Yonsei Med J.
2007 Aug;48(4):711-714. 10.3349/ymj.2007.48.4.711.
Paraspinal Abscess Communicated with Epidural Abscess after Extra-Articular Facet Joint Injection
- Affiliations
-
- 1Department of Orthopaedic Surgery, Hangang Sacred Heart Hospital, Hallyn University College of Medicine, Seoul, Korea. amhangpark@yahoo.co.kr
- 2Department of Orthopaedic Surgery, Yonsei University College of Medicine, Seoul, Korea.
- KMID: 2158180
- DOI: http://doi.org/10.3349/ymj.2007.48.4.711
Abstract
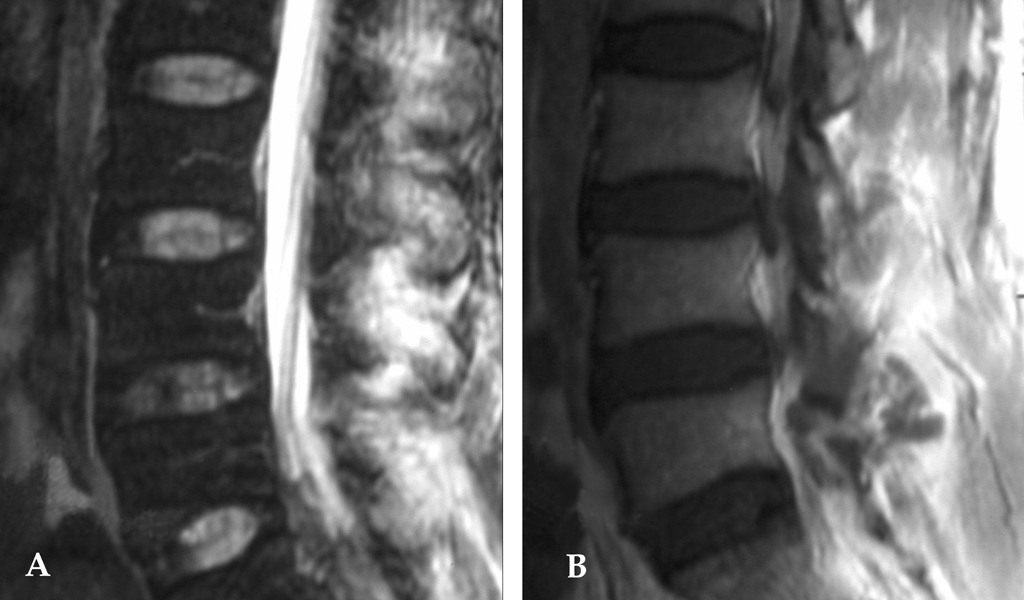
- Facet joint injection is considered to be a safe procedure. There have been some reported cases of facet joint pyogenic infection and also 3 cases of facet joint infection spreading to paraspinal muscle and epidural space due to intra-articular injections. To the author's knowledge, paraspinal and epidural abscesses after facet joint injection without facet joint pyogenic infection have not been reported. Here we report a case in which extra-articular facet joint injection resulted in paraspinal and epidural abscesses without facet joint infection. A 50-year-old man presenting with acute back pain and fever was admitted to the hospital. He had the history of diabetes mellitus and had undergone the extra-articular facet joint injection due to a facet joint syndrome diagnosis at a private clinic 5 days earlier. Physical examination showed tenderness over the paraspinal region. Magnetic resonance image (MRI) demonstrated the paraspinal abscess around the fourth and fifth spinous processes with an additional epidural abscess compressing the thecal sac. The facet joints were preserved. The laboratory results showed a white blood cell count of 14.9x10(9) per liter, an erythrocyte sedimentation rate of 52mm/hour, and 10.88mg/dL of C-reactive protein. Laminectomy and drainage were performed. The pus was found in the paraspinal muscles, which was communicated with the epidural space through a hole in the ligamentum flavum. Cultures grew Staphylococcus aureus. Paraspinal abscess communicated with epidural abscess is a rare complication of extra-articular facet joint injection demonstrating an abscess formation after an invasive procedure near the spine is highly possible.
Keyword
MeSH Terms
Figure
Cited by 2 articles
-
Generalized infection following facet joint injection -A case report-
Sae Young Kim, Sung Ho Han, Min Woo Jung, Ji Hee Hong
Korean J Anesthesiol. 2010;58(4):401-404. doi: 10.4097/kjae.2010.58.4.401.Diagnosis and management of infections related to spinal pain interventions
Sang Cheol Yoon, Eun Joo Choi
Anesth Pain Med. 2024;19(4):294-301. doi: 10.17085/apm.24140.
