Yonsei Med J.
2013 Jul;54(4):1020-1025. 10.3349/ymj.2013.54.4.1020.
Posterior Ligamentous Complex Injuries Are Related to Fracture Severity and Neurological Damage in Patients with Acute Thoracic and Lumbar Burst Fractures
- Affiliations
-
- 1Department of Orthopedic Surgery, Chubu Rosai Hospital, Japan Labor Health and Welfare Organization, Nagoya, Aichi, Japan. masaaki_machino_5445_2@yahoo.co.jp
- KMID: 2158240
- DOI: http://doi.org/10.3349/ymj.2013.54.4.1020
Abstract
- PURPOSE
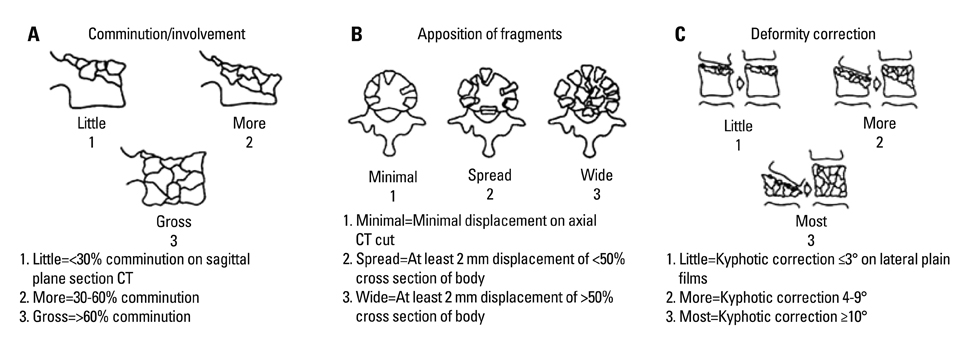
The proposed the thoracolumbar injury classification system (TLICS) for thoracolumbar injury cites the integrity of the posterior ligamentous complex (PLC). However, no report has elucidated the severity of damage in thoracic and lumbar injury with classification schemes by presence of the PLC injury. The purpose of this study was to accurately assess the severity of damage in thoracic and lumbar burst fractures with the PLC injuries.
MATERIALS AND METHODS
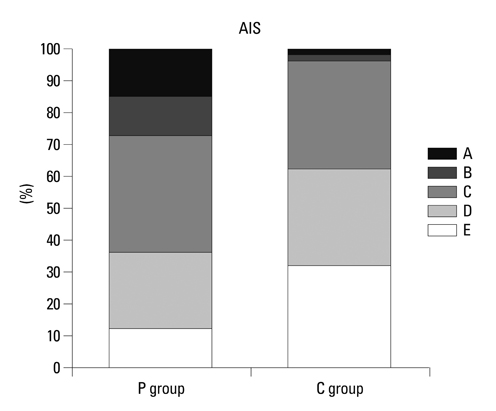
One hundred consecutive patients treated surgically for thoracic and lumbar burst fractures were enrolled in this study. There were 71 men and 29 women whose mean age was 36 years. Clinical and radiologic data were investigated, and the thoracolumbar injury classification schemes were also evaluated. All patients were divided into two groups (the P group with PLC injuries and the C group without PLC injuries) for comparative examination.
RESULTS
Fourth-one of 100 cases showed PLC injuries in MRI study. The load sharing classification score was significantly higher in the P group [7.8+/-0.2 points for the P group and 6.9+/-1.1 points for the C group (p<0.001)]. The TLICS (excluded PLC score) score was also significantly higher in the P group [6.2+/-1.1 points for the P group and 4.0+/-1.4 points for the C group (p<0.001)].
CONCLUSION
The presence of PLC injury significantly influenced the severity of damage. In management of thoracic lumbar burst fractures, evaluation of PLC injury is important to accurately assess the severity of damage.
MeSH Terms
Figure
Reference
-
1. Vaccaro AR, Kim DH, Brodke DS, Harris M, Chapman JR, Schildhauer T, et al. Diagnosis and management of thoracolumbar spine fractures. Instr Course Lect. 2004; 53:359–373.
Article2. Verlaan JJ, Diekerhof CH, Buskens E, van der Tweel I, Verbout AJ, Dhert WJ, et al. Surgical treatment of traumatic fractures of the thoracic and lumbar spine: a systematic review of the literature on techniques, complications, and outcome. Spine (Phila Pa 1976). 2004; 29:803–814.
Article3. van der Roer N, de Lange ES, Bakker FC, de Vet HC, van Tulder MW. Management of traumatic thoracolumbar fractures: a systematic review of the literature. Eur Spine J. 2005; 14:527–534.
Article4. Siebenga J, Leferink VJ, Segers MJ, Elzinga MJ, Bakker FC, Haarman HJ, et al. Treatment of traumatic thoracolumbar spine fractures: a multicenter prospective randomized study of operative versus nonsurgical treatment. Spine (Phila Pa 1976). 2006; 31:2881–2890.
