J Korean Med Sci.
2013 Jan;28(1):152-155. 10.3346/jkms.2013.28.1.152.
An Adult Case of Fisher Syndrome Subsequent to Mycoplasma pneumoniae Infection
- Affiliations
-
- 1Department of Internal Medicine, Kyungpook National University School of Medicine, Daegu, Korea. jaelee@knu.ac.kr
- 2Department of Ophthalmology, Kyungpook National University School of Medicine, Daegu, Korea.
- KMID: 2158015
- DOI: http://doi.org/10.3346/jkms.2013.28.1.152
Abstract
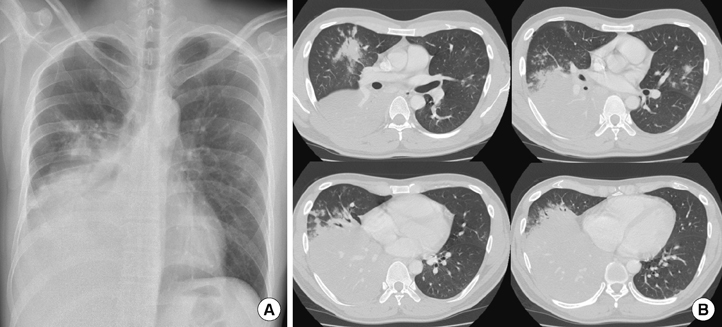
- Reported herein is an adult case of Fisher syndrome (FS) that occurred as a complication during the course of community-acquired pneumonia caused by Mycoplasma pneumoniae. A 38-yr-old man who had been treated with antibiotics for serologically proven M. pneumoniae pneumonia presented with a sudden onset of diplopia, ataxic gait, and areflexia. A thorough evaluation including brain imaging, cerebrospinal fluid examination, a nerve conduction study, and detection of serum anti-ganglioside GQ1b antibody titers led to the diagnosis of FS. Antibiotic treatment of the underlying M. pneumoniae pneumonia was maintained without additional immunomodulatory agents. A complete and spontaneous resolution of neurologic abnormalities was observed within 1 month, accompanied by resolution of lung lesions.
MeSH Terms
-
Adult
Anti-Bacterial Agents/therapeutic use
Antibodies/blood
Diplopia/etiology
Erythrocyte Count
Gangliosides/immunology
Humans
Lung/radiography
Male
Miller Fisher Syndrome/*diagnosis/etiology
Pneumonia, Mycoplasma/complications/*diagnosis/drug therapy
Tomography, X-Ray Computed
Anti-Bacterial Agents
Antibodies
Gangliosides
Figure
Reference
-
1. Koskiniemi M. CNS manifestations associated with Mycoplasma pneumoniae infections: summary of cases at the University of Helsinki and review. Clin Infect Dis. 1993. 17:S52–S57.2. Cassell GH, Cole BC. Mycoplasmas as agents of human disease. N Engl J Med. 198. 304:80–89.3. Lo YL. Clinical and immunological spectrum of the Miller Fisher syndrome. Muscle Nerve. 2007. 36:615–627.4. Loewenbruck KF, Putz V, Schafer J, Reichmann H, Storch A. Parainfectious polyneuropathy and miller-fisher-syndrome in combination with anemia in Mycoplasma pneumoniae infection. Fortschr Neurol Psychiatr. 2008. 76:361–365.5. Fisher M. An unusual variant of acute idiopathic polyneuritis (syndrome of ophthalmoplegia, ataxia and areflexia). N Engl J Med. 1956. 255:57–65.6. Chiba A, Kusunoki S, Obata H, Machinami R, Kanazawa I. Serum anti-GQ1b IgG antibody is associated with ophthalmoplegia in Miller Fisher syndrome and Guillain-Barre syndrome: clinical and immunohistochemical studies. Neurology. 1993. 43:1911–1917.7. Merkx H, De Keyser J, Ebinger G. Miller Fisher syndrome associated with Mycoplasma pneumoniae infection: report of a case. Clin Neurol Neurosurg. 1994. 96:96–99.8. Tsiodras S, Kelesidis I, Kelesidis T, Stamboulis E, Giamarellou H. Central nervous system manifestations of Mycoplasma pneumoniae infections. J Infect. 2005. 51:343–354.9. Narita M. Pathogenesis of neurologic manifestations of Mycoplasma pneumoniae infection. Pediatr Neurol. 2009. 41:159–166.10. Yang J, Hooper WC, Phillips DJ, Talkington DF. Cytokines in Mycoplasma pneumoniae infections. Cytokine Growth Factor Rev. 2004. 15:157–168.11. Biberfeld G. Antibodies to brain and other tissues in cases of Mycoplasma pneumoniae infection. Clin Exp Immunol. 1971. 8:319–333.12. Jacobs BC, Rothbarth PH, van der Meche FG, Herbrink P, Schmitz PI, de Klerk MA, van Doorn PA. The spectrum of antecedent infections in Guillain-Barre syndrome: a case-control study. Neurology. 1998. 51:1110–1115.13. Goldschmidt B, Menonna J, Fortunato J, Dowling P, Cook S. Mycoplasma antibody in Guillain-Barre syndrome and other neurological disorders. Ann Neurol. 1980. 7:108–112.14. Kitazawa K, Tagawa Y, Honda A, Yuki N. Guillain-Barre syndrome associated with IgG anti-GM1b antibody subsequent to Mycoplasma pneumoniae infection. J Neurol Sci. 1998. 156:99–101.15. Yuki N. Infectious origins of, and molecular mimicry in, Guillain-Barre and Fisher syndromes. Lancet Infect Dis. 2001. 1:29–37.16. Mori M, Kuwabara S, Yuki N. Fisher syndrome: clinical features, immunopathogenesis and management. Expert Rev Neurother. 2012. 12:39–51.17. Koga M, Gilbert M, Li J, Koike S, Takahashi M, Furukawa K, Hirata K, Yuki N. Antecedent infections in Fisher syndrome: a common pathogenesis of molecular mimicry. Neurology. 2005. 64:1605–1611.18. Aranyi Z, Kovacs T, Sipos I, Bereczki D. Miller Fisher syndrome: brief overview and update with a focus on electrophysiological findings. Eur J Neurol. 2012. 19:15–20.19. Hsueh KC, Chou IC, Hsu CH, Kuo HT, Tsai FJ, Tsai CH. Miller Fisher syndrome possibly related to mycoplasma pneumoniae infection: report of one case. Acta Paediatr Taiwan. 2004. 45:168–170.20. San-Juan OD, Martinez-Herrera JF, Garcia JM, Gonzalez-Aragon MF, Del Castillo-Calcaneo Jde D, Perez-Neri I. Miller fisher syndrome: 10 years' experience in a third-level center. Eur Neurol. 2009. 62:149–154.
- Full Text Links
- Actions
-
Cited
- CITED
-
- Close
- Share
- Similar articles
-
- A Case of Erythema Multiforme in Adults Associated with Mycoplasma pneumoniae Infection
- A Case of Child with Miller Fisher Syndrome Diagnosed by Anti-GQ1b Antibody from Mycoplasma Pneumoniae
- A Case of Cerebral Infarction Complicated by Mycoplasma pneumoniae Pneumonia
- Bullous Erythema Multiforme and Stevens-Johnson Syndrome Caused by Mycoplasma pneumoniae Infection
- One case of bronchiolitis obliterans associated with Stevens-Johnson syndrome due to mycoplasma pneumoniae infection