Reference
-
1. Alcock E, Regaard A, Browne J. Facet joint injection: a rare form cause of epidural abscess formation. Pain. 2003. 103:209–210.
Article2. Cook NJ, Hanrahan P, Song S. Paraspinal abscess following facet joint injection. Clin Rheumatol. 1999. 18:52–53.
Article3. Ergan M, Macro M, Benhamou CL, Vandermarcq P, Colin T, L'Hirondel JL, et al. Septic arthritis of lumbar facet joints. A review of six cases. Rev Rhum Engl Ed. 1997. 64:386–395.4. Magee M, Kannangara S, Dennien B, Lonergan R, Emmett L, Van der Wall H. Paraspinal abscess complicating facet joint injection. Clin Nucl Med. 2000. 25:71–73.
Article5. Okazaki K, Sasaki K, Matsuda S, Yuge I, Omiya K, Kido H, et al. Pyogenic arthritis of a lumbar facet joint. Am J Orthop. 2000. 29:222–224.6. Orpen NM, Birch NC. Delayed presentation of septic arthritis of a lumbar facet joint after diagnostic facet joint injection. J Spinal Disord Tech. 2003. 16:285–287.
Article7. Pilleul F, Garcia J. Septic arthritis of the spine facet joint: early positive diagnosis on magnetic resonance imaging. Review of two cases. Joint Bone Spine. 2000. 67:234–237.8. Lynch MC, Taylor JF. Facet joint injection for low back pain. A clinical study. J Bone Joint Surg Br. 1986. 68:138–141.
Article9. Muffoletto AJ, Ketonen LM, Mader JT, Crow WN, Hadjipavlou AG. Hematogenous pyogenic facet joint infection. Spine. 2001. 26:1570–1576.
Article10. Baltz MS, Tate DE, Glaser JA. Lumbar facet joint infection associated with epidural and paraspinal abscess. Clin Orthop Relat Res. 1997. 339:109–112.
Article11. Dauwe DM, Van Oyen JJ, Samson IR, Hoogmartens MJ. Septic arthritis of a lumbar facet joint and a sternoclavicular joint. Spine. 1995. 20:1304–1306.
Article12. Rousselin B, Gires F, Vallée C, Chevrot A. Case report 627: Septic arthritis of lumbar facet joint as initial manifestation of spondylodiscitis. Skeletal Radiol. 1990. 19:453–455.13. Swayne LC, Dorsky S, Caruana V, Kaplan IL. Septic arthritis of a lumbar facet joint: detection with bone SPECT imaging. J Nucl Med. 1989. 30:1408–1411.14. Marson F, Cognard C, Guillem P, Sévely A, Manelfe C. Septic arthritis of a lumbar facet joint associated with epidural and paravertebral soft tissue abscess. J Radiol. 2001. 82:63–66.15. Roberts WA. Pyogenic vertebral osteomyelitis of a lumbar facet joint with associated epidural abscess. A case report with review of the literature. Spine. 1988. 13:948–952.
Article16. Kannangara DW, Tanaka T, Thadepalli H. Spinal epidural abscess due to Actinomyces israelii. Neurology. 1981. 31:202–204.
Article17. Bertol V, Ara JR, Oliveros A, Gros B. Neurologic complications of lumbar epidural analgesia: spinal and paraspinal abscess. Neurology. 1997. 48:1732–1733.
Article18. Hill JS, Hughes EW, Robertson PA. A Staphylococcus aureus paraspinal abscess associated with epidural analgesia in labour. Anaesthesia. 2001. 56:873–878.
Article19. Pegues DA, Carr DB, Hopkins CC. Infectious complications associated with temporary epidural catheters. Clin Infect Dis. 1994. 19:970–972.
Article20. Raj V, Foy J. Paraspinal abscess associated with epidural in labour. Anaesth Intensive Care. 1998. 26:424–426.
Article
- Full Text Links
- Actions
-
Cited
- CITED
-
- Close
- Share
- Similar articles
-
- Pyogenic Arthritis of the Facet Joint with Concurrent Epidural and Paraspinal Abscess: A Case Report
- Pyogenic Arthritis and Paraspinal Abscess Following Facet Joint Steroid Injection: A Case Report
- Generalized infection following facet joint injection: A case report
- Epidural Abscess and Vertebral Osteomyelitis Induced by Epidural Injection: A case report
- Spinal Epidural Abscess with Pyogenic Arthritis of Facet Joint Treated with Antibiotic-Bone Cement Beads: A Case Report