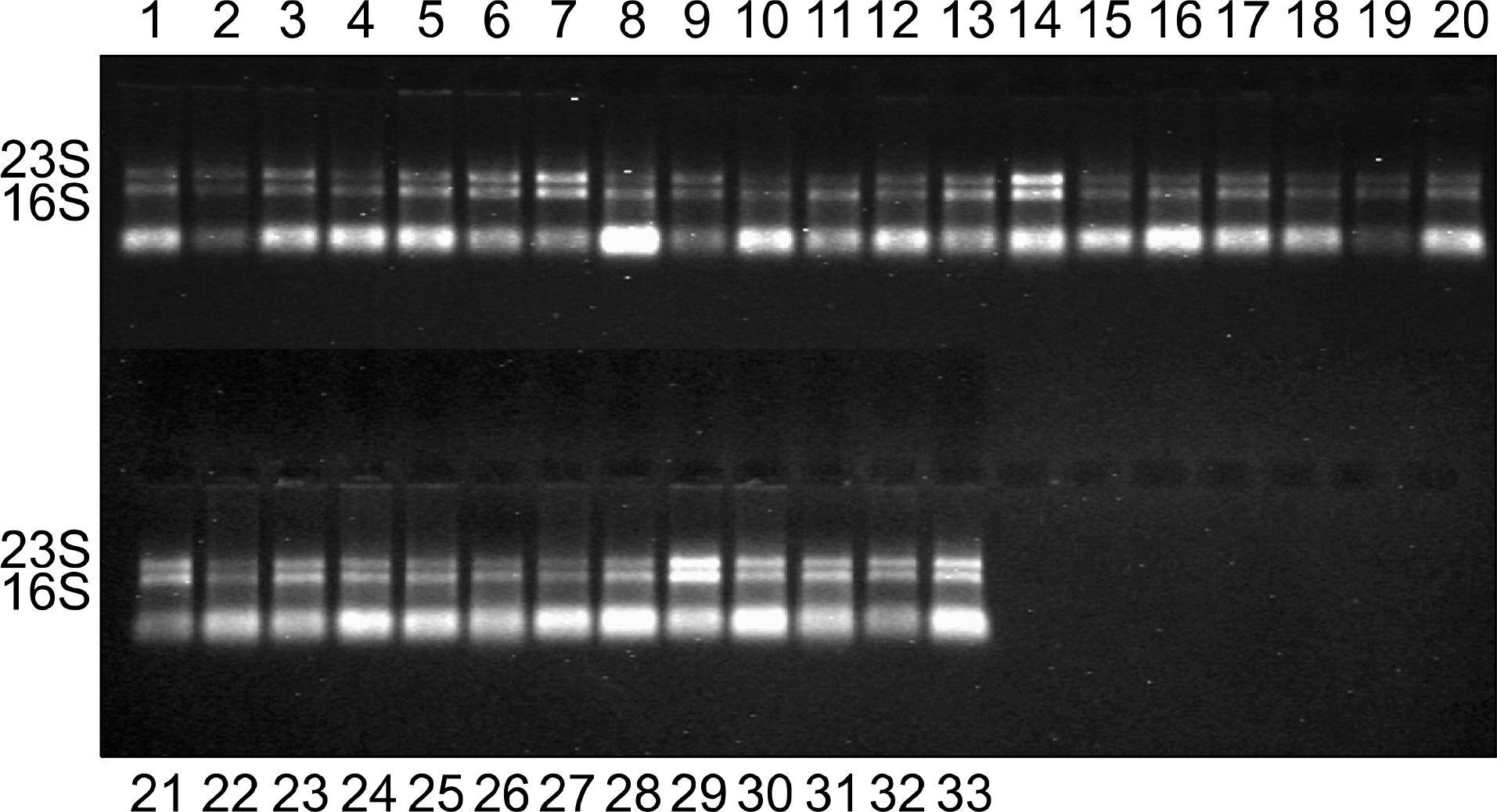
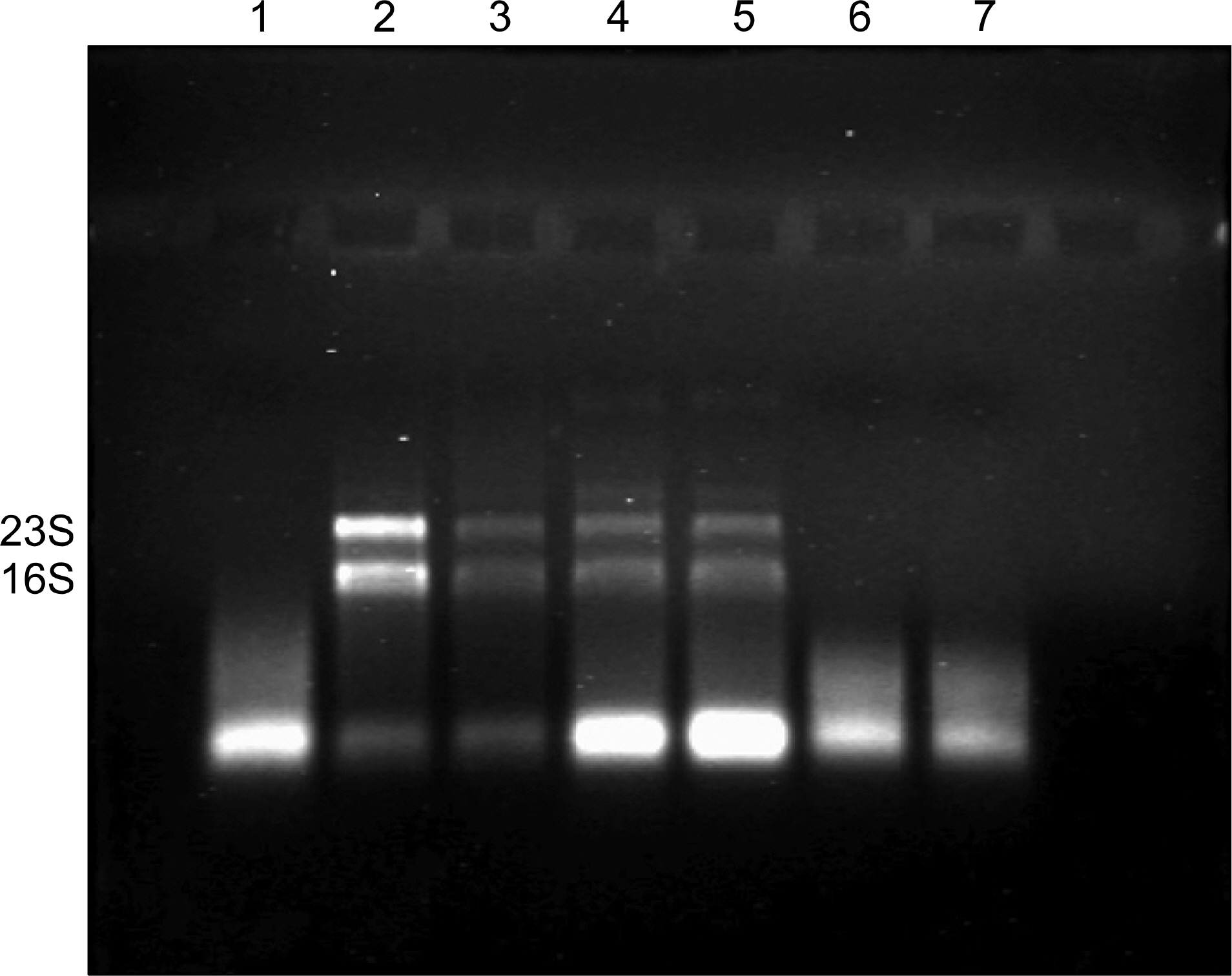
- In the RNA-based study, it is important to extract high-quality RNA. However, RNA extraction from Mycobacterium tuberculosis is problematic due to its thick, waxy cell wall rich in mycolic acid, which renders the cells resistant to lysis. Using TRIzol reagent and several powerful bead-beating steps, a high quantity of RNA was obtained.
Keyword
Figure
Reference
-
References
1. World Health Organization. Global tuberculosis report 2014. World Health Organization;2014.2. Mangan JA, Sole KM, Mitchison DA, Butcher PD. An effective method of RNA extraction from bacteria refractory to disruption, including mycobacteria. Nucleic Acids Res. 1997; 25:675–6.
Article3. Fleige S and Pfaffl MW. RNA integrity and the effect on the real-time qRT-PCR performance. Mol Aspects Med. 2006; 27:126–39.4. Hia F, Chionh YH, Pang YL, DeMott MS, McBee ME, Dedon PC. Mycobacterial RNA isolation optimized for non-coding RNA: high fidelity isolation of 5S rRNA from Mycobacterium bovis BCG reveals novel post-transcriptional processing and a complete spectrum of modified ribonucleosides. Nucleic Acids Res. 2015; 43:e32.
Article5. Pérez-Novo CA, Claeys C, Speleman F, Van Cauwenberge P, Bachert C, Vandesompele J. Impact of RNA quality on reference gene expression stability. Biotechniques. 2005; 39:52. 54, 56.
Article
- Full Text Links
- Actions
-
Cited
- CITED
-
- Close
- Share
- Similar articles
-
- Comparison of DNA Extraction Methods for the Polymerase Chain Reaction of Mycobacterium tuberculosis
- Differentiation between Mycobacterium bovis and Mycobacterium tuberculosis Infection
- Use of RNA/RNA Duplex, Base Pair-mismatch Assay and 3-(4,5-dimethylthiazol- 2-yl)-2,5-diphenyl Tetrazolium Bromide (MTT) Assay for Rapid Detection of Rifampin-resistant Mycobacterium tuberculosis
- A Case of Tuberculosis Verrucosa Cutis with Ulcer in a Patient with Pulmonary Tuberculosis
- A Case of Tuberculosis Verrucosa Cutis Confirmed by Detection of Mycobacterium tuberculosis DNA Using by Polymerase Chain Reaction