Article5. Denis F. The three column spine and its significance in the classification of acute thoracolumbar spinal injuries. Spine (Phila Pa 1976). 1983; 8:817–831.
Article6. Magerl F, Aebi M, Gertzbein SD, Harms J, Nazarian S. A comprehensive classification of thoracic and lumbar injuries. Eur Spine J. 1994; 3:184–201.
Article7. McCormack T, Karaikovic E, Gaines RW. The load sharing classification of spine fractures. Spine (Phila Pa 1976). 1994; 19:1741–1744.
Article8. Vaccaro AR, Lehman RA Jr, Hurlbert RJ, Anderson PA, Harris M, Hedlund R, et al. A new classification of thoracolumbar injuries: the importance of injury morphology, the integrity of the posterior ligamentous complex, and neurologic status. Spine (Phila Pa 1976). 2005; 30:2325–2333.9. Dai LY, Jin WJ. Interobserver and intraobserver reliability in the load sharing classification of the assessment of thoracolumbar burst fractures. Spine (Phila Pa 1976). 2005; 30:354–358.
Article10. Wang XY, Dai LY, Xu HZ, Chi YL. The load-sharing classification of thoracolumbar fractures: an in vitro biomechanical validation. Spine (Phila Pa 1976). 2007; 32:1214–1219.11. Joaquim AF, Fernandes YB, Cavalcante RA, Fragoso RM, Honorato DC, Patel AA. Evaluation of the thoracolumbar injury classification system in thoracic and lumbar spinal trauma. Spine (Phila Pa 1976). 2011; 36:33–36.
Article12. Oner FC, Wood KB, Smith JS, Shaffrey CI. Therapeutic decision making in thoracolumbar spine trauma. Spine (Phila Pa 1976). 2010; 35:21 Suppl. S235–S244.13. Vaccaro AR, Rihn JA, Saravanja D, Anderson DG, Hilibrand AS, Albert TJ, et al. Injury of the posterior ligamentous complex of the thoracolumbar spine: a prospective evaluation of the diagnostic accuracy of magnetic resonance imaging. Spine (Phila Pa 1976). 2009; 34:E841–E847.14. Yukawa Y. Anterior and posterior surgery and fixation for burst fractures. In : Patel VV, Burger E, Brown CW, editors. Spine Trauma, Surgical techniques. 2010. 1st ed. Berlin, Heidelberg: Springer-Verlag;p. 299–310.15. Machino M, Yukawa Y, Ito K, Nakashima H, Kato F. Posterior/anterior combined surgery for thoracolumbar burst fractures--posterior instrumentation with pedicle screws and laminar hooks, anterior decompression and strut grafting. Spinal Cord. 2011; 49:573–579.
Article16. White AA 3rd, Panjabi MM. Update on the evaluation of instability of the lower cervical spine. Instr Course Lect. 1987; 36:513–520.17. White AA III, Panjabi MM. Clinical Biomechanics of the Spine. 1990. 2nd ed. Philadelphia, PA: JB Lippincott.18. Vaccaro AR, Baron EM, Sanfilippo J, Jacoby S, Steuve J, Grossman E, et al. Reliability of a novel classification system for thoracolumbar injuries: the Thoracolumbar Injury Severity Score. Spine (Phila Pa 1976). 2006; 31:11 Suppl. S62–S69.
Article19. Harrop JS, Vaccaro AR, Hurlbert RJ, Wilsey JT, Baron EM, Shaffrey CI, et al. Intrarater and interrater reliability and validity in the assessment of the mechanism of injury and integrity of the posterior ligamentous complex: a novel injury severity scoring system for thoracolumbar injuries. Invited submission from the Joint Section Meeting On Disorders of the Spine and Peripheral Nerves, March 2005. J Neurosurg Spine. 2006; 4:118–122.
Article20. Patel AA, Vaccaro AR, Albert TJ, Hilibrand AS, Harrop JS, Anderson DG, et al. The adoption of a new classification system: time-dependent variation in interobserver reliability of the thoracolumbar injury severity score classification system. Spine (Phila Pa 1976). 2007; 32:E105–E110.21. Raja Rampersaud Y, Fisher C, Wilsey J, Arnold P, Anand N, Bono CM, et al. Agreement between orthopedic surgeons and neurosurgeons regarding a new algorithm for the treatment of thoracolumbar injuries: a multicenter reliability study. J Spinal Disord Tech. 2006; 19:477–482.
Article
- Full Text Links
- Actions
-
Cited
- CITED
-
- Close
- Share
- Similar articles
-
- Evaluation of Posterior Element Injury in Traumatic Thoraco-Lumbar Burst Fractures
- Three-column reconstruction through the posterior approach alone for the treatment of a severe lumbar burst fracture: a case report
- MRI Findings of Posterior Ligament Complex Injury in Thorcolumbar Bursting Fractures
- Thracia and Lumbar Fracture: Classification According to Three Column Theory and its Relationship to Paralysis
- Screw Fixation without Fusion for Low Lumbar Burst Fracture : A Severe Canal Compromise But Neurologically Intact